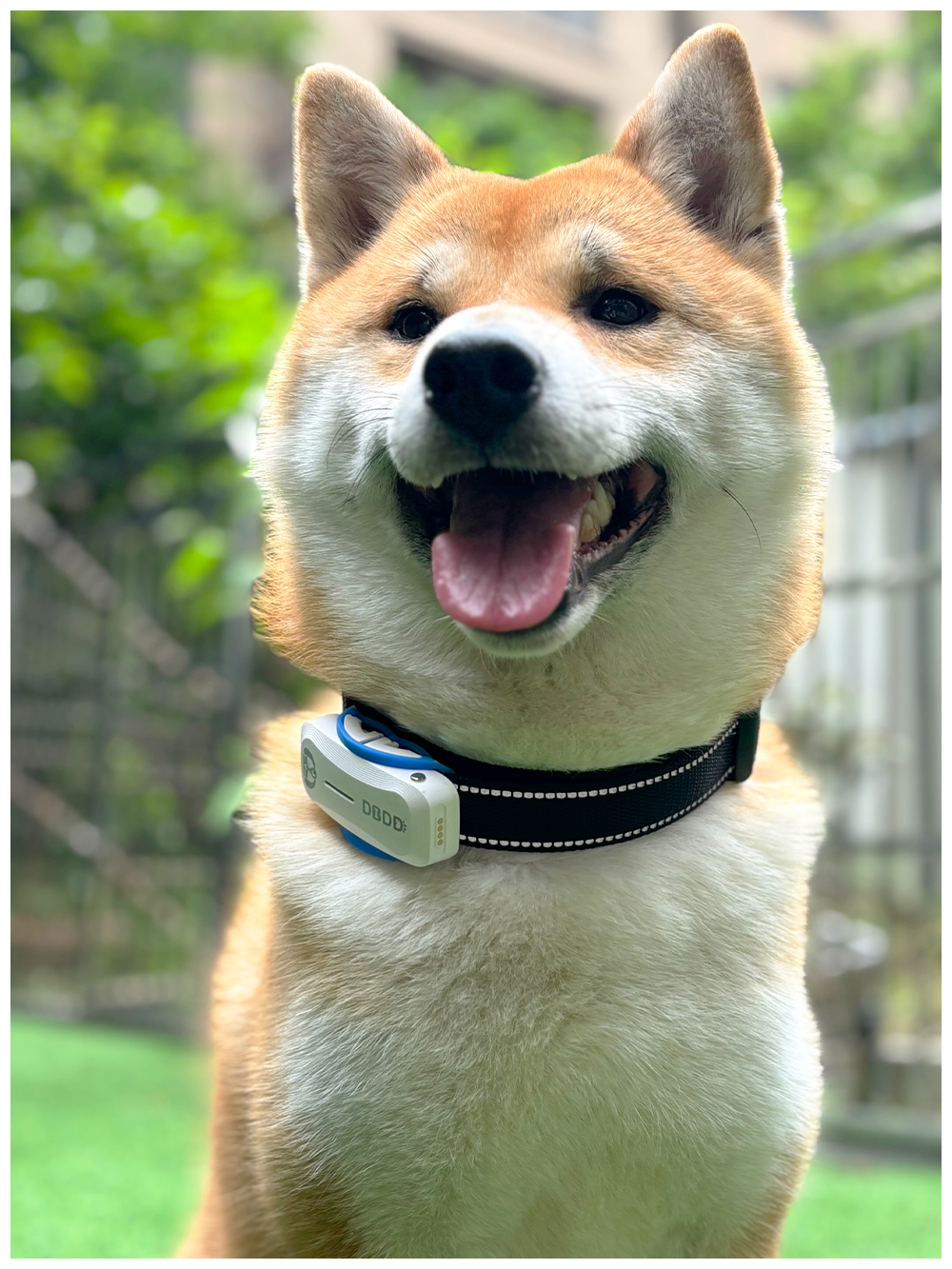
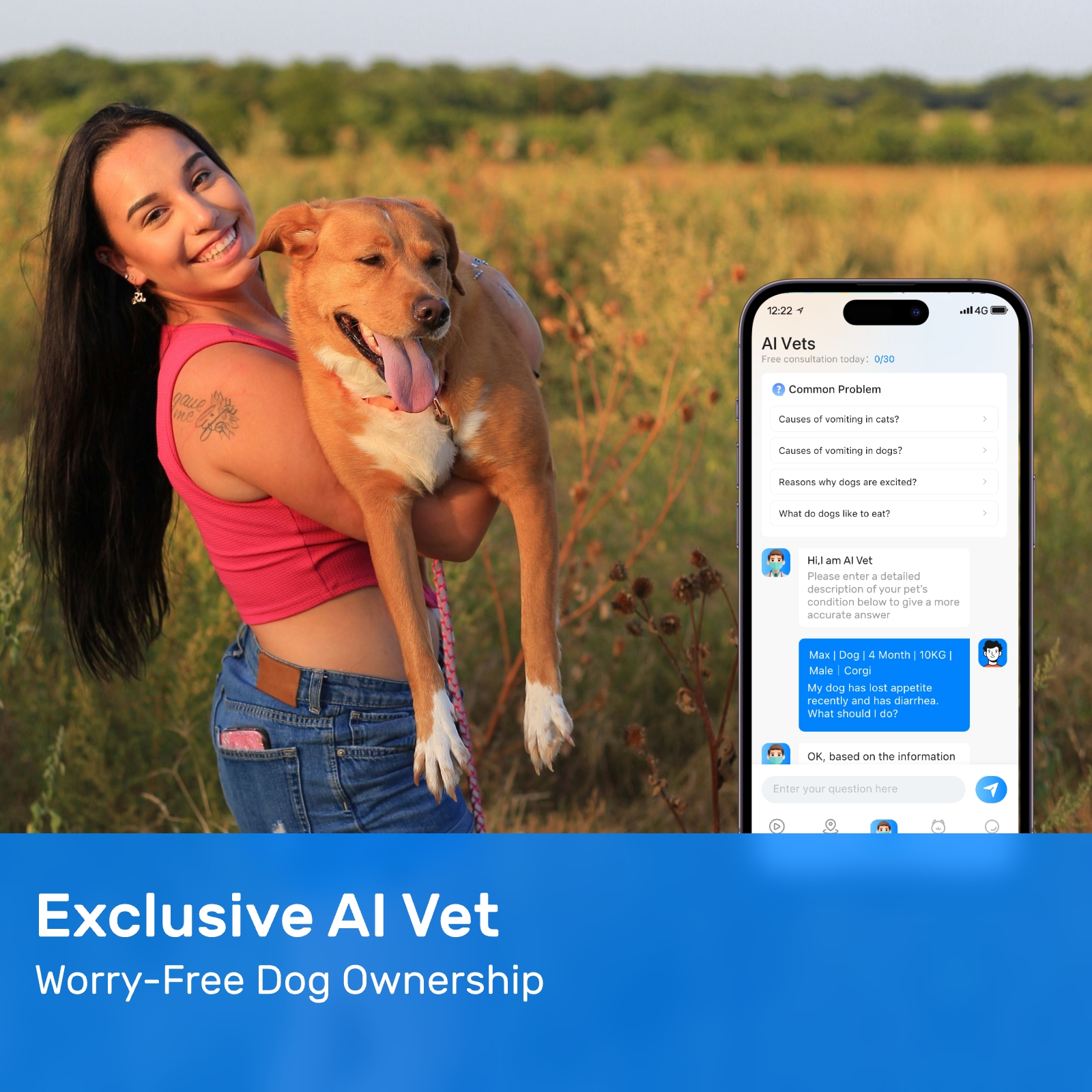
New ArrivalsBack in stock
dog barking sound
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D844348110 second hand :D844348110 |
Manufacturer | dog barking | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $40 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | barking sound | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Pet Consumer Electronics#GPS Gadgets
In recent years, the use of technology to track and analyze animal behavior has become increasingly sophisticated. Among these advancements, dog locator systems have emerged as a powerful tool for pet owners and researchers alike. These systems are designed to track the movement and activities of dogs, providing insights into their daily routines and behaviors. One particularly intriguing aspect of this technology is its ability to analyze dog barking sound, offering a deeper understanding of canine communication.
Dog barking sound is one of the most common ways that dogs communicate with humans and other animals. It can convey a range of emotions and intentions, from alerting to distress or even playfulness. Analyzing the accuracy of dog locators in capturing and interpreting these sounds can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of these devices. This article delves into the intricacies of dog locator accuracy analysis, focusing on how these systems handle dog barking sound data.
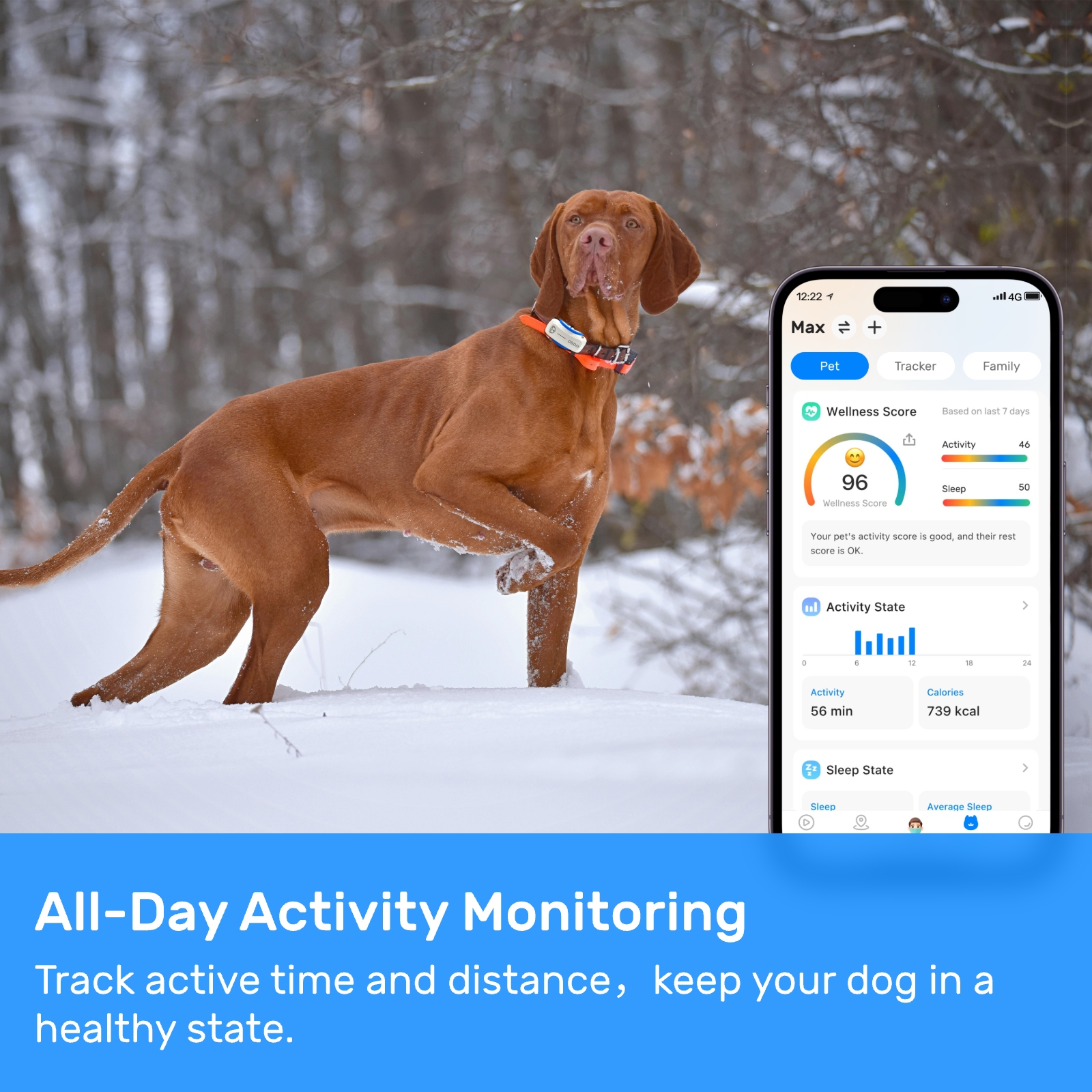
The primary function of a dog locator is to track the physical location of a dog using GPS or similar technologies. However, many modern locators also incorporate audio sensors capable of picking up ambient sounds, including dog barking sound. These audio capabilities allow the system to not only track where the dog is but also what it might be doing based on the sounds it makes. For instance, frequent barking could indicate that the dog is distressed, lonely, or attempting to communicate something important.

When evaluating the accuracy of dog locators in analyzing dog barking sound, several factors come into play. The first is the sensitivity of the audio sensors. High-quality sensors can capture subtle variations in barking patterns, which may indicate different emotional states or contexts. On the other hand, less sensitive sensors might miss crucial details, leading to inaccurate interpretations of the dog's behavior.
Another critical factor is the algorithm used to process and interpret the captured sounds. Advanced algorithms can differentiate between various types of barks, such as warning barks, playful barks, or anxious barks. They can also filter out background noise, ensuring that the dog barking sound is accurately identified and analyzed. However, developing such algorithms requires extensive research and testing to ensure they can handle the complexity and variability of real-world scenarios.
One of the challenges in analyzing dog barking sound is the variability in individual dogs' vocalizations. Just as humans have unique voices, so do dogs. A bark from one dog might differ significantly in pitch, tone, and rhythm from another dog's bark. Therefore, an effective dog locator must be able to adapt to these differences, providing personalized analysis for each dog. This adaptability often involves machine learning techniques, where the system learns from previous recordings to better understand the specific characteristics of a particular dog's barking.
Moreover, environmental factors can influence the accuracy of dog barking sound analysis. Outdoor conditions, such as wind, rain, or traffic noise, can interfere with the clarity of the recorded sounds. Similarly, indoor environments with multiple sound sources, such as televisions or other pets, can complicate the task of isolating the dog barking sound. To address these challenges, some dog locators incorporate noise-canceling features or directional microphones that focus on the dog's location, minimizing external interference.
The application of dog locator accuracy analysis extends beyond mere curiosity about canine behavior. For pet owners, understanding the nuances of their dog's barking can lead to improved care and training. For example, if a dog locator indicates frequent anxiety-related barking when left alone, the owner might consider strategies to alleviate separation anxiety, such as interactive toys or behavioral therapy. In research settings, accurate analysis of dog barking sound can contribute to studies on animal cognition, social behavior, and stress responses.
Despite the potential benefits, there are limitations to current dog locator technology. One limitation is the reliance on battery power, which can restrict the duration and frequency of sound recordings. Additionally, while many locators offer real-time tracking, the processing and analysis of complex audio data might involve delays, especially if cloud-based services are required for advanced computations. Furthermore, privacy concerns arise when considering the collection and storage of audio data, necessitating clear guidelines and protections for both human and animal participants.
To enhance the accuracy of dog barking sound analysis, ongoing improvements in hardware and software are essential. Innovations in sensor technology, such as more sensitive and durable microphones, can improve the quality of sound capture. At the same time, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning can refine the algorithms used to interpret these sounds, making them more precise and adaptable. Collaborative efforts between engineers, biologists, and veterinarians can further optimize these systems, ensuring they meet the diverse needs of users.
Case studies and field tests play a crucial role in validating the accuracy of dog locators in analyzing dog barking sound. By comparing the system's output with direct observations of dog behavior, researchers can assess the reliability of the technology. These studies often involve controlled experiments where dogs are placed in various situations likely to elicit different types of barks. The results are then compared to the locator's analysis to determine its precision and consistency.
For example, a study might involve recording the barking of a dog left alone at home versus one playing in a park. The dog locator's ability to distinguish between these contexts would demonstrate its effectiveness in capturing meaningful data. Such studies not only test the technical capabilities of the device but also explore the broader implications of accurate sound analysis for dog welfare and management.

In conclusion, the accuracy of dog locators in analyzing dog barking sound represents a fascinating intersection of technology and animal behavior. As these systems continue to evolve, they offer increasingly sophisticated tools for understanding and improving the lives of our canine companions. While challenges remain, the potential benefits of accurate sound analysis make it a worthwhile pursuit for both practical applications and scientific exploration. Through continued innovation and research, dog locators can become even more reliable and insightful, bridging the gap between human and animal communication.
Update Time:2025-05-15 01:55:37
Dog barking sound is one of the most common ways that dogs communicate with humans and other animals. It can convey a range of emotions and intentions, from alerting to distress or even playfulness. Analyzing the accuracy of dog locators in capturing and interpreting these sounds can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of these devices. This article delves into the intricacies of dog locator accuracy analysis, focusing on how these systems handle dog barking sound data.

The primary function of a dog locator is to track the physical location of a dog using GPS or similar technologies. However, many modern locators also incorporate audio sensors capable of picking up ambient sounds, including dog barking sound. These audio capabilities allow the system to not only track where the dog is but also what it might be doing based on the sounds it makes. For instance, frequent barking could indicate that the dog is distressed, lonely, or attempting to communicate something important.

When evaluating the accuracy of dog locators in analyzing dog barking sound, several factors come into play. The first is the sensitivity of the audio sensors. High-quality sensors can capture subtle variations in barking patterns, which may indicate different emotional states or contexts. On the other hand, less sensitive sensors might miss crucial details, leading to inaccurate interpretations of the dog's behavior.
Another critical factor is the algorithm used to process and interpret the captured sounds. Advanced algorithms can differentiate between various types of barks, such as warning barks, playful barks, or anxious barks. They can also filter out background noise, ensuring that the dog barking sound is accurately identified and analyzed. However, developing such algorithms requires extensive research and testing to ensure they can handle the complexity and variability of real-world scenarios.
One of the challenges in analyzing dog barking sound is the variability in individual dogs' vocalizations. Just as humans have unique voices, so do dogs. A bark from one dog might differ significantly in pitch, tone, and rhythm from another dog's bark. Therefore, an effective dog locator must be able to adapt to these differences, providing personalized analysis for each dog. This adaptability often involves machine learning techniques, where the system learns from previous recordings to better understand the specific characteristics of a particular dog's barking.
Moreover, environmental factors can influence the accuracy of dog barking sound analysis. Outdoor conditions, such as wind, rain, or traffic noise, can interfere with the clarity of the recorded sounds. Similarly, indoor environments with multiple sound sources, such as televisions or other pets, can complicate the task of isolating the dog barking sound. To address these challenges, some dog locators incorporate noise-canceling features or directional microphones that focus on the dog's location, minimizing external interference.
The application of dog locator accuracy analysis extends beyond mere curiosity about canine behavior. For pet owners, understanding the nuances of their dog's barking can lead to improved care and training. For example, if a dog locator indicates frequent anxiety-related barking when left alone, the owner might consider strategies to alleviate separation anxiety, such as interactive toys or behavioral therapy. In research settings, accurate analysis of dog barking sound can contribute to studies on animal cognition, social behavior, and stress responses.
Despite the potential benefits, there are limitations to current dog locator technology. One limitation is the reliance on battery power, which can restrict the duration and frequency of sound recordings. Additionally, while many locators offer real-time tracking, the processing and analysis of complex audio data might involve delays, especially if cloud-based services are required for advanced computations. Furthermore, privacy concerns arise when considering the collection and storage of audio data, necessitating clear guidelines and protections for both human and animal participants.
To enhance the accuracy of dog barking sound analysis, ongoing improvements in hardware and software are essential. Innovations in sensor technology, such as more sensitive and durable microphones, can improve the quality of sound capture. At the same time, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning can refine the algorithms used to interpret these sounds, making them more precise and adaptable. Collaborative efforts between engineers, biologists, and veterinarians can further optimize these systems, ensuring they meet the diverse needs of users.
Case studies and field tests play a crucial role in validating the accuracy of dog locators in analyzing dog barking sound. By comparing the system's output with direct observations of dog behavior, researchers can assess the reliability of the technology. These studies often involve controlled experiments where dogs are placed in various situations likely to elicit different types of barks. The results are then compared to the locator's analysis to determine its precision and consistency.
For example, a study might involve recording the barking of a dog left alone at home versus one playing in a park. The dog locator's ability to distinguish between these contexts would demonstrate its effectiveness in capturing meaningful data. Such studies not only test the technical capabilities of the device but also explore the broader implications of accurate sound analysis for dog welfare and management.

In conclusion, the accuracy of dog locators in analyzing dog barking sound represents a fascinating intersection of technology and animal behavior. As these systems continue to evolve, they offer increasingly sophisticated tools for understanding and improving the lives of our canine companions. While challenges remain, the potential benefits of accurate sound analysis make it a worthwhile pursuit for both practical applications and scientific exploration. Through continued innovation and research, dog locators can become even more reliable and insightful, bridging the gap between human and animal communication.
Update Time:2025-05-15 01:55:37
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form