New ArrivalsBack in stock
tractive
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D217649799 second hand :D217649799 |
Manufacturer | tractive | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $37 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | tractive | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
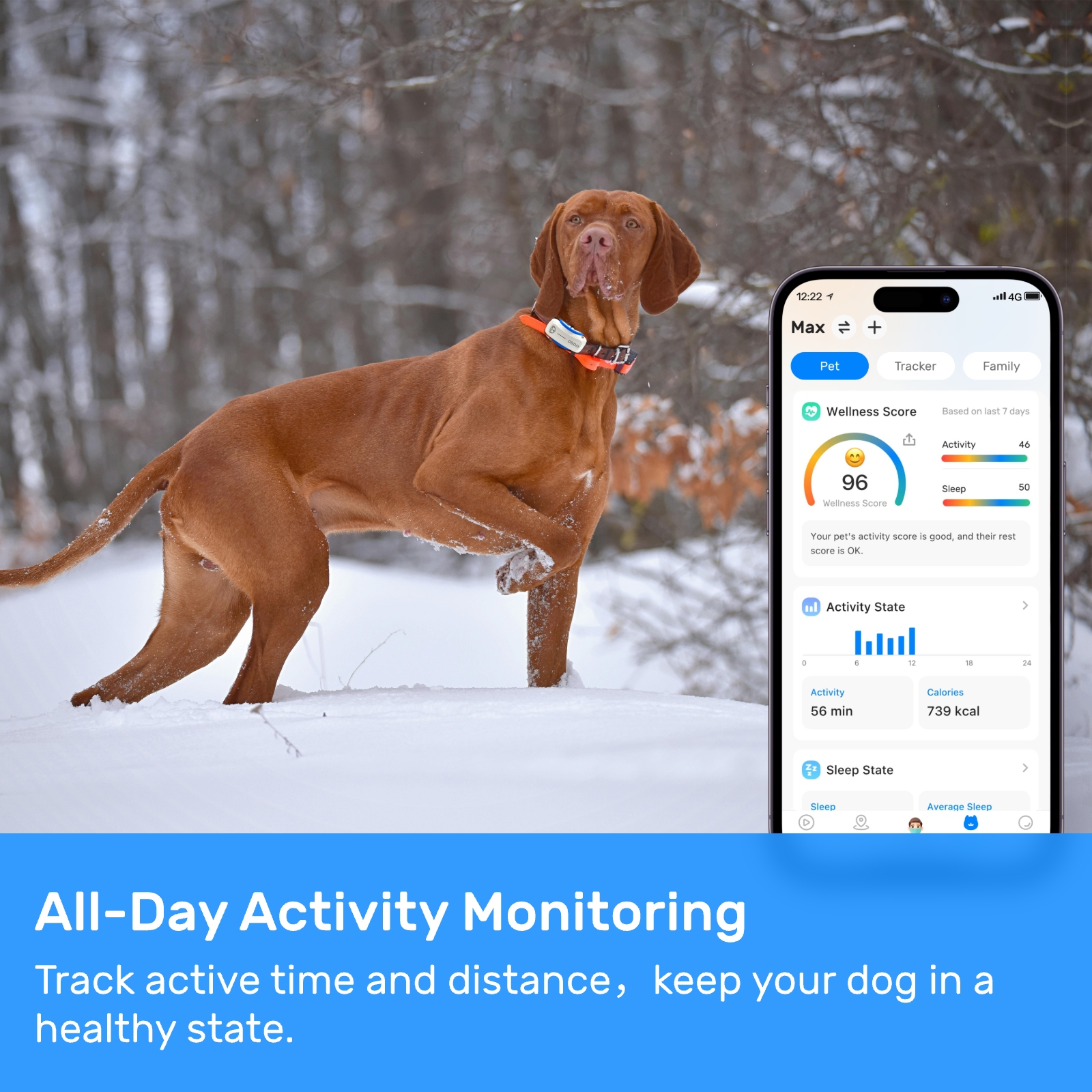
Pet Smart Hardware#Wearable Devices










Introduction

Tractive, a term derived from the Latin word "tractus," meaning "to pull or draw," has been a crucial aspect of human progress and development throughout history. From the invention of the wheel to the advent of modern machinery, tractive power has played a vital role in shaping our world. This article aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of tractive power and its impact on various industries, including agriculture, transportation, and construction. We will explore the different types of tractive power, their applications, and the challenges faced in harnessing and optimizing this force.

Historical Context of Tractive Power
The concept of tractive power can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where humans harnessed the power of animals to move heavy loads and plow fields. Horses, oxen, and even elephants were used to pull carts, chariots, and plows, providing the necessary force for transportation and agriculture. The development of the wheel and axle system further revolutionized the way humans moved goods and people, making the use of tractive power more efficient and widespread.
As technology advanced, humans began to explore alternative sources of tractive power. The steam engine, invented in the early 18th century, marked a significant shift in the way people harnessed energy. Steam-powered locomotives and ships transformed transportation, allowing for the movement of goods and people over long distances at unprecedented speeds. The advent of the internal combustion engine in the late 19th century further revolutionized tractive power, paving the way for the development of automobiles, trucks, and heavy machinery.
Types of Tractive Power
Tractive power can be broadly classified into two categories: mechanical and non-mechanical. Mechanical tractive power relies on the physical interaction between two surfaces to generate force, while non-mechanical tractive power harnesses natural forces like wind, water, and electricity.
1. Mechanical Tractive Power
a. Animal Power: As mentioned earlier, animals have been a significant source of tractive power throughout history. Horses, oxen, and elephants were used to pull carts, chariots, and plows, providing the necessary force for transportation and agriculture.
b. Wheel and Axle System: The invention of the wheel and axle system revolutionized the way humans moved goods and people. This system involves a wheel rotating around an axle, which transfers the tractive force from the wheel to the axle and ultimately to the object being moved.
c. Internal Combustion Engine: The internal combustion engine, fueled by gasoline or diesel, is a widely used source of tractive power in modern vehicles and machinery. This engine converts the chemical energy stored in fuel into mechanical energy, which is then used to propel vehicles or operate machinery.
d. Electric Motor: Electric motors convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, providing tractive power for electric vehicles and machinery. These motors are increasingly being used in various industries due to their efficiency, low emissions, and ease of maintenance.
2. Non-Mechanical Tractive Power

a. Wind Power: Wind power harnesses the force of the wind to generate tractive power, primarily for transportation and electricity generation. Wind-powered ships have been used for centuries, while modern wind turbines convert wind energy into electricity.
b. Water Power: Water power harnesses the force of flowing water to generate tractive power, primarily for electricity generation and industrial processes. Hydroelectric power plants use the kinetic energy of flowing water to generate electricity, while water wheels have been used for centuries to power machinery in various industries.
c. Magnetic Levitation: Magnetic levitation, or maglev, is a technology that uses magnetic forces to levitate and propel vehicles. This system eliminates the friction between the vehicle and the track, reducing energy consumption and increasing efficiency.
Applications of Tractive Power in Various Industries
1. Agriculture

In the agriculture industry, tractive power is essential for plowing, planting, harvesting, and transporting crops. Traditionally, animals like horses and oxen were used to pull plows and carts, but modern agricultural machinery has largely replaced these methods. Tractors, powered by internal combustion engines or electric motors, are now the primary source of tractive power for agricultural tasks. These machines can perform multiple tasks, such as plowing, planting, and harvesting, increasing efficiency and productivity in the agriculture industry.

2. Transportation
Tractive power plays a crucial role in the transportation industry, where it is used to propel vehicles and transport goods and people. In the automotive sector, internal combustion engines and electric motors are the primary sources of tractive power, powering cars, trucks, and buses. In the maritime industry, tractive power is provided by diesel engines, steam turbines, and electric motors, while wind power is harnessed by sailboats and wind-powered ships. In the aviation industry, jet engines and propellers provide tractive power for airplanes, while rockets provide tractive power for space vehicles.

3. Construction
In the construction industry, tractive power is essential for
Update Time:2025-05-15 22:15:07
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form