New ArrivalsBack in stock
can dogs eat pineapple
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D339286731 second hand :D339286731 |
Manufacturer | can dogs | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $38 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | dogs eat | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
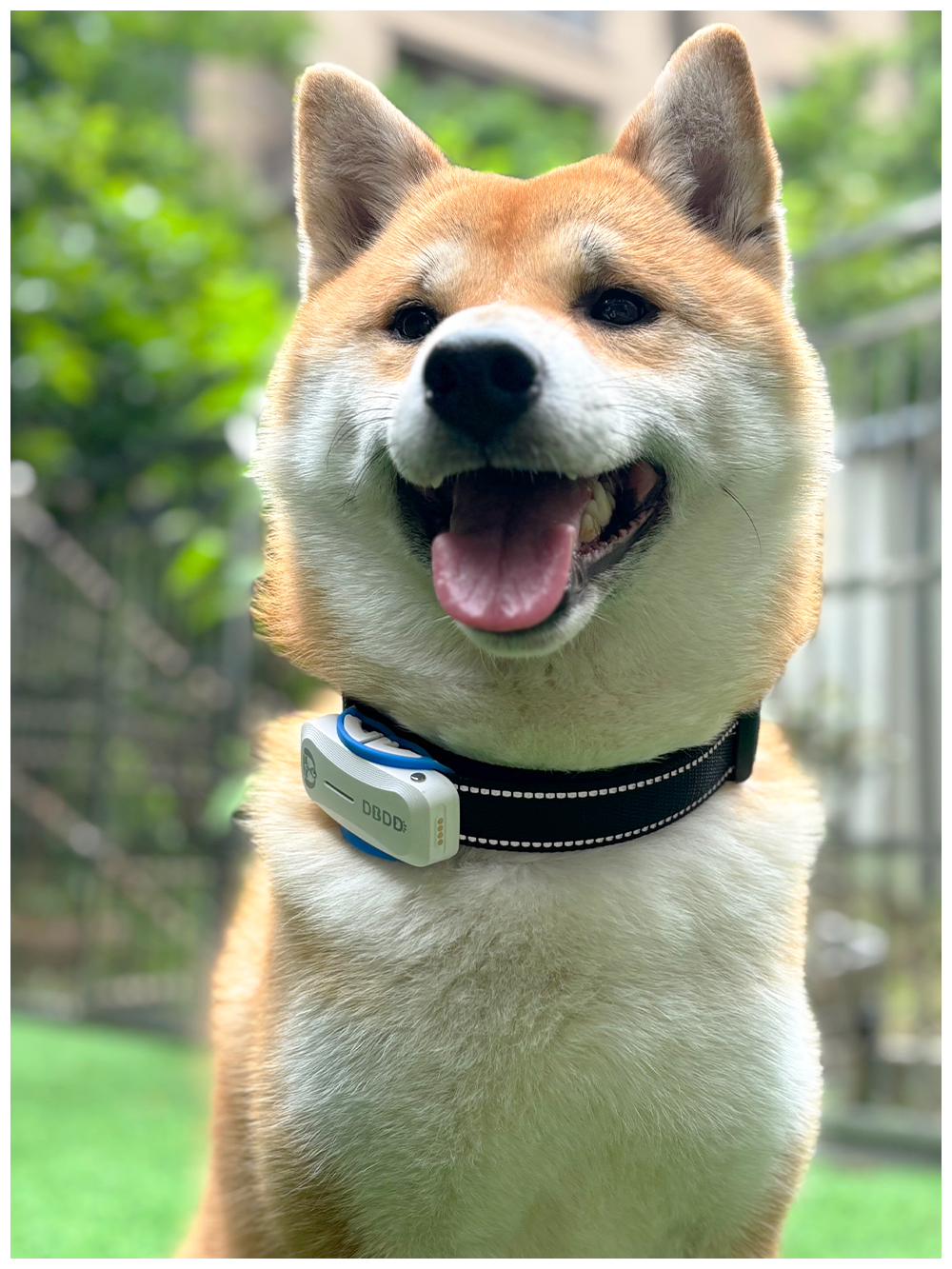
Military Tech#Search & Rescue Devices
Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are two of the most common wireless technologies used in our daily lives. These technologies have been adapted for various applications, including pet tracking devices. In particular, dog locator devices that utilize Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connectivity have become increasingly popular among pet owners who want to ensure their furry friends remain safe. While these devices provide peace of mind, they also raise questions about other aspects of pet care. For instance, one might wonder: can dogs eat pineapple? This article explores the differences between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators while addressing this canine dietary query.
Bluetooth dog locators operate on short-range wireless technology, allowing users to track their pets within a specific radius. Typically, these devices connect directly to a smartphone app via Bluetooth, enabling real-time updates when the dog is nearby. The primary advantage of Bluetooth-based locators is their low power consumption, making them ideal for situations where constant monitoring isn't necessary. However, their effectiveness diminishes once the dog moves out of range, which can vary from 30 feet to several hundred feet depending on the model and environmental factors.

On the other hand, Wi-Fi dog locators offer greater range capabilities by connecting to the internet through a home network or cellular data plan. These devices often upload location data to cloud servers, allowing owners to access information remotely even if their dogs wander far away. Although Wi-Fi systems tend to consume more energy than Bluetooth ones, advancements in battery technology have made it possible for some models to last days or weeks on a single charge. Additionally, many modern Wi-Fi trackers include GPS functionality, providing pinpoint accuracy regardless of proximity.
When choosing between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators, several considerations come into play. Budget constraints may favor Bluetooth options since they generally cost less upfront compared to their Wi-Fi counterparts. Ease of use could sway decisions as well; Bluetooth setups usually require fewer steps during installation but lack advanced features like geofencing alerts offered by certain Wi-Fi products. Ultimately, personal preferences regarding desired coverage area and frequency of updates will dictate which type best suits individual needs.
Now let us shift gears slightly and address another pertinent question for responsible pet owners: can dogs eat pineapple? The answer is yes—with caveats. Pineapple contains vitamins C and B6, manganese, fiber, and bromelain, all beneficial nutrients that promote overall health in moderation. Vitamin C supports immune function, while vitamin B6 aids nerve transmission and red blood cell formation. Manganese plays a role in bone development and enzyme activation, whereas fiber helps maintain digestive regularity. Bromelain, an enzyme found primarily in the core and juice of pineapples, has anti-inflammatory properties that may assist with joint pain relief.
Despite its nutritional merits, feeding pineapple to your dog requires caution due to potential risks associated with excessive consumption. High sugar content means too much pineapple can lead to obesity or diabetes over time. Furthermore, raw pineapple poses choking hazards because of tough outer rinds and fibrous interiors. Always remove the prickly skin, crown, and center core before offering small bite-sized pieces as treats. Moderation remains key; limit servings to no more than one inch cube per ten pounds of body weight daily.
Another factor worth noting relates to allergies. Some dogs exhibit adverse reactions upon ingesting pineapple, characterized by symptoms such as itching, swelling, vomiting, diarrhea, or difficulty breathing. If you notice any signs indicating sensitivity after introducing pineapple into your dog's diet, discontinue feeding immediately and consult your veterinarian. Regular monitoring ensures early detection of intolerance issues so adjustments can be made accordingly.
Returning to the realm of connectivity solutions for lost pets, both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators serve distinct purposes based on user requirements. Owners seeking economical yet reliable methods for locating nearby missing animals might find satisfaction using Bluetooth-enabled devices. Conversely, those prioritizing extended reach combined with sophisticated analytics prefer investing in premium Wi-Fi alternatives capable of delivering comprehensive insights beyond mere positional data. Regardless of choice, incorporating either option enhances safety measures already established within households containing beloved four-legged companions.
In conclusion, selecting appropriate wireless communication protocols depends largely on intended usage scenarios alongside financial limitations imposed by available budgets. Meanwhile, answering queries concerning whether can dogs eat pineapple reveals importance attached not only towards technological innovation safeguarding our pets' physical presence but also dietary knowledge ensuring optimal nourishment supporting long-term vitality. By balancing practical tools promoting security alongside informed decisions guiding nutrition, we empower ourselves as conscientious caretakers committed to fostering happy, healthy lifestyles shared amongst family members across species lines alike.
Update Time:2025-05-15 06:01:16
Bluetooth dog locators operate on short-range wireless technology, allowing users to track their pets within a specific radius. Typically, these devices connect directly to a smartphone app via Bluetooth, enabling real-time updates when the dog is nearby. The primary advantage of Bluetooth-based locators is their low power consumption, making them ideal for situations where constant monitoring isn't necessary. However, their effectiveness diminishes once the dog moves out of range, which can vary from 30 feet to several hundred feet depending on the model and environmental factors.

On the other hand, Wi-Fi dog locators offer greater range capabilities by connecting to the internet through a home network or cellular data plan. These devices often upload location data to cloud servers, allowing owners to access information remotely even if their dogs wander far away. Although Wi-Fi systems tend to consume more energy than Bluetooth ones, advancements in battery technology have made it possible for some models to last days or weeks on a single charge. Additionally, many modern Wi-Fi trackers include GPS functionality, providing pinpoint accuracy regardless of proximity.
When choosing between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators, several considerations come into play. Budget constraints may favor Bluetooth options since they generally cost less upfront compared to their Wi-Fi counterparts. Ease of use could sway decisions as well; Bluetooth setups usually require fewer steps during installation but lack advanced features like geofencing alerts offered by certain Wi-Fi products. Ultimately, personal preferences regarding desired coverage area and frequency of updates will dictate which type best suits individual needs.
Now let us shift gears slightly and address another pertinent question for responsible pet owners: can dogs eat pineapple? The answer is yes—with caveats. Pineapple contains vitamins C and B6, manganese, fiber, and bromelain, all beneficial nutrients that promote overall health in moderation. Vitamin C supports immune function, while vitamin B6 aids nerve transmission and red blood cell formation. Manganese plays a role in bone development and enzyme activation, whereas fiber helps maintain digestive regularity. Bromelain, an enzyme found primarily in the core and juice of pineapples, has anti-inflammatory properties that may assist with joint pain relief.
Despite its nutritional merits, feeding pineapple to your dog requires caution due to potential risks associated with excessive consumption. High sugar content means too much pineapple can lead to obesity or diabetes over time. Furthermore, raw pineapple poses choking hazards because of tough outer rinds and fibrous interiors. Always remove the prickly skin, crown, and center core before offering small bite-sized pieces as treats. Moderation remains key; limit servings to no more than one inch cube per ten pounds of body weight daily.
Another factor worth noting relates to allergies. Some dogs exhibit adverse reactions upon ingesting pineapple, characterized by symptoms such as itching, swelling, vomiting, diarrhea, or difficulty breathing. If you notice any signs indicating sensitivity after introducing pineapple into your dog's diet, discontinue feeding immediately and consult your veterinarian. Regular monitoring ensures early detection of intolerance issues so adjustments can be made accordingly.
Returning to the realm of connectivity solutions for lost pets, both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators serve distinct purposes based on user requirements. Owners seeking economical yet reliable methods for locating nearby missing animals might find satisfaction using Bluetooth-enabled devices. Conversely, those prioritizing extended reach combined with sophisticated analytics prefer investing in premium Wi-Fi alternatives capable of delivering comprehensive insights beyond mere positional data. Regardless of choice, incorporating either option enhances safety measures already established within households containing beloved four-legged companions.
In conclusion, selecting appropriate wireless communication protocols depends largely on intended usage scenarios alongside financial limitations imposed by available budgets. Meanwhile, answering queries concerning whether can dogs eat pineapple reveals importance attached not only towards technological innovation safeguarding our pets' physical presence but also dietary knowledge ensuring optimal nourishment supporting long-term vitality. By balancing practical tools promoting security alongside informed decisions guiding nutrition, we empower ourselves as conscientious caretakers committed to fostering happy, healthy lifestyles shared amongst family members across species lines alike.
Update Time:2025-05-15 06:01:16
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form