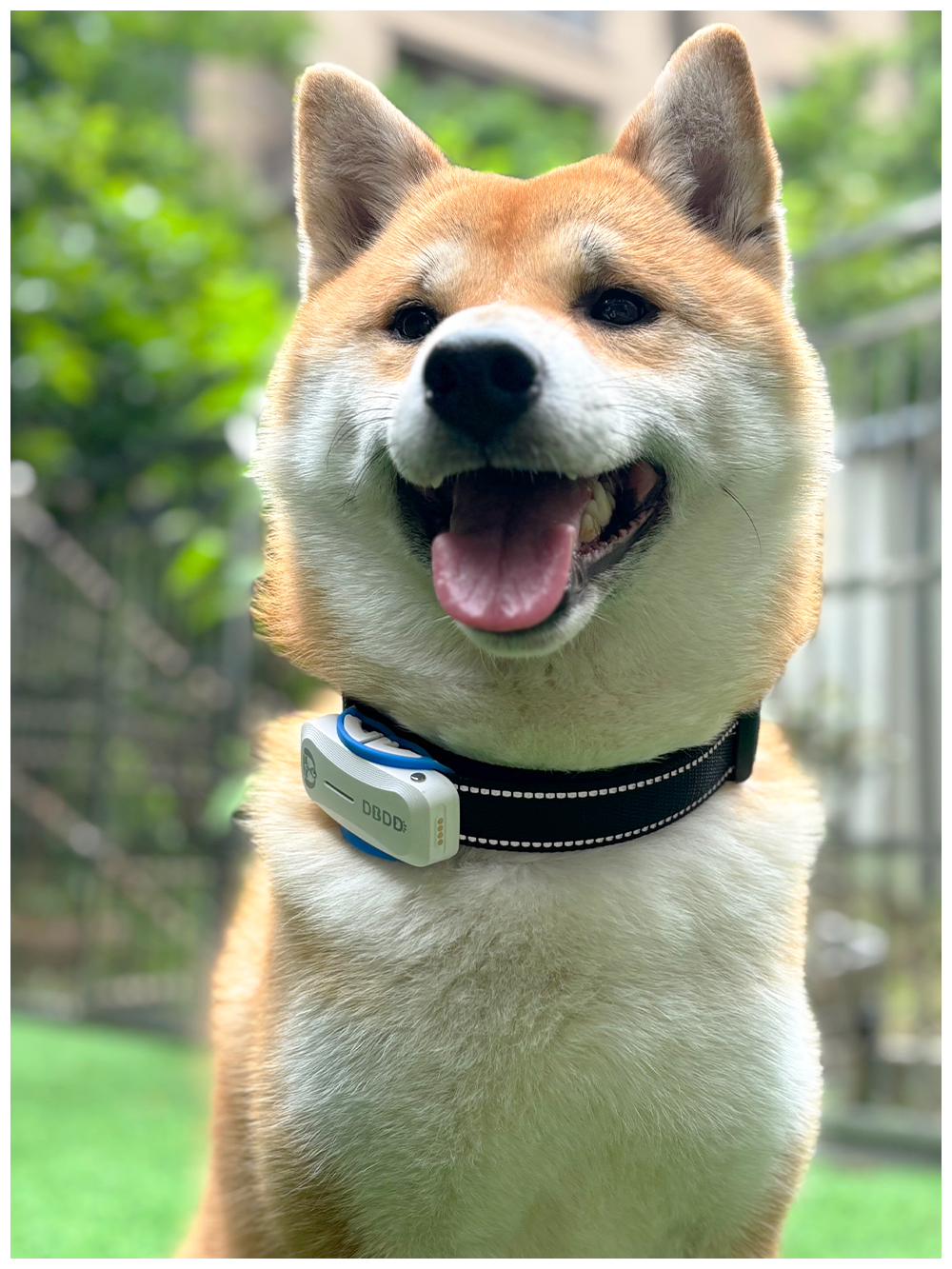
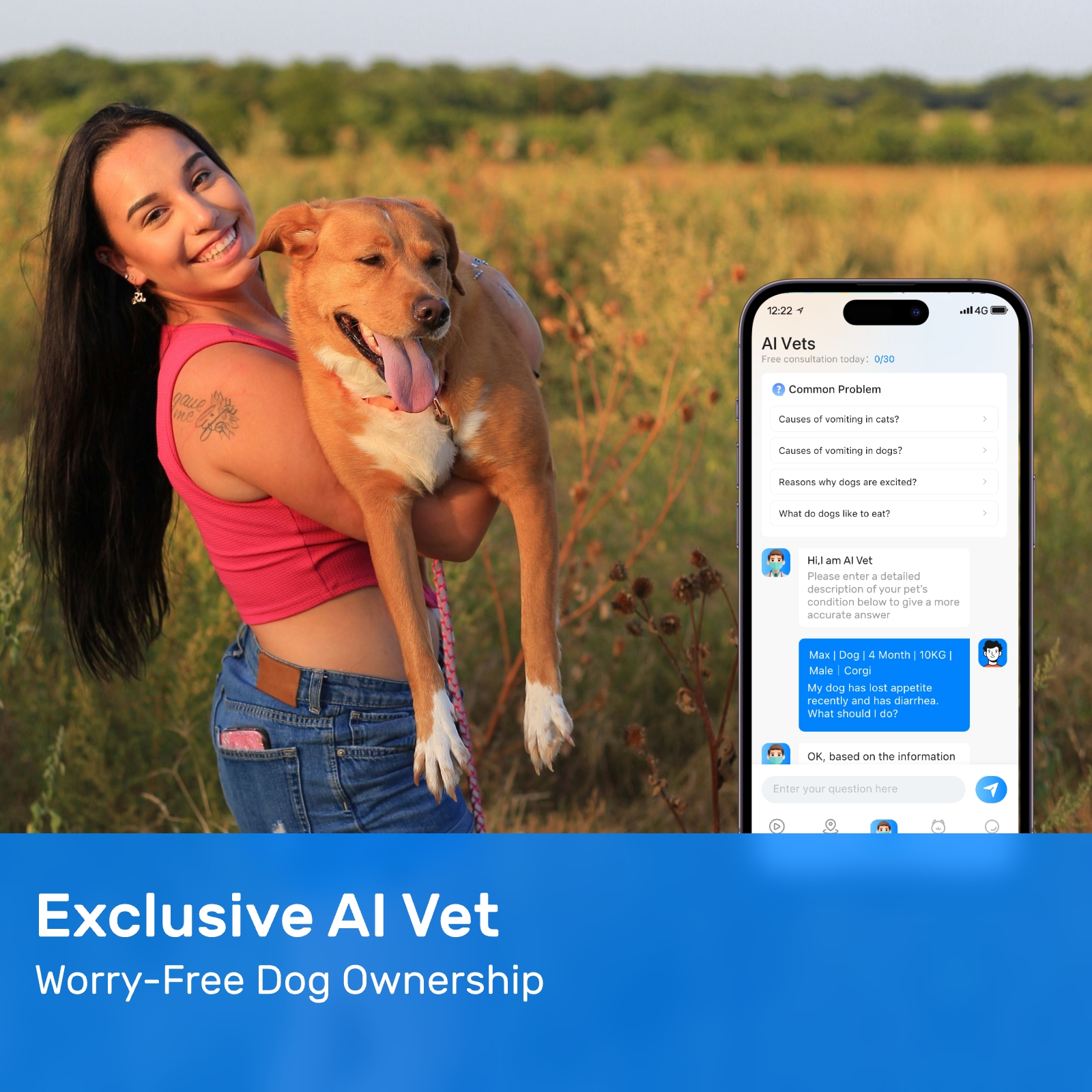
New ArrivalsBack in stock
lymphoma in dogs
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D989921870 second hand :D989921870 |
Manufacturer | lymphoma in | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $38 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | in dogs | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Pet Healthcare#Vital Monitoring Systems
Leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) in the realm of veterinary medicine has opened new doors for diagnosing and predicting various health conditions in pets, including lymphoma in dogs. AI-powered lost pet prediction systems are not only transforming how we locate missing animals but also enhancing our ability to foresee and manage diseases like canine lymphoma. These advanced technologies are enabling veterinarians and pet owners to take proactive steps towards improving the health and well-being of their furry companions.
The integration of AI into veterinary diagnostics is a rapidly evolving field. Machine learning algorithms can now analyze vast datasets derived from medical records, genetic information, and imaging studies. This data-driven approach allows for more accurate predictions regarding the onset and progression of illnesses such as lymphoma in dogs. Lymphoma, a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system, is one of the most common cancers diagnosed in dogs. Early detection and intervention significantly improve outcomes, making predictive tools invaluable in managing this disease.
AI systems designed to predict the likelihood of a dog developing lymphoma utilize sophisticated algorithms capable of identifying patterns within complex biological data. By examining factors such as breed predisposition, age, lifestyle, and previous medical history, these systems provide veterinarians with insights that might otherwise go unnoticed. For instance, certain breeds, like Golden Retrievers and Boxers, have a higher incidence of lymphoma compared to others. An AI model trained on extensive datasets could recognize these breed-specific risks and alert veterinarians accordingly.
Moreover, AI-powered systems contribute to personalized medicine by tailoring diagnostic and treatment plans based on individual characteristics of each dog. Predictive analytics enable veterinarians to anticipate potential health issues before they manifest clinically. In the case of lymphoma in dogs, early identification through predictive modeling permits timely interventions, potentially halting disease progression or mitigating its severity.
Another significant aspect of AI applications in veterinary care involves the use of imaging technology. Radiology plays an essential role in diagnosing lymphoma, where enlarged lymph nodes serve as a critical indicator. AI-enhanced imaging analysis software improves the accuracy and efficiency of interpreting radiographs, ultrasounds, and CT scans. These tools assist veterinarians in detecting subtle changes indicative of lymphoma at earlier stages than traditional methods alone.
Furthermore, AI facilitates continuous monitoring of a dog's health status post-diagnosis. Regular updates fed into the system allow it to adapt and refine its predictions over time. As new research findings emerge about lymphoma in dogs, AI models can incorporate this knowledge, ensuring they remain up-to-date and effective. This dynamic capability ensures that predictions stay relevant even as scientific understanding evolves.
Beyond direct clinical applications, AI contributes to broader epidemiological studies concerning lymphoma in dogs. Analyzing large-scale population data helps identify trends and correlations that may inform prevention strategies. Understanding geographic variations in lymphoma prevalence, for example, could lead to targeted public health initiatives aimed at reducing risk factors specific to certain regions.
However, implementing AI-powered lost pet prediction systems for lymphoma in dogs comes with challenges. One primary concern revolves around data quality and availability. Accurate predictions necessitate comprehensive and reliable datasets, which can be difficult to obtain consistently across different veterinary practices. Ensuring privacy and security when handling sensitive health information is another crucial consideration. Safeguards must be in place to protect both the pets' and owners' personal data while maintaining compliance with relevant regulations.

Additionally, there exists a need for education and training among veterinary professionals regarding the appropriate use and interpretation of AI-generated predictions. While these systems offer powerful capabilities, they should complement rather than replace human expertise. Veterinarians play a vital role in contextualizing AI outputs and applying them effectively within patient care contexts.
Looking ahead, advancements in AI technology promise even greater strides in predicting and managing lymphoma in dogs. Emerging techniques such as deep learning and natural language processing hold immense potential for enhancing diagnostic precision and expanding the scope of what AI can achieve in veterinary medicine. Deep learning models, for instance, excel at recognizing intricate patterns within unstructured data types like images or free-text notes found in electronic health records. Natural language processing enables extraction of meaningful insights from written descriptions provided by veterinarians during consultations.
Collaboration between technologists, veterinarians, and researchers will be key to realizing the full potential of AI in combating lymphoma in dogs. Developing standardized protocols for collecting and sharing data across institutions would enhance the robustness of AI models. Additionally, fostering interdisciplinary partnerships encourages innovation and accelerates progress toward creating more sophisticated predictive tools.
In conclusion, AI-powered lost pet prediction systems represent a groundbreaking advancement in veterinary healthcare, particularly concerning lymphoma in dogs. Through leveraging machine learning algorithms and big data analytics, these systems empower veterinarians to make informed decisions regarding diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing management of this challenging condition. Despite existing obstacles related to data acquisition, privacy concerns, and professional training requirements, the future outlook remains promising. Continued investment in research and development coupled with strong collaborative efforts promises to yield increasingly effective solutions for addressing lymphoma in dogs and improving overall animal welfare. As technology continues to evolve, so too does the opportunity to revolutionize how we safeguard our beloved pets' health and longevity.
Update Time:2025-05-15 13:36:29
The integration of AI into veterinary diagnostics is a rapidly evolving field. Machine learning algorithms can now analyze vast datasets derived from medical records, genetic information, and imaging studies. This data-driven approach allows for more accurate predictions regarding the onset and progression of illnesses such as lymphoma in dogs. Lymphoma, a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system, is one of the most common cancers diagnosed in dogs. Early detection and intervention significantly improve outcomes, making predictive tools invaluable in managing this disease.
AI systems designed to predict the likelihood of a dog developing lymphoma utilize sophisticated algorithms capable of identifying patterns within complex biological data. By examining factors such as breed predisposition, age, lifestyle, and previous medical history, these systems provide veterinarians with insights that might otherwise go unnoticed. For instance, certain breeds, like Golden Retrievers and Boxers, have a higher incidence of lymphoma compared to others. An AI model trained on extensive datasets could recognize these breed-specific risks and alert veterinarians accordingly.
Moreover, AI-powered systems contribute to personalized medicine by tailoring diagnostic and treatment plans based on individual characteristics of each dog. Predictive analytics enable veterinarians to anticipate potential health issues before they manifest clinically. In the case of lymphoma in dogs, early identification through predictive modeling permits timely interventions, potentially halting disease progression or mitigating its severity.
Another significant aspect of AI applications in veterinary care involves the use of imaging technology. Radiology plays an essential role in diagnosing lymphoma, where enlarged lymph nodes serve as a critical indicator. AI-enhanced imaging analysis software improves the accuracy and efficiency of interpreting radiographs, ultrasounds, and CT scans. These tools assist veterinarians in detecting subtle changes indicative of lymphoma at earlier stages than traditional methods alone.
Furthermore, AI facilitates continuous monitoring of a dog's health status post-diagnosis. Regular updates fed into the system allow it to adapt and refine its predictions over time. As new research findings emerge about lymphoma in dogs, AI models can incorporate this knowledge, ensuring they remain up-to-date and effective. This dynamic capability ensures that predictions stay relevant even as scientific understanding evolves.
Beyond direct clinical applications, AI contributes to broader epidemiological studies concerning lymphoma in dogs. Analyzing large-scale population data helps identify trends and correlations that may inform prevention strategies. Understanding geographic variations in lymphoma prevalence, for example, could lead to targeted public health initiatives aimed at reducing risk factors specific to certain regions.
However, implementing AI-powered lost pet prediction systems for lymphoma in dogs comes with challenges. One primary concern revolves around data quality and availability. Accurate predictions necessitate comprehensive and reliable datasets, which can be difficult to obtain consistently across different veterinary practices. Ensuring privacy and security when handling sensitive health information is another crucial consideration. Safeguards must be in place to protect both the pets' and owners' personal data while maintaining compliance with relevant regulations.

Additionally, there exists a need for education and training among veterinary professionals regarding the appropriate use and interpretation of AI-generated predictions. While these systems offer powerful capabilities, they should complement rather than replace human expertise. Veterinarians play a vital role in contextualizing AI outputs and applying them effectively within patient care contexts.
Looking ahead, advancements in AI technology promise even greater strides in predicting and managing lymphoma in dogs. Emerging techniques such as deep learning and natural language processing hold immense potential for enhancing diagnostic precision and expanding the scope of what AI can achieve in veterinary medicine. Deep learning models, for instance, excel at recognizing intricate patterns within unstructured data types like images or free-text notes found in electronic health records. Natural language processing enables extraction of meaningful insights from written descriptions provided by veterinarians during consultations.
Collaboration between technologists, veterinarians, and researchers will be key to realizing the full potential of AI in combating lymphoma in dogs. Developing standardized protocols for collecting and sharing data across institutions would enhance the robustness of AI models. Additionally, fostering interdisciplinary partnerships encourages innovation and accelerates progress toward creating more sophisticated predictive tools.
In conclusion, AI-powered lost pet prediction systems represent a groundbreaking advancement in veterinary healthcare, particularly concerning lymphoma in dogs. Through leveraging machine learning algorithms and big data analytics, these systems empower veterinarians to make informed decisions regarding diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing management of this challenging condition. Despite existing obstacles related to data acquisition, privacy concerns, and professional training requirements, the future outlook remains promising. Continued investment in research and development coupled with strong collaborative efforts promises to yield increasingly effective solutions for addressing lymphoma in dogs and improving overall animal welfare. As technology continues to evolve, so too does the opportunity to revolutionize how we safeguard our beloved pets' health and longevity.
Update Time:2025-05-15 13:36:29
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form