New ArrivalsBack in stock
can dogs eat shrimp
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D487079284 second hand :D487079284 |
Manufacturer | can dogs | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $42 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | dogs eat | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Precision Agriculture#Livestock Tracking
Pet Locator Data Privacy Concerns and the Controversy Surrounding "Can Dogs Eat Shrimp"
Introduction

In today's digital age, pet owners are increasingly relying on technology to keep track of their furry friends. Pet locator devices, such as GPS collars and mobile apps, have become popular tools for monitoring the whereabouts of pets and ensuring their safety. However, these devices raise significant data privacy concerns, particularly in relation to the sharing of pet health information. One such example is the debate surrounding "can dogs eat shrimp," which has sparked discussions on the potential consequences of sharing pet dietary preferences and medical data online. This article will explore the data privacy concerns associated with pet locator devices, the controversy surrounding "can dogs eat shrimp," and the potential risks of sharing pet health information online.
Pet Locator Data Privacy Concerns
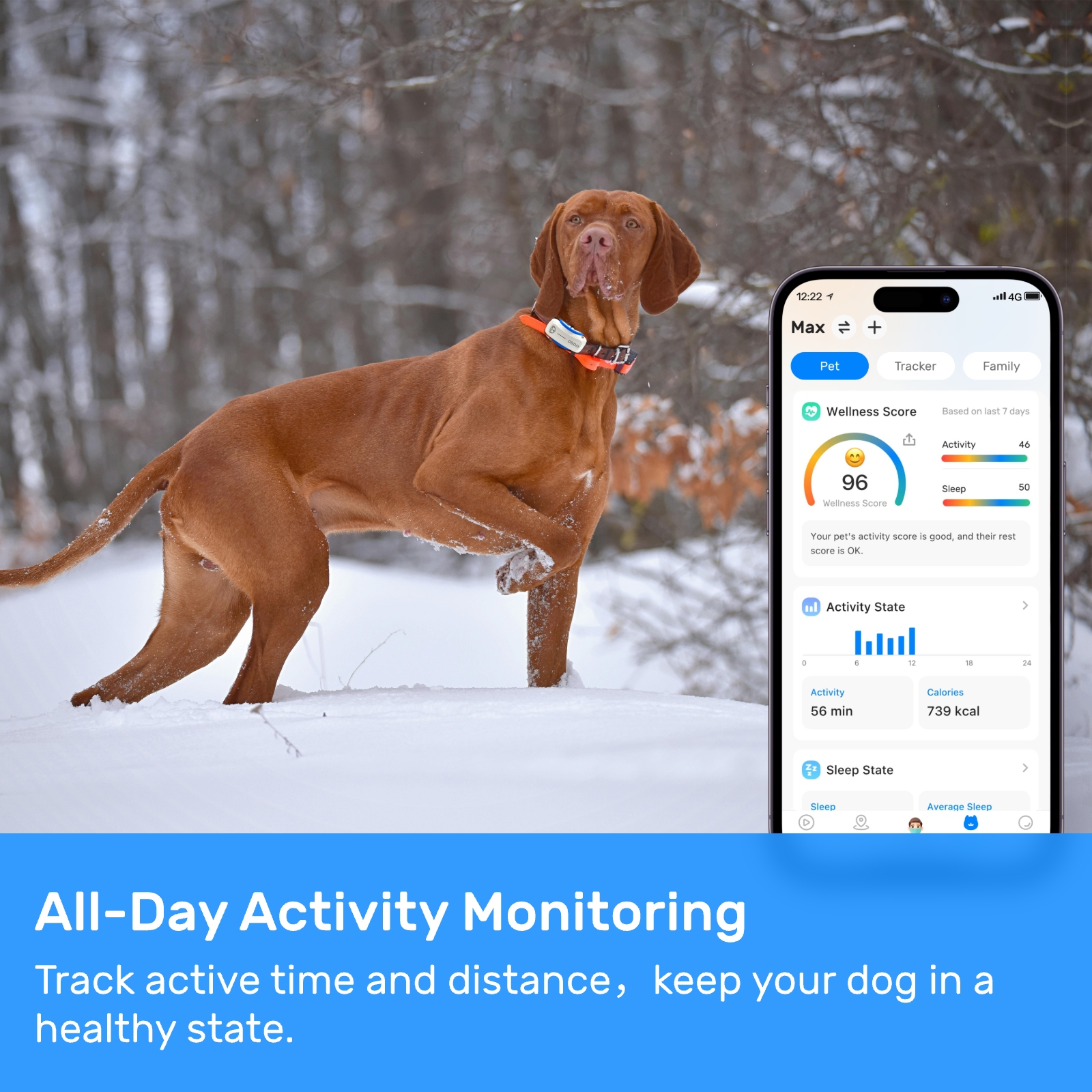
Pet locator devices and mobile apps are designed to provide pet owners with peace of mind by allowing them to track their pets' movements and locate them in case of emergencies. However, these devices and apps collect and store a wealth of personal information, including the pet's location, name, breed, and owner's contact details. This data can be vulnerable to hacking, data breaches, and unauthorized access, raising concerns about the privacy and security of pet owners and their pets.
Data breaches involving pet locator devices and apps can lead to the unauthorized disclosure of sensitive information, such as the pet's location, which could be used for malicious purposes. For instance, a hacker could use this information to locate a pet and steal it or use it for ransom. Additionally, the disclosure of the owner's contact details could lead to targeted phishing attacks, identity theft, and other forms of online fraud.
Moreover, the collection and storage of pet health information, such as dietary preferences and medical history, raise concerns about data privacy and the potential misuse of this information. Pet owners may be unaware of the extent to which their pet's health data is being collected and stored, and the potential consequences of sharing this information online.
Controversy Surrounding "Can Dogs Eat Shrimp"
The debate surrounding "can dogs eat shrimp" highlights the potential risks of sharing pet health information online. Shrimp is a popular food choice for humans, but it is not universally recommended for dogs due to concerns about allergies, food poisoning, and the risk of choking on shrimp shells. While some pet owners may believe that their dogs can safely consume shrimp, others argue that doing so poses significant health risks.

The sharing of pet dietary preferences and health information online can lead to the spread of misinformation and the perpetuation of unsafe practices. For example, a pet owner who believes that their dog can safely eat shrimp may share this information on social media or in online forums, leading other pet owners to follow suit without considering the potential risks. This can result in a chain reaction of misinformation that puts other pets' health and safety at risk.
Furthermore, the sharing of pet health information online can lead to the unauthorized collection and use of this data by third parties, such as pet food companies, veterinarians, and insurance providers. This data can be used to target pet owners with personalized marketing campaigns, influence their decision-making, and potentially affect their pet insurance premiums.

Potential Risks of Sharing Pet Health Information Online
Sharing pet health information online, including dietary preferences and medical history, can have several potential risks:
1. Data breaches and unauthorized access: As mentioned earlier, sharing pet health information online can make this data vulnerable to hacking, data breaches, and unauthorized access. This can lead to the disclosure of sensitive information, such as the pet's location and the owner's contact details, which can be used for malicious purposes.
2. Misinformation and unsafe practices: The sharing of pet health information online can lead to the spread of misinformation and the perpetuation of unsafe practices, such as feeding dogs shrimp. This can put pets' health and safety at risk and result in costly veterinary bills and other consequences.
3. Targeted marketing and influence: The unauthorized collection and use of pet health information by third parties can lead to targeted marketing campaigns and attempts to influence pet owners' decision-making. This can result in pet owners being pressured to buy certain products or services, even if they are not in the best interest of their pets' health.

4. Privacy concerns: Sharing pet health information online can lead to privacy concerns for pet owners, who may be unaware of the extent to which their pet's data is being collected and stored. This can result in a lack of trust in the companies and organizations that collect and use this data, leading to a loss of confidence in the pet industry.

5. Legal and regulatory risks: The sharing of pet health information online can also raise legal and regulatory risks, particularly if this data is not properly protected and secured. This can result in fines, penalties, and other legal consequences for companies and organizations that fail to comply with data privacy regulations.
Conclusion

Pet locator devices and apps offer a valuable service to pet owners, providing them with the ability to track their pets' movements and locate them in case of emergencies. However,
Update Time:2025-05-15 07:12:31
Introduction

In today's digital age, pet owners are increasingly relying on technology to keep track of their furry friends. Pet locator devices, such as GPS collars and mobile apps, have become popular tools for monitoring the whereabouts of pets and ensuring their safety. However, these devices raise significant data privacy concerns, particularly in relation to the sharing of pet health information. One such example is the debate surrounding "can dogs eat shrimp," which has sparked discussions on the potential consequences of sharing pet dietary preferences and medical data online. This article will explore the data privacy concerns associated with pet locator devices, the controversy surrounding "can dogs eat shrimp," and the potential risks of sharing pet health information online.
Pet Locator Data Privacy Concerns
Pet locator devices and mobile apps are designed to provide pet owners with peace of mind by allowing them to track their pets' movements and locate them in case of emergencies. However, these devices and apps collect and store a wealth of personal information, including the pet's location, name, breed, and owner's contact details. This data can be vulnerable to hacking, data breaches, and unauthorized access, raising concerns about the privacy and security of pet owners and their pets.
Data breaches involving pet locator devices and apps can lead to the unauthorized disclosure of sensitive information, such as the pet's location, which could be used for malicious purposes. For instance, a hacker could use this information to locate a pet and steal it or use it for ransom. Additionally, the disclosure of the owner's contact details could lead to targeted phishing attacks, identity theft, and other forms of online fraud.
Moreover, the collection and storage of pet health information, such as dietary preferences and medical history, raise concerns about data privacy and the potential misuse of this information. Pet owners may be unaware of the extent to which their pet's health data is being collected and stored, and the potential consequences of sharing this information online.
Controversy Surrounding "Can Dogs Eat Shrimp"
The debate surrounding "can dogs eat shrimp" highlights the potential risks of sharing pet health information online. Shrimp is a popular food choice for humans, but it is not universally recommended for dogs due to concerns about allergies, food poisoning, and the risk of choking on shrimp shells. While some pet owners may believe that their dogs can safely consume shrimp, others argue that doing so poses significant health risks.

The sharing of pet dietary preferences and health information online can lead to the spread of misinformation and the perpetuation of unsafe practices. For example, a pet owner who believes that their dog can safely eat shrimp may share this information on social media or in online forums, leading other pet owners to follow suit without considering the potential risks. This can result in a chain reaction of misinformation that puts other pets' health and safety at risk.
Furthermore, the sharing of pet health information online can lead to the unauthorized collection and use of this data by third parties, such as pet food companies, veterinarians, and insurance providers. This data can be used to target pet owners with personalized marketing campaigns, influence their decision-making, and potentially affect their pet insurance premiums.

Potential Risks of Sharing Pet Health Information Online
Sharing pet health information online, including dietary preferences and medical history, can have several potential risks:
1. Data breaches and unauthorized access: As mentioned earlier, sharing pet health information online can make this data vulnerable to hacking, data breaches, and unauthorized access. This can lead to the disclosure of sensitive information, such as the pet's location and the owner's contact details, which can be used for malicious purposes.
2. Misinformation and unsafe practices: The sharing of pet health information online can lead to the spread of misinformation and the perpetuation of unsafe practices, such as feeding dogs shrimp. This can put pets' health and safety at risk and result in costly veterinary bills and other consequences.
3. Targeted marketing and influence: The unauthorized collection and use of pet health information by third parties can lead to targeted marketing campaigns and attempts to influence pet owners' decision-making. This can result in pet owners being pressured to buy certain products or services, even if they are not in the best interest of their pets' health.

4. Privacy concerns: Sharing pet health information online can lead to privacy concerns for pet owners, who may be unaware of the extent to which their pet's data is being collected and stored. This can result in a lack of trust in the companies and organizations that collect and use this data, leading to a loss of confidence in the pet industry.

5. Legal and regulatory risks: The sharing of pet health information online can also raise legal and regulatory risks, particularly if this data is not properly protected and secured. This can result in fines, penalties, and other legal consequences for companies and organizations that fail to comply with data privacy regulations.
Conclusion

Pet locator devices and apps offer a valuable service to pet owners, providing them with the ability to track their pets' movements and locate them in case of emergencies. However,
Update Time:2025-05-15 07:12:31
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form