New ArrivalsBack in stock
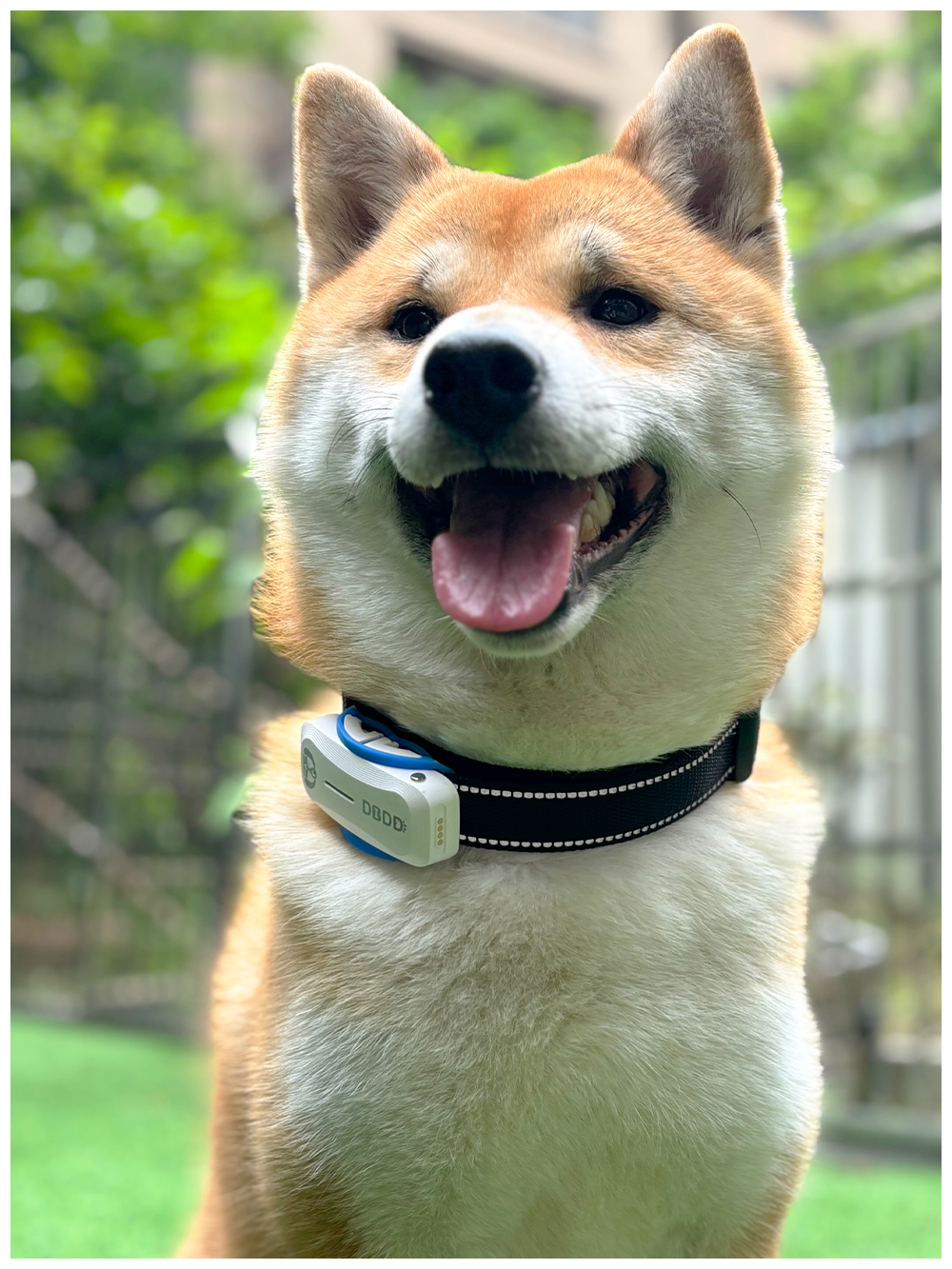
dog tracking collar with gps
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D717162745 second hand :D717162745 |
Manufacturer | dog tracking | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $44 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | tracking collar | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Military Tech#Search & Rescue Devices
When it comes to keeping track of our beloved pets, technology has advanced significantly in recent years. Two popular options for pet tracking are collar-mounted and implantable pet trackers. Both types of trackers have their own set of advantages and disadvantages, making the decision between them a critical one for pet owners. This article delves into the differences between these two types of pet trackers, focusing on the dog tracking collar with GPS as well as the more invasive option of an implantable tracker.
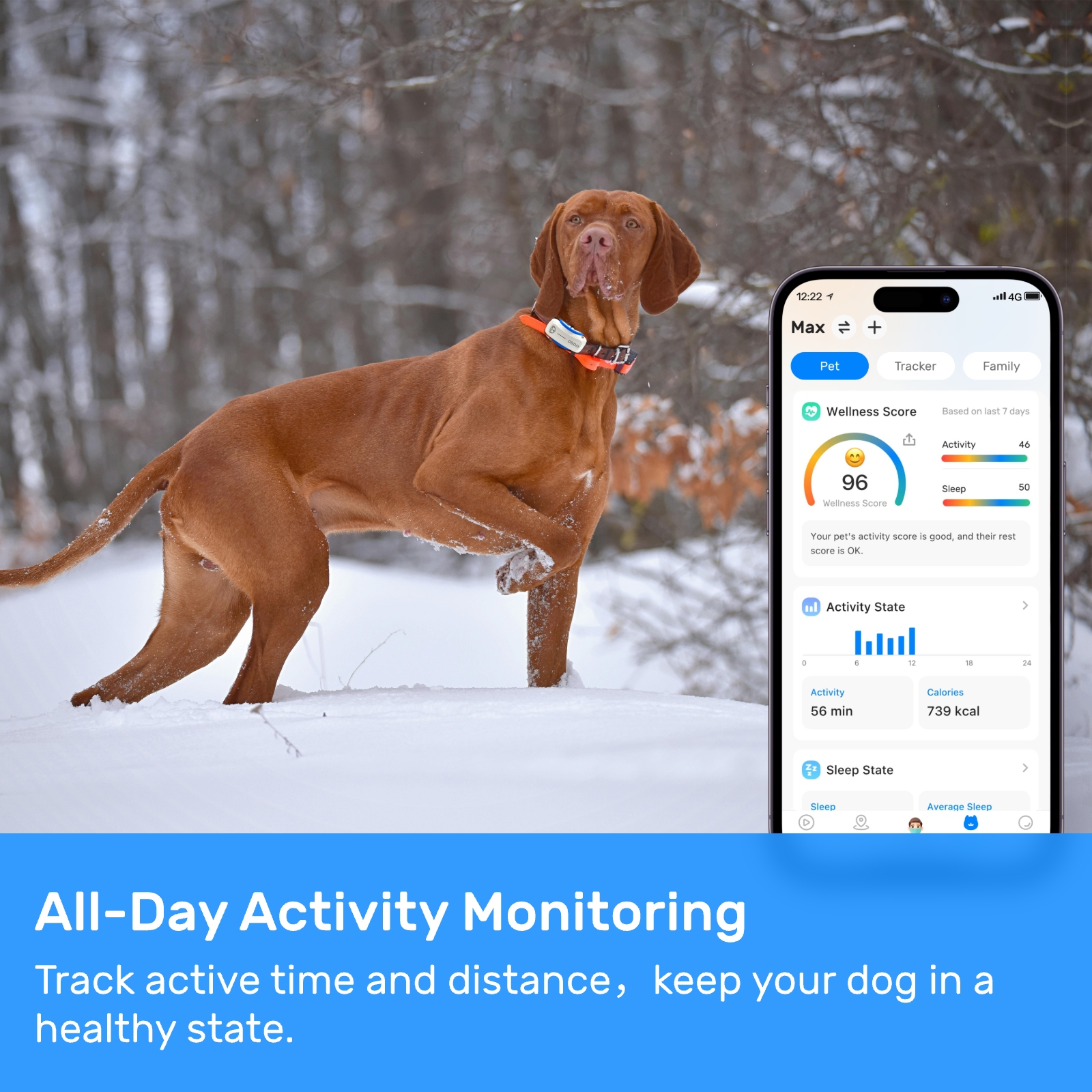
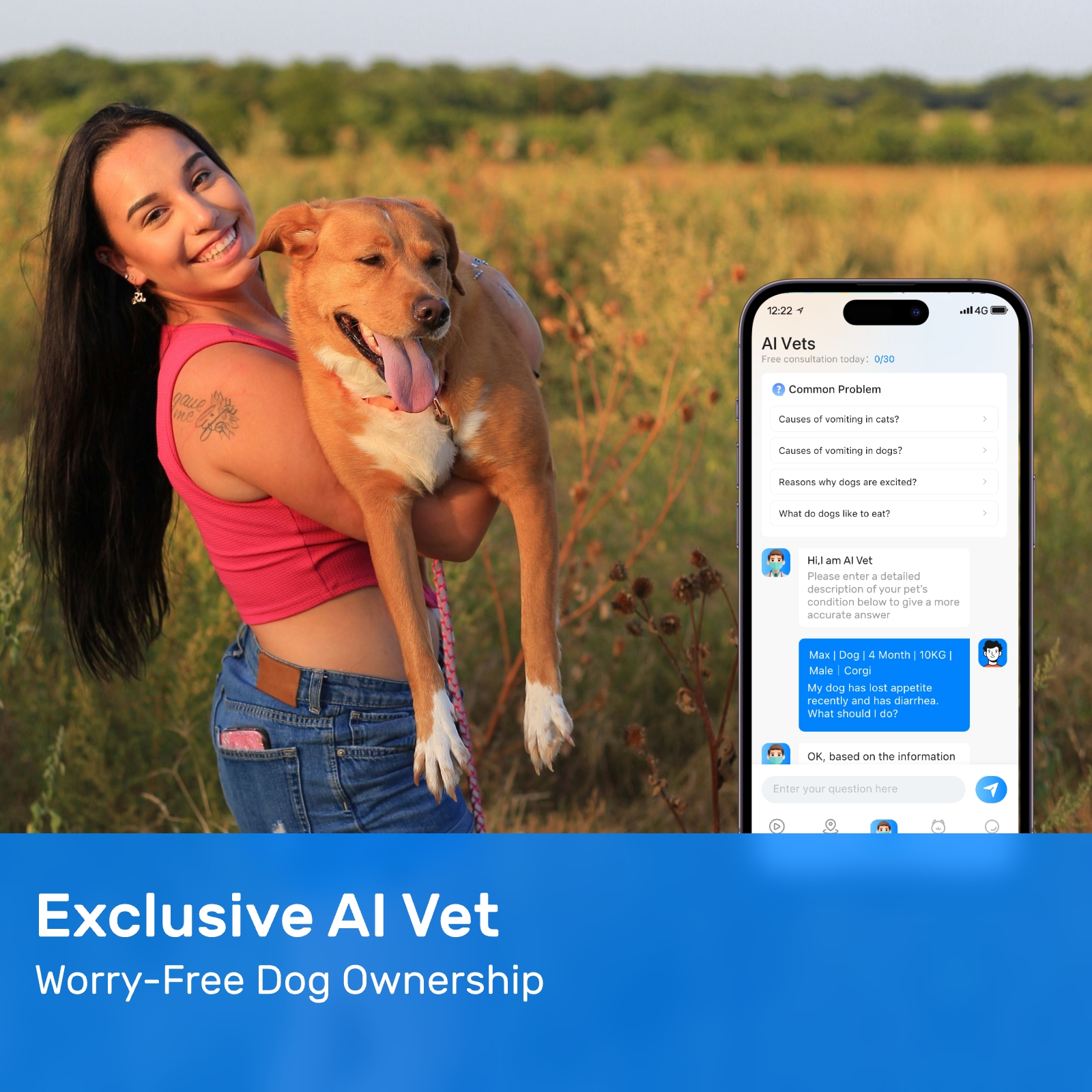
Collar-mounted trackers, specifically the dog tracking collar with GPS, are the most common form of pet tracking devices. These devices attach to your dog's collar and use GPS technology to provide real-time location updates. They are relatively easy to install and remove, which makes them convenient for pet owners who frequently take their dogs out for walks or travel with them. One of the primary benefits of a collar-mounted tracker is its accessibility. Most models come equipped with features such as geofencing, activity monitoring, and even health alerts. The geofencing feature allows pet owners to set virtual boundaries around specific areas, triggering an alert if the dog ventures outside those boundaries. Additionally, many collar-mounted trackers offer companion apps that allow users to monitor their dog's movements from their smartphones.

However, there are some drawbacks to using a dog tracking collar with GPS. First, the device relies on the collar itself, meaning that if the collar is removed or lost, so too is the tracker. This can be a significant concern for pet owners whose dogs are particularly adept at slipping out of collars or losing them during play. Furthermore, collar-mounted trackers require regular charging, which can be inconvenient if the battery dies while the dog is out of sight. Some models also suffer from bulkiness, which might not be suitable for smaller breeds or dogs with sensitive skin.

On the other hand, implantable pet trackers offer a more permanent solution to pet tracking. These tiny devices are inserted under the dog's skin, usually in the scruff of the neck, through a minor surgical procedure. Implantable trackers eliminate the risk of the device being lost or removed, as they are securely embedded within the dog's body. This permanence provides peace of mind for pet owners who worry about their dogs wandering off or getting lost. Moreover, since implantable trackers do not rely on external batteries, they generally have a longer operational lifespan compared to collar-mounted alternatives.
Despite these advantages, implantable pet trackers also come with certain limitations. The initial cost of implantation can be higher than that of a dog tracking collar with GPS, and the procedure itself may cause some discomfort or anxiety for the dog. While complications from the surgery are rare, there is still a small risk of infection or rejection. Additionally, the technology behind implantable trackers is often less advanced than that of collar-mounted devices. Many implantable trackers lack the sophisticated features found in modern dog tracking collars with GPS, such as geofencing, activity monitoring, and detailed location data. As a result, they may not provide the same level of insight into a dog's daily activities or whereabouts.

Another consideration when choosing between collar-mounted and implantable pet trackers is the ease of use. A dog tracking collar with GPS typically requires minimal setup and can be easily adjusted or replaced as needed. Most models are designed to be user-friendly, with straightforward interfaces and intuitive apps. In contrast, implantable trackers require professional installation and cannot be easily modified or upgraded once implanted. This means that if new technology becomes available or if the current tracker malfunctions, replacing it could involve another surgical procedure.

Privacy concerns are another factor to consider when evaluating these two types of pet trackers. Collar-mounted trackers, like the dog tracking collar with GPS, transmit data via cellular networks or Wi-Fi, which raises potential issues regarding data security and privacy. Owners must ensure that their chosen device adheres to strict data protection standards to safeguard their pet's information. Meanwhile, implantable trackers store data internally, reducing the risk of unauthorized access but potentially limiting the amount of data that can be collected and analyzed.
Cost is yet another important aspect to weigh when deciding between collar-mounted and implantable pet trackers. Dog tracking collars with GPS tend to have lower upfront costs compared to implantable trackers, although ongoing subscription fees for GPS services should also be factored in. Over time, these subscription fees could add up, potentially exceeding the initial cost of an implantable tracker. It is essential for pet owners to carefully evaluate their budget and long-term needs before making a purchase.
Environmental factors also play a role in determining the best type of tracker for your dog. For instance, if you live in an area with poor cellular coverage, a dog tracking collar with GPS may not function optimally due to limited signal strength. In such cases, an implantable tracker that uses alternative technologies, such as radio frequency identification (RFID), might be a better choice. Conversely, if your dog spends a lot of time outdoors in rugged terrain, a durable collar-mounted tracker designed to withstand harsh conditions could be preferable.
Ultimately, the decision between a dog tracking collar with GPS and an implantable pet tracker depends on individual preferences and circumstances. For pet owners seeking a non-invasive, feature-rich solution that offers flexibility and convenience, a collar-mounted tracker is likely the best option. These devices provide comprehensive monitoring capabilities and are suitable for most dogs, especially those who wear collars consistently. However, for those prioritizing permanence and reliability above all else, an implantable tracker may be worth considering despite its higher cost and potential risks.
In conclusion, both collar-mounted and implantable pet trackers have their merits and drawbacks. A dog tracking collar with GPS provides ease of use, advanced features, and affordability, while an implantable tracker ensures permanence and reduces the likelihood of loss. Pet owners must assess their specific needs, taking into account factors such as budget, lifestyle, and technological requirements, to determine which type of tracker aligns best with their goals. Regardless of the choice made, investing in a reliable pet tracking system demonstrates a commitment to ensuring the safety and well-being of our furry companions.

Update Time:2025-05-15 22:51:56
Collar-mounted trackers, specifically the dog tracking collar with GPS, are the most common form of pet tracking devices. These devices attach to your dog's collar and use GPS technology to provide real-time location updates. They are relatively easy to install and remove, which makes them convenient for pet owners who frequently take their dogs out for walks or travel with them. One of the primary benefits of a collar-mounted tracker is its accessibility. Most models come equipped with features such as geofencing, activity monitoring, and even health alerts. The geofencing feature allows pet owners to set virtual boundaries around specific areas, triggering an alert if the dog ventures outside those boundaries. Additionally, many collar-mounted trackers offer companion apps that allow users to monitor their dog's movements from their smartphones.

However, there are some drawbacks to using a dog tracking collar with GPS. First, the device relies on the collar itself, meaning that if the collar is removed or lost, so too is the tracker. This can be a significant concern for pet owners whose dogs are particularly adept at slipping out of collars or losing them during play. Furthermore, collar-mounted trackers require regular charging, which can be inconvenient if the battery dies while the dog is out of sight. Some models also suffer from bulkiness, which might not be suitable for smaller breeds or dogs with sensitive skin.

On the other hand, implantable pet trackers offer a more permanent solution to pet tracking. These tiny devices are inserted under the dog's skin, usually in the scruff of the neck, through a minor surgical procedure. Implantable trackers eliminate the risk of the device being lost or removed, as they are securely embedded within the dog's body. This permanence provides peace of mind for pet owners who worry about their dogs wandering off or getting lost. Moreover, since implantable trackers do not rely on external batteries, they generally have a longer operational lifespan compared to collar-mounted alternatives.
Despite these advantages, implantable pet trackers also come with certain limitations. The initial cost of implantation can be higher than that of a dog tracking collar with GPS, and the procedure itself may cause some discomfort or anxiety for the dog. While complications from the surgery are rare, there is still a small risk of infection or rejection. Additionally, the technology behind implantable trackers is often less advanced than that of collar-mounted devices. Many implantable trackers lack the sophisticated features found in modern dog tracking collars with GPS, such as geofencing, activity monitoring, and detailed location data. As a result, they may not provide the same level of insight into a dog's daily activities or whereabouts.

Another consideration when choosing between collar-mounted and implantable pet trackers is the ease of use. A dog tracking collar with GPS typically requires minimal setup and can be easily adjusted or replaced as needed. Most models are designed to be user-friendly, with straightforward interfaces and intuitive apps. In contrast, implantable trackers require professional installation and cannot be easily modified or upgraded once implanted. This means that if new technology becomes available or if the current tracker malfunctions, replacing it could involve another surgical procedure.

Privacy concerns are another factor to consider when evaluating these two types of pet trackers. Collar-mounted trackers, like the dog tracking collar with GPS, transmit data via cellular networks or Wi-Fi, which raises potential issues regarding data security and privacy. Owners must ensure that their chosen device adheres to strict data protection standards to safeguard their pet's information. Meanwhile, implantable trackers store data internally, reducing the risk of unauthorized access but potentially limiting the amount of data that can be collected and analyzed.
Cost is yet another important aspect to weigh when deciding between collar-mounted and implantable pet trackers. Dog tracking collars with GPS tend to have lower upfront costs compared to implantable trackers, although ongoing subscription fees for GPS services should also be factored in. Over time, these subscription fees could add up, potentially exceeding the initial cost of an implantable tracker. It is essential for pet owners to carefully evaluate their budget and long-term needs before making a purchase.
Environmental factors also play a role in determining the best type of tracker for your dog. For instance, if you live in an area with poor cellular coverage, a dog tracking collar with GPS may not function optimally due to limited signal strength. In such cases, an implantable tracker that uses alternative technologies, such as radio frequency identification (RFID), might be a better choice. Conversely, if your dog spends a lot of time outdoors in rugged terrain, a durable collar-mounted tracker designed to withstand harsh conditions could be preferable.
Ultimately, the decision between a dog tracking collar with GPS and an implantable pet tracker depends on individual preferences and circumstances. For pet owners seeking a non-invasive, feature-rich solution that offers flexibility and convenience, a collar-mounted tracker is likely the best option. These devices provide comprehensive monitoring capabilities and are suitable for most dogs, especially those who wear collars consistently. However, for those prioritizing permanence and reliability above all else, an implantable tracker may be worth considering despite its higher cost and potential risks.
In conclusion, both collar-mounted and implantable pet trackers have their merits and drawbacks. A dog tracking collar with GPS provides ease of use, advanced features, and affordability, while an implantable tracker ensures permanence and reduces the likelihood of loss. Pet owners must assess their specific needs, taking into account factors such as budget, lifestyle, and technological requirements, to determine which type of tracker aligns best with their goals. Regardless of the choice made, investing in a reliable pet tracking system demonstrates a commitment to ensuring the safety and well-being of our furry companions.

Update Time:2025-05-15 22:51:56
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form