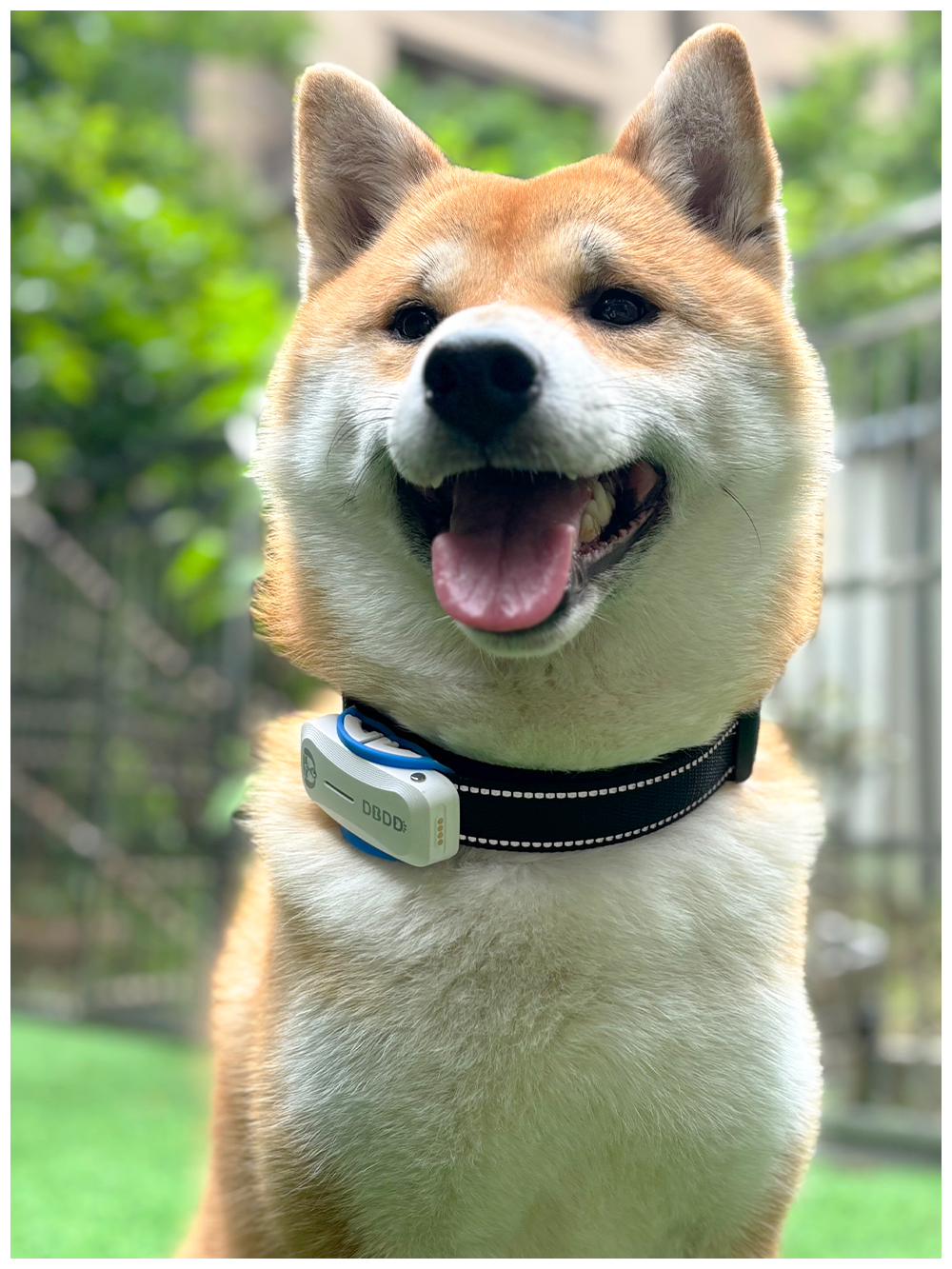
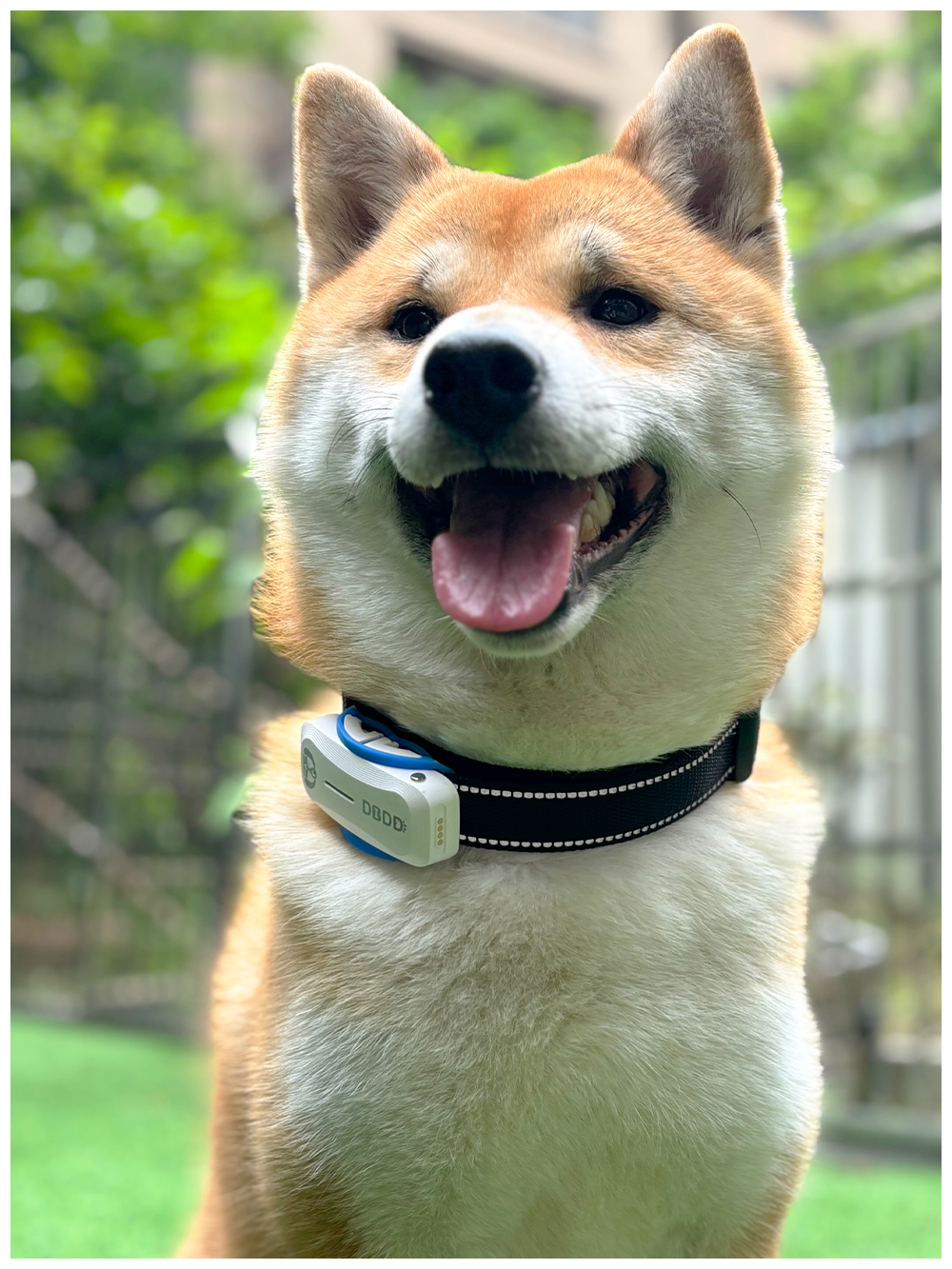
New ArrivalsBack in stock
tractive
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D759971510 second hand :D759971510 |
Manufacturer | tractive | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $44 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | tractive | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
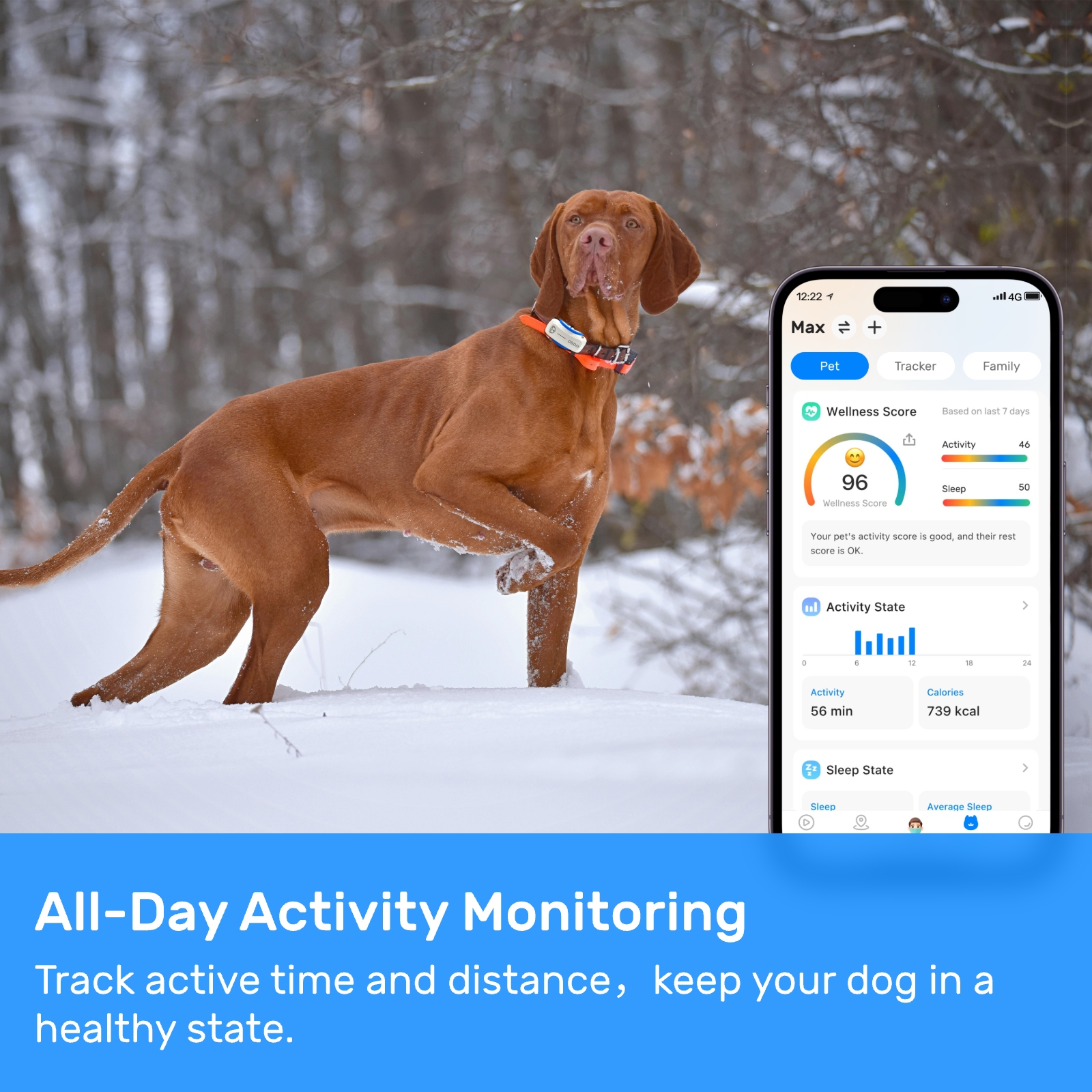
Retail Analytics#Pet Behavior Insights










Introduction

Tractive force is a fundamental concept in the realm of physics and engineering. It refers to the force that causes an object to move or accelerate across a surface. Understanding tractive force is essential in various industries, including transportation, logistics, and manufacturing. In this article, we will explore the different types of tractive technologies, their applications, and the benefits they offer.
Types of Tractive Technologies
1. Wheeled Traction
Wheeled traction is the most common form of tractive force, found in various vehicles such as cars, bicycles, and trains. The wheels provide the necessary grip and friction to move the vehicle forward or backward. Wheeled traction is highly efficient and versatile, making it the preferred method of transportation for millions of people worldwide.
2. Tracked Traction
Tracked traction is another form of tractive force, commonly used in heavy machinery and military vehicles. The tracks provide a larger surface area in contact with the ground, resulting in greater stability and reduced ground pressure. This type of tractive force is particularly useful in off-road environments, where the terrain may be uneven or soft, such as mud, sand, or snow.

3. Magnetic Traction

Magnetic traction, also known as magnetic levitation (maglev), is a technology that uses magnetic forces to levitate and propel vehicles. This system eliminates friction and wear, resulting in smooth and efficient movement. Maglev trains are an example of magnetic traction, offering high-speed transportation with minimal energy loss.
4. Linear Motors and Propulsion
Linear motors and propulsion systems use electromagnetic forces to move objects along a straight path. These systems are commonly found in applications such as elevators, conveyor belts, and linear induction motors. Linear propulsion offers precise control and high efficiency, making it an attractive option for various industrial and transportation applications.
Applications of Tractive Technologies
1. Transportation
Tractive technologies play a crucial role in the transportation sector. From personal vehicles to public transportation systems, tractive force is essential for moving people and goods efficiently. For instance, electric vehicles rely on electric motors to generate tractive force, reducing emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
2. Logistics and Material Handling
In the logistics and material handling industry, tractive technologies are used to move heavy loads and large quantities of goods. Forklifts, pallet movers, and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) all rely on tractive force to transport materials within warehouses and distribution centers.
3. Construction and Agriculture
Tractive force is vital in construction and agriculture, where heavy machinery is used to move and manipulate large objects. Tractors, excavators, and bulldozers all require tractive force to perform their tasks efficiently.

4. Industrial Automation
In the realm of industrial automation, tractive technologies are used to transport parts and components along assembly lines. Linear motors and magnetic traction systems enable precise control and high-speed movement, increasing productivity and efficiency in manufacturing processes.
Benefits of Tractive Technologies

1. Efficiency and Performance
Tractive technologies offer numerous benefits in terms of efficiency and performance. By reducing friction and wear, these systems can significantly improve energy consumption and overall performance. For example, maglev trains consume less energy than conventional trains, resulting in lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact.
2. Safety and Stability
Tractive technologies can also enhance safety and stability in various applications. Tracked vehicles, for instance, provide better traction and stability on uneven terrain, reducing the risk of accidents and improving overall safety.
3. Precision and Control
Linear motors and magnetic traction systems offer precise control and positioning capabilities, which are essential in applications such as industrial automation and precision manufacturing. By accurately controlling the movement of objects, these systems can improve product quality and reduce waste.
4. Environmental Benefits
Many tractive technologies, such as electric vehicles and maglev trains, offer environmental benefits by reducing emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. By promoting the adoption of cleaner and more sustainable transportation methods, tractive technologies can help combat climate change and promote a greener future.
Challenges and Future Developments
Despite the numerous benefits of tractive technologies, there are still challenges that need to be addressed. Some of these challenges include:

1. Cost and Complexity
Some tractive technologies, such as maglev trains and linear motors, can be expensive and complex to implement. Reducing the cost and complexity of these systems is essential for widespread adoption and deployment.
2. Infrastructure Requirements

Implementing tractive technologies often requires significant infrastructure investments, such as the construction of dedicated tracks for maglev trains or the installation of charging stations for electric vehicles. Addressing these infrastructure requirements is crucial for the successful integration of tractive technologies into existing systems.
3. Energy Efficiency
While many tractive technologies offer energy efficiency benefits, further improvements are needed to maximize energy savings and reduce environmental impact. Research and development efforts should focus on

Update Time:2025-05-15 22:26:17
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form