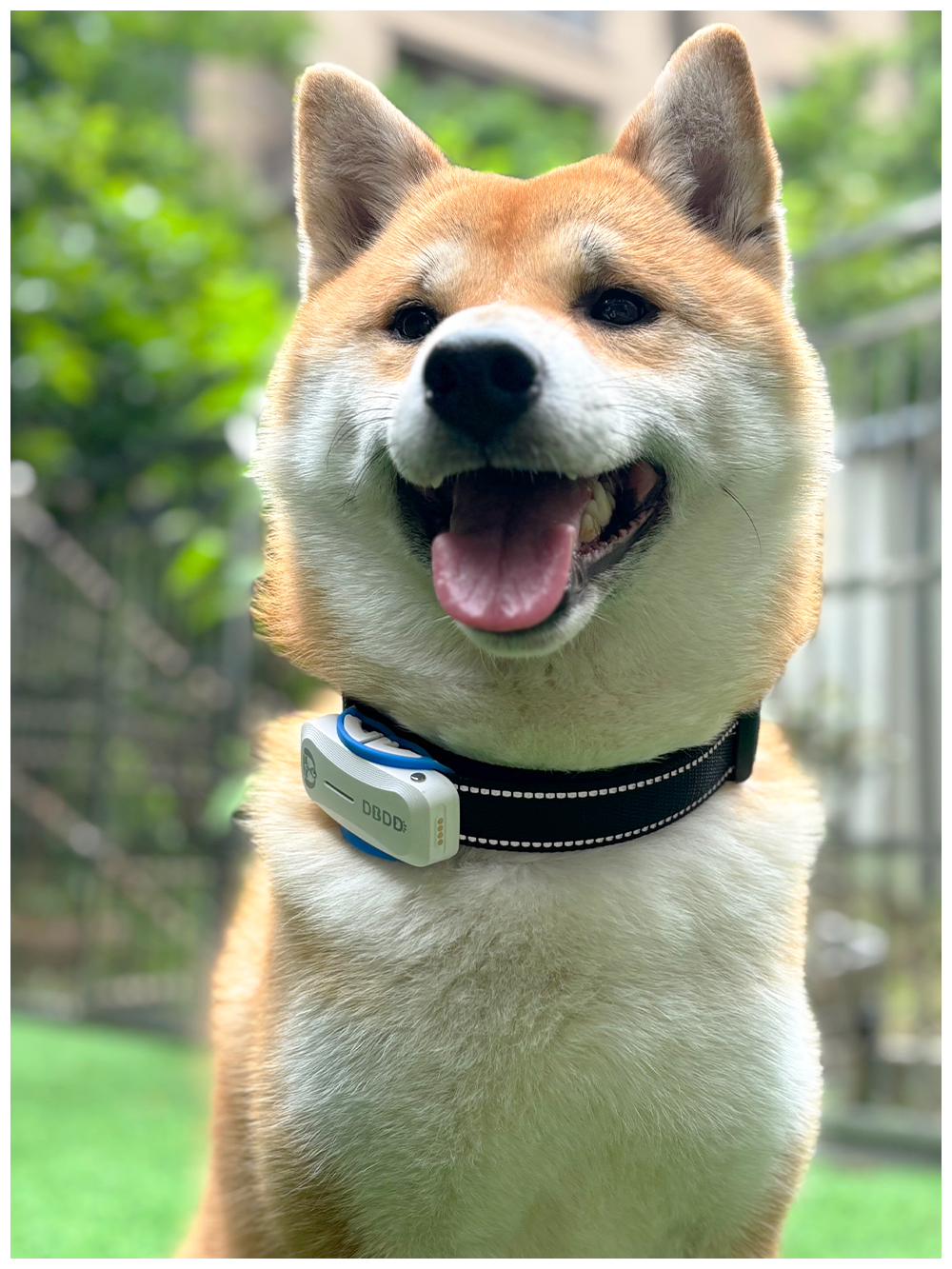
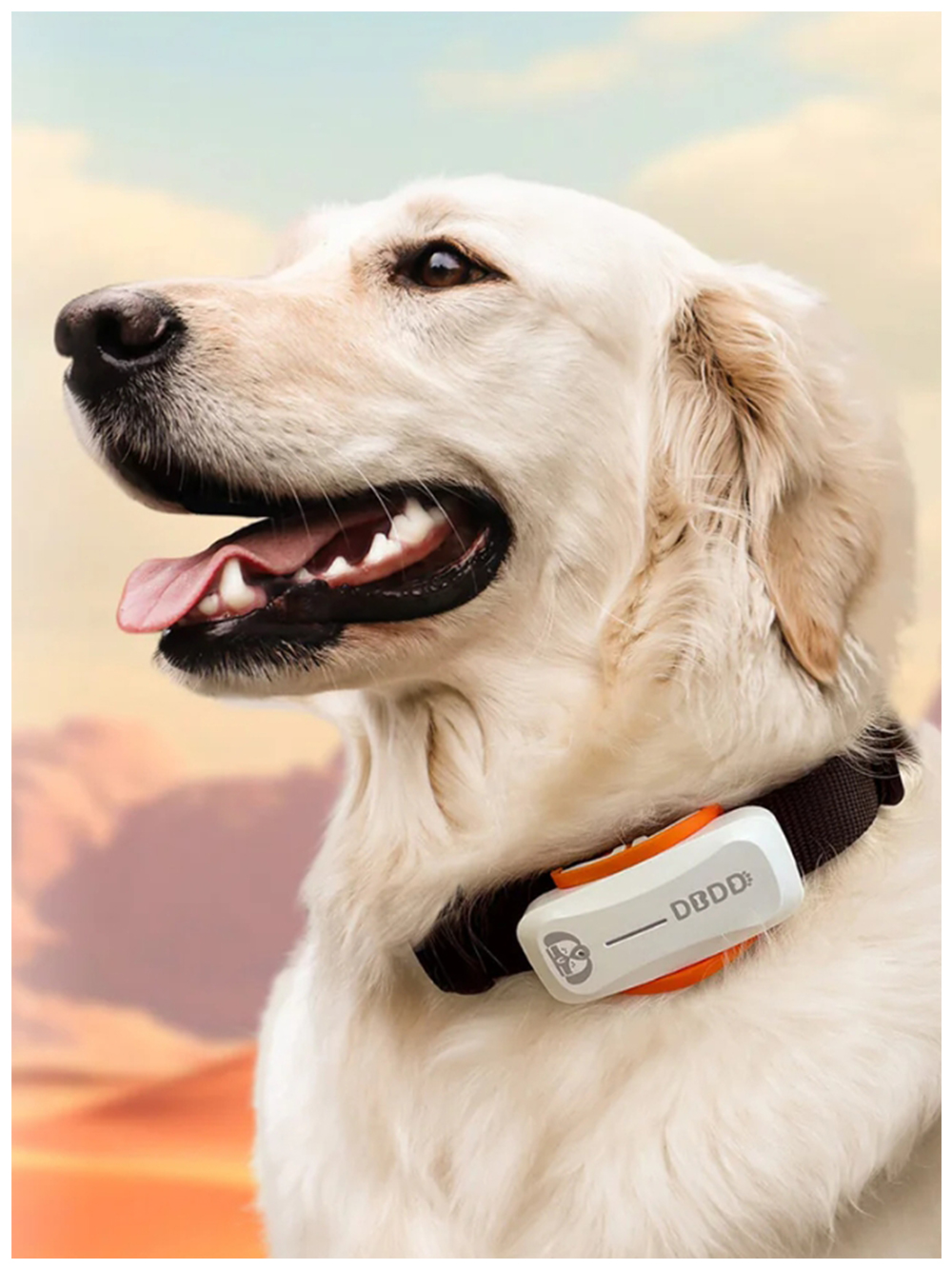
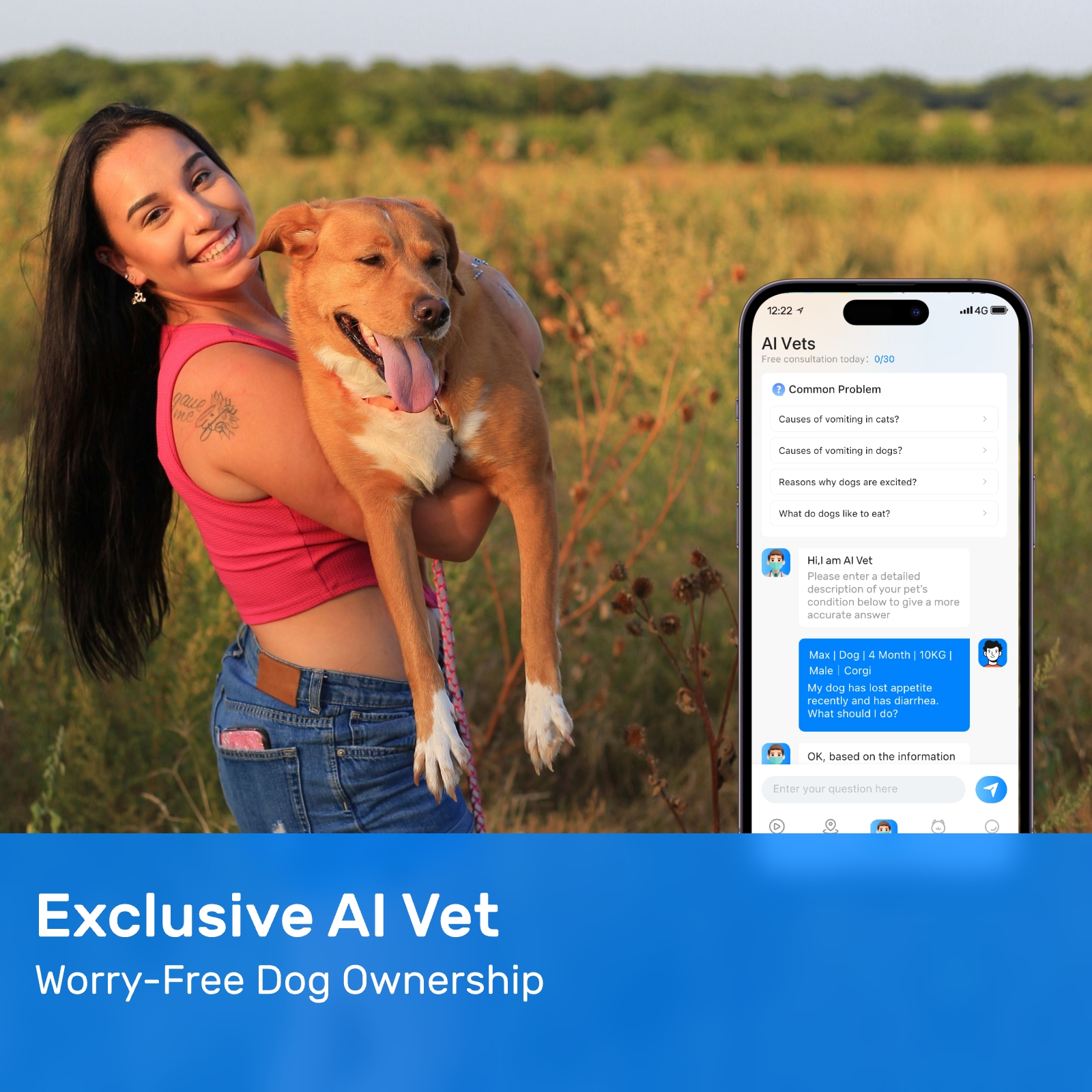
New ArrivalsBack in stock
gps collar dogs
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D689231006 second hand :D689231006 |
Manufacturer | gps collar | release date | 2025-05-16 | List price | $37 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | collar dogs | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Behavioral Science#Activity Analysis Tools
The durability of GPS collar dogs is a critical aspect that influences their effectiveness in tracking and monitoring animals. These collars are essential tools for wildlife researchers, conservationists, and pet owners who need to keep track of the movements and behaviors of their animals. The materials used in manufacturing these collars play a significant role in determining their longevity and performance under various environmental conditions. This article explores recent studies on collar material durability specifically related to GPS collar dogs, examining how different materials withstand wear and tear over time.
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated GPS collar dogs. These devices provide real-time location data, which is invaluable for understanding animal behavior patterns and migration routes. However, the effectiveness of these collars largely depends on the quality and durability of the materials used in their construction. Researchers have conducted numerous studies to evaluate the performance of various materials under different environmental conditions, focusing on factors such as abrasion resistance, water resistance, and overall lifespan.
One of the primary concerns regarding GPS collar dogs is their ability to withstand harsh weather conditions. Collars made from synthetic materials like nylon and polyester are often preferred due to their high tensile strength and resistance to moisture. Studies indicate that these materials maintain their integrity even after prolonged exposure to rain, snow, and extreme temperatures. For instance, a study conducted by the Wildlife Conservation Society found that nylon-based collars retained their functionality and structural integrity over a two-year period, despite being exposed to varying climatic conditions in the field.
Another crucial factor in assessing the durability of GPS collar dogs is their resistance to physical damage caused by the animal's activities. Dogs, especially those in the wild or engaged in active outdoor pursuits, can subject their collars to significant wear and tear. Materials such as Kevlar and other high-strength fibers have been shown to offer superior abrasion resistance compared to traditional materials like leather or cotton. A research project carried out by the University of California demonstrated that Kevlar-reinforced collars experienced significantly less wear and tear over an 18-month observation period, making them a more durable option for GPS collar dogs.

Water resistance is another key attribute evaluated in studies concerning the durability of GPS collar dogs. Animals often come into contact with water sources, whether through swimming, rainfall, or other means. Collars that fail to adequately repel water can suffer from corrosion of internal components, leading to reduced functionality. Research conducted by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) highlighted the importance of using waterproof coatings and materials in the construction of GPS collars. Collars treated with hydrophobic coatings showed enhanced water resistance, preserving their operational capabilities even after repeated submersion tests.
The lifespan of GPS collar dogs is also influenced by the degradation of materials over time. Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight can cause certain materials to break down, compromising the collar's structural integrity. Studies have shown that UV-resistant polymers, such as polyurethane and polycarbonate, offer increased protection against photodegradation. A long-term field study conducted in Australia revealed that collars made from UV-resistant materials lasted up to three times longer than those constructed from standard plastics, underscoring the importance of selecting appropriate materials to enhance collar durability.
Furthermore, the comfort and fit of GPS collar dogs are important considerations when evaluating material durability. Materials that are too rigid or inflexible can cause discomfort to the animal, potentially leading to behavioral issues or attempts to remove the collar. Flexible yet durable materials, such as neoprene and silicone, have been found to strike a balance between comfort and longevity. Research published in the Journal of Animal Science indicated that collars made from these materials were less likely to cause irritation or injury to the animal, promoting better acceptance and compliance.
In addition to material composition, the design and construction of GPS collar dogs also impact their durability. Reinforced stitching, secure fastening mechanisms, and protective housings for electronic components contribute to the overall robustness of the collar. Studies have shown that collars featuring double-stitched seams and reinforced stress points exhibit greater resistance to tearing and breaking. Moreover, the inclusion of shock-absorbing materials in the collar's design can help protect sensitive electronic components from damage caused by sudden impacts or falls.
Environmental sustainability is increasingly becoming a consideration in the choice of materials for GPS collar dogs. As awareness grows about the ecological impact of discarded collars, researchers are exploring biodegradable and recyclable materials that maintain the necessary durability characteristics. A study conducted by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) identified several promising alternatives, including bio-based polymers and plant-derived fibers, which could potentially replace conventional materials without compromising collar performance.

Despite the advances in material science and engineering, challenges remain in ensuring the long-term durability of GPS collar dogs. Variability in environmental conditions, individual animal behaviors, and unforeseen circumstances can all affect the performance of these devices. Ongoing research is essential to identify new materials and technologies that can further enhance the durability and reliability of GPS collars. Collaborative efforts between material scientists, engineers, and wildlife experts are crucial in developing innovative solutions that address the unique demands of tracking and monitoring animals.
In conclusion, the durability of GPS collar dogs is heavily dependent on the choice of materials used in their construction. Studies have consistently shown that synthetic materials like nylon, polyester, and Kevlar offer superior resistance to wear and tear, while UV-resistant polymers and hydrophobic coatings enhance the collar's ability to withstand environmental stresses. Comfort-enhancing materials such as neoprene and silicone, along with thoughtful design features, contribute to the overall effectiveness and longevity of these devices. As research continues to evolve, the integration of sustainable and advanced materials will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in improving the durability and functionality of GPS collar dogs, benefiting both animals and the humans who rely on them for tracking and monitoring purposes.
Update Time:2025-05-16 02:20:26
In recent years, advancements in technology have led to the development of more sophisticated GPS collar dogs. These devices provide real-time location data, which is invaluable for understanding animal behavior patterns and migration routes. However, the effectiveness of these collars largely depends on the quality and durability of the materials used in their construction. Researchers have conducted numerous studies to evaluate the performance of various materials under different environmental conditions, focusing on factors such as abrasion resistance, water resistance, and overall lifespan.
One of the primary concerns regarding GPS collar dogs is their ability to withstand harsh weather conditions. Collars made from synthetic materials like nylon and polyester are often preferred due to their high tensile strength and resistance to moisture. Studies indicate that these materials maintain their integrity even after prolonged exposure to rain, snow, and extreme temperatures. For instance, a study conducted by the Wildlife Conservation Society found that nylon-based collars retained their functionality and structural integrity over a two-year period, despite being exposed to varying climatic conditions in the field.
Another crucial factor in assessing the durability of GPS collar dogs is their resistance to physical damage caused by the animal's activities. Dogs, especially those in the wild or engaged in active outdoor pursuits, can subject their collars to significant wear and tear. Materials such as Kevlar and other high-strength fibers have been shown to offer superior abrasion resistance compared to traditional materials like leather or cotton. A research project carried out by the University of California demonstrated that Kevlar-reinforced collars experienced significantly less wear and tear over an 18-month observation period, making them a more durable option for GPS collar dogs.

Water resistance is another key attribute evaluated in studies concerning the durability of GPS collar dogs. Animals often come into contact with water sources, whether through swimming, rainfall, or other means. Collars that fail to adequately repel water can suffer from corrosion of internal components, leading to reduced functionality. Research conducted by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) highlighted the importance of using waterproof coatings and materials in the construction of GPS collars. Collars treated with hydrophobic coatings showed enhanced water resistance, preserving their operational capabilities even after repeated submersion tests.
The lifespan of GPS collar dogs is also influenced by the degradation of materials over time. Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight can cause certain materials to break down, compromising the collar's structural integrity. Studies have shown that UV-resistant polymers, such as polyurethane and polycarbonate, offer increased protection against photodegradation. A long-term field study conducted in Australia revealed that collars made from UV-resistant materials lasted up to three times longer than those constructed from standard plastics, underscoring the importance of selecting appropriate materials to enhance collar durability.
Furthermore, the comfort and fit of GPS collar dogs are important considerations when evaluating material durability. Materials that are too rigid or inflexible can cause discomfort to the animal, potentially leading to behavioral issues or attempts to remove the collar. Flexible yet durable materials, such as neoprene and silicone, have been found to strike a balance between comfort and longevity. Research published in the Journal of Animal Science indicated that collars made from these materials were less likely to cause irritation or injury to the animal, promoting better acceptance and compliance.
In addition to material composition, the design and construction of GPS collar dogs also impact their durability. Reinforced stitching, secure fastening mechanisms, and protective housings for electronic components contribute to the overall robustness of the collar. Studies have shown that collars featuring double-stitched seams and reinforced stress points exhibit greater resistance to tearing and breaking. Moreover, the inclusion of shock-absorbing materials in the collar's design can help protect sensitive electronic components from damage caused by sudden impacts or falls.
Environmental sustainability is increasingly becoming a consideration in the choice of materials for GPS collar dogs. As awareness grows about the ecological impact of discarded collars, researchers are exploring biodegradable and recyclable materials that maintain the necessary durability characteristics. A study conducted by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) identified several promising alternatives, including bio-based polymers and plant-derived fibers, which could potentially replace conventional materials without compromising collar performance.

Despite the advances in material science and engineering, challenges remain in ensuring the long-term durability of GPS collar dogs. Variability in environmental conditions, individual animal behaviors, and unforeseen circumstances can all affect the performance of these devices. Ongoing research is essential to identify new materials and technologies that can further enhance the durability and reliability of GPS collars. Collaborative efforts between material scientists, engineers, and wildlife experts are crucial in developing innovative solutions that address the unique demands of tracking and monitoring animals.
In conclusion, the durability of GPS collar dogs is heavily dependent on the choice of materials used in their construction. Studies have consistently shown that synthetic materials like nylon, polyester, and Kevlar offer superior resistance to wear and tear, while UV-resistant polymers and hydrophobic coatings enhance the collar's ability to withstand environmental stresses. Comfort-enhancing materials such as neoprene and silicone, along with thoughtful design features, contribute to the overall effectiveness and longevity of these devices. As research continues to evolve, the integration of sustainable and advanced materials will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in improving the durability and functionality of GPS collar dogs, benefiting both animals and the humans who rely on them for tracking and monitoring purposes.
Update Time:2025-05-16 02:20:26
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form