New ArrivalsBack in stock
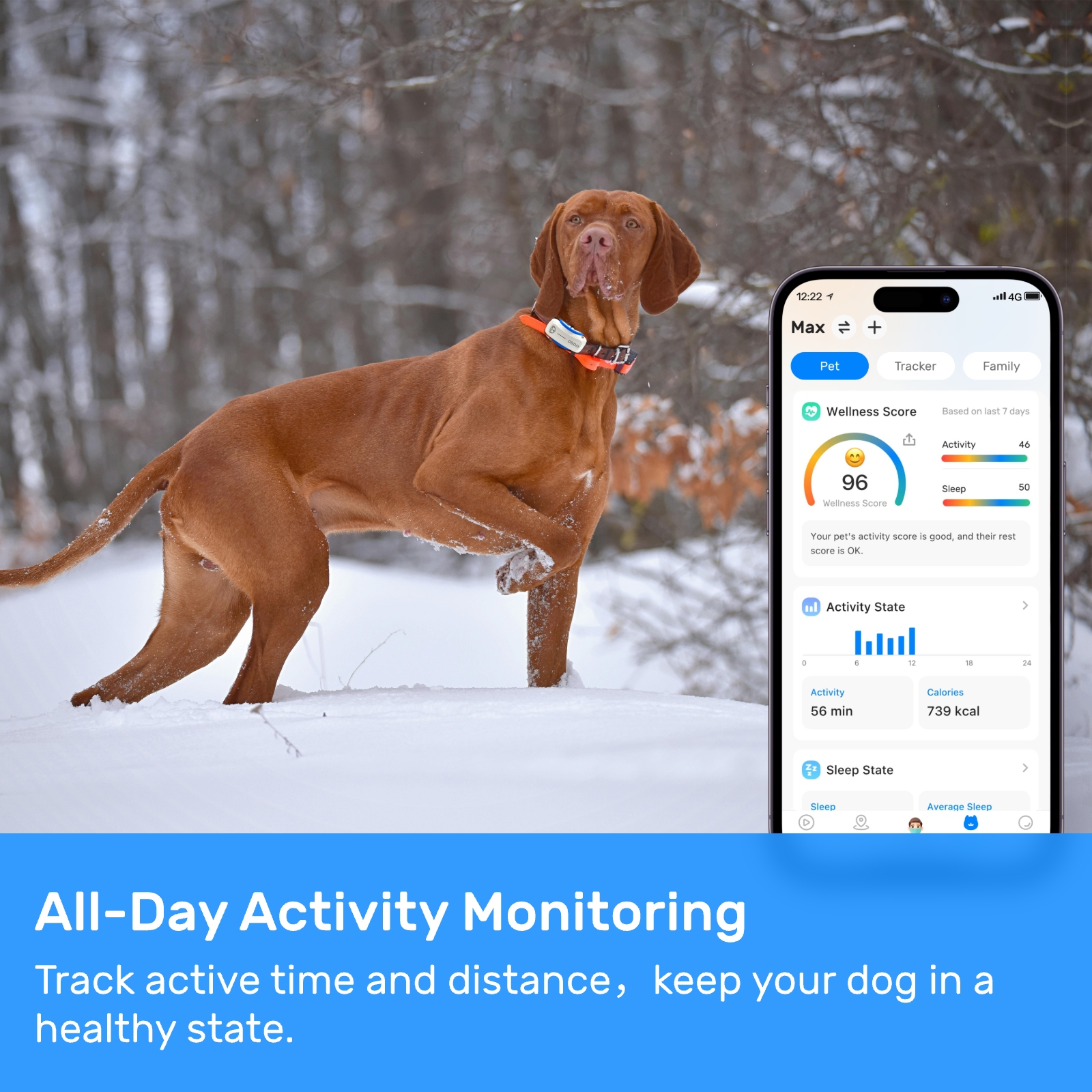
tiny tracker with gps
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D778260096 second hand :D778260096 |
Manufacturer | tiny tracker | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $33 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | tracker with | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Satellite Tech#Global Positioning Modules
In today's fast-paced world, technology has become an integral part of our daily lives. From smartphones to smartwatches, we are surrounded by devices that make our lives easier and more connected. Among these innovations, the tiny tracker with GPS stands out as a remarkable tool designed to enhance safety, security, and convenience. This compact device, often no larger than a coin, leverages advanced GPS technology to provide real-time location tracking. Whether it's for personal use, business applications, or ensuring the safety of loved ones, the tiny tracker with GPS offers a multitude of benefits that cater to diverse needs.
The concept of GPS tracking is not new; however, the miniaturization and affordability of these devices have made them accessible to a broader audience. These trackers can be discreetly attached to various items such as keys, bags, vehicles, or even pets, allowing users to monitor their whereabouts from anywhere in the world via a smartphone app or web interface. The integration of GPS technology ensures pinpoint accuracy, providing users with peace of mind knowing they can locate their belongings or loved ones at any given moment.
Moreover, the tiny tracker with GPS plays a crucial role in industries such as logistics, transportation, and asset management. Companies utilize these devices to track shipments, optimize delivery routes, and ensure the security of valuable assets. In personal contexts, parents can use them to keep tabs on their children's movements, while pet owners can quickly locate lost animals. Additionally, hikers and adventurers rely on these trackers to stay safe during outdoor expeditions, ensuring they can be located if an emergency arises.
As society continues to embrace technological advancements, the demand for reliable and efficient tracking solutions grows. The tiny tracker with GPS addresses this need by offering a versatile, user-friendly, and cost-effective solution. Its ability to seamlessly integrate into various aspects of life makes it an indispensable tool for both individuals and businesses alike. With ongoing developments in GPS technology, the future holds even greater potential for these diminutive yet powerful devices.
The functionality of a tiny tracker with GPS revolves around several core components that work together to provide accurate and reliable tracking capabilities. At its heart lies the GPS module, which communicates with satellites orbiting the Earth to determine the tracker's precise location. This information is then transmitted through a cellular network using a built-in SIM card, enabling the device to send location data to a central server. Users can access this information via a dedicated smartphone application or web platform, where they can view the tracker's real-time position on an interactive map.

One of the key advantages of a tiny tracker with GPS is its ability to offer customizable settings tailored to individual needs. For instance, users can set up geofencing parameters, which allow them to define specific areas where the tracked item or person should remain. If the tracker moves outside these boundaries, the system automatically sends an alert notification to the user's device. This feature proves invaluable for parents monitoring their children's activities or businesses ensuring the security of valuable assets.
Battery life represents another critical aspect of the tiny tracker with GPS. Modern designs incorporate energy-efficient technologies that maximize battery performance while maintaining compact size. Many models offer long-lasting batteries capable of operating for weeks or even months before requiring recharging. Some advanced versions include motion detection sensors that activate the tracker only when movement occurs, further extending battery life. Additionally, solar-powered options are becoming increasingly popular, providing a sustainable solution for extended usage without frequent charging.
Data privacy and security measures play a pivotal role in the design of these devices. Manufacturers implement robust encryption protocols to safeguard sensitive location information from unauthorized access. Two-factor authentication and secure login procedures ensure only authorized users can access tracking data. Furthermore, some models feature tamper-proof mechanisms that notify users if someone attempts to interfere with the device, adding an extra layer of protection.
The versatility of a tiny tracker with GPS extends beyond mere location tracking. Many models incorporate additional features such as SOS buttons, audio recording capabilities, and temperature sensors. These enhancements broaden the device's applicability across various scenarios, from personal safety applications to industrial asset monitoring. The combination of cutting-edge technology and user-friendly interfaces makes the tiny tracker with GPS an essential tool for anyone seeking enhanced situational awareness and control over their environment.

The adoption of tiny trackers with GPS has revolutionized numerous industries, transforming traditional practices into more efficient and secure operations. In the realm of logistics and transportation, companies leverage these devices to track shipments in real-time, optimizing delivery schedules and reducing operational costs. By attaching tiny trackers to cargo containers or individual packages, businesses gain unprecedented visibility into their supply chains, enabling them to respond swiftly to potential delays or security breaches. This level of transparency not only enhances customer satisfaction but also strengthens trust between partners throughout the distribution process.

In the automotive industry, tiny trackers with GPS serve multiple purposes, ranging from vehicle recovery systems to fleet management solutions. Car rental agencies deploy these devices to monitor vehicle locations, ensuring timely returns and preventing misuse. Similarly, taxi services utilize GPS tracking to improve route planning, enhance passenger safety, and streamline billing processes. For private vehicle owners, the installation of a tiny tracker provides peace of mind knowing their car can be easily located in case of theft or unauthorized use.
The healthcare sector has also embraced the capabilities of tiny trackers with GPS, particularly in patient monitoring and elderly care applications. Caregivers employ these devices to ensure the safety of patients suffering from conditions like Alzheimer's disease or dementia, who may wander away from designated areas. The geofencing feature alerts caregivers immediately if the patient ventures beyond predefined boundaries, enabling swift intervention and preventing potentially dangerous situations. Additionally, wearable versions of these trackers help monitor vital signs alongside location data, providing comprehensive health insights for medical professionals.
Retail businesses benefit significantly from implementing tiny trackers with GPS in inventory management and loss prevention strategies. Retailers attach these devices to high-value merchandise, allowing staff to track product movement within stores and identify potential theft incidents promptly. During transit, retailers use GPS tracking to monitor shipments closely, ensuring goods arrive safely at their destinations. This proactive approach minimizes losses due to shrinkage and improves overall profitability.
Law enforcement agencies increasingly adopt tiny trackers with GPS as part of their investigative toolkit. Officers utilize these devices to monitor suspects covertly, gather evidence, and coordinate surveillance operations more effectively. The compact size and long battery life of modern trackers make them ideal for prolonged stakeouts without drawing attention. Furthermore, first responders rely on GPS tracking to locate missing persons quickly, especially in challenging environments such as dense forests or urban areas.
Educational institutions implement tiny trackers with GPS to enhance campus security and student safety. Schools equip buses with these devices to monitor routes and arrival times accurately, ensuring students reach their destinations safely. Administrators also use GPS tracking to manage school assets efficiently, reducing instances of misplaced equipment and improving resource allocation. Parents appreciate the added reassurance provided by knowing their children's whereabouts during school hours.
The widespread adoption of tiny trackers with GPS across various industries demonstrates their versatility and effectiveness in addressing complex challenges. As organizations continue to recognize the value of real-time location data, the demand for innovative tracking solutions will undoubtedly grow, driving further advancements in this transformative technology.
When selecting a tiny tracker with GPS, consumers face a myriad of options catering to different needs and preferences. Key factors influencing the decision-making process include battery life, range, precision, and additional features offered by each model. Battery life remains one of the most critical considerations, as longer-lasting batteries reduce the frequency of recharging and maintenance requirements. Models equipped with motion-activated sensors or solar power extend usability significantly, making them ideal for extended tracking periods without constant supervision.

Range and precision directly impact the effectiveness of a tiny tracker with GPS. Consumers must evaluate whether the device operates globally or within specific regions, considering their intended usage scenarios. High-precision models utilizing advanced satellite technology ensure accurate location data even in challenging environments such as urban canyons or dense forests. For applications requiring extreme accuracy, some trackers incorporate GLONASS or GALILEO systems alongside GPS, enhancing coverage and reliability.
Additional features differentiate premium models from basic versions, offering enhanced functionality tailored to specific needs. SOS buttons provide instant emergency alerts, crucial for personal safety applications. Audio recording capabilities enable users to capture ambient sounds near the tracker, useful for investigating suspicious activities or recovering stolen property. Temperature sensors prove valuable in industrial settings, monitoring environmental conditions of transported goods or stored assets. Geofencing functionality allows users to set virtual boundaries, triggering alerts when the tracker enters or exits designated areas, enhancing security and control.
Cost considerations vary widely depending on the desired features and brand reputation. Entry-level models typically focus on fundamental tracking capabilities at affordable prices, suitable for casual users monitoring everyday items. Mid-range options balance price and performance, incorporating additional features while maintaining competitive pricing. High-end models cater to professional users requiring robust functionality, superior build quality, and extensive support services, justifying higher price points. Subscription fees for data plans and software updates further influence total ownership costs, necessitating careful evaluation of long-term expenses.
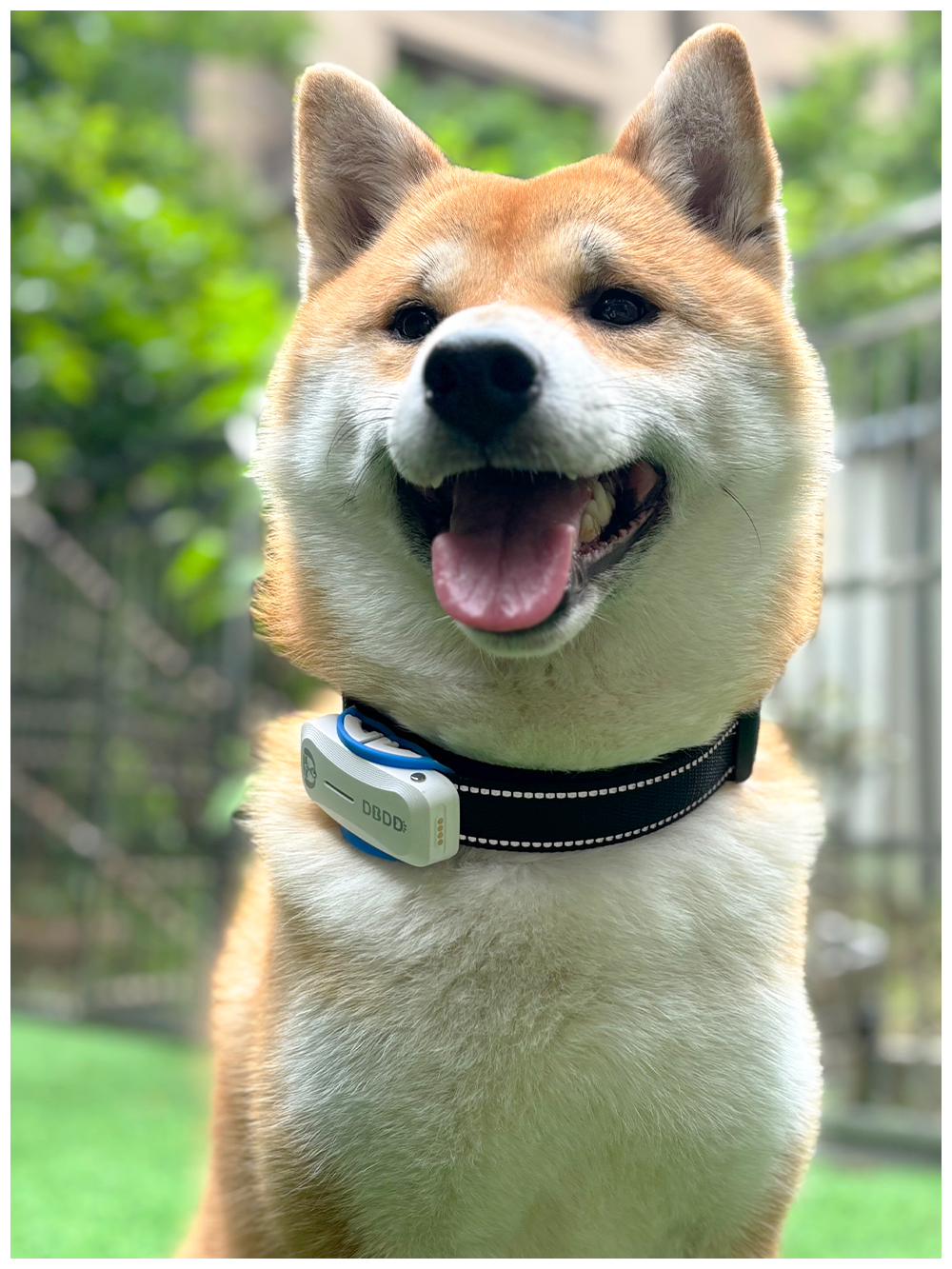

Brand reputation and customer support play significant roles in the selection process. Established manufacturers with proven track records offer greater assurance regarding product quality and reliability. Comprehensive warranty programs, accessible technical support, and regular firmware updates contribute to positive user experiences. Reading reviews and comparing user feedback helps prospective buyers assess real-world performance and identify potential issues before committing to a purchase. Ultimately, matching the chosen tiny tracker with GPS to specific needs and budget constraints ensures optimal satisfaction and effective utilization of the device.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into tiny trackers with GPS marks a significant advancement in tracking technology, enhancing their capabilities far beyond simple location monitoring. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data collected by these devices, identifying patterns and predicting potential issues before they occur. For instance, in fleet management applications, AI-enhanced trackers monitor vehicle performance metrics alongside location data, detecting anomalies that could indicate mechanical failures or unsafe driving behaviors. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and improves overall operational efficiency.
Machine learning techniques enable tiny trackers with GPS to adapt to changing environments and user habits over time. Through continuous data collection and analysis, these devices learn to distinguish between normal and abnormal movements, refining their alert systems accordingly. In personal safety applications, AI-powered trackers assess contextual information such as time of day, weather conditions, and surrounding activity levels to determine appropriate responses to detected threats. This intelligent processing ensures minimal false alarms while maximizing user protection.
Predictive analytics represents another groundbreaking development facilitated by AI integration. By analyzing historical tracking data, these systems forecast future trends and behaviors, providing valuable insights for strategic planning. For example, retail businesses utilize predictive analytics to anticipate peak demand periods for certain products, optimizing inventory levels and reducing stockouts. Similarly, logistics companies leverage AI-driven forecasts to plan optimal delivery routes based on expected traffic conditions and weather patterns, ensuring timely and cost-effective transportation of goods.
Voice recognition technology adds another layer of functionality to tiny trackers with GPS, enabling hands-free operation and improved accessibility. Users can issue voice commands to activate specific features or request location updates without needing physical interaction with the device. This capability proves particularly beneficial in scenarios where manual operation might be inconvenient or impossible, such as during outdoor adventures or emergency situations. Advanced models incorporate natural language processing to understand complex queries and provide detailed responses, enhancing overall user experience.
The fusion of AI with GPS tracking technology creates opportunities for entirely new applications previously unimaginable. Smart cities initiatives incorporate AI-enhanced trackers to monitor public infrastructure usage patterns, optimizing resource allocation and improving service delivery. Environmental conservation efforts benefit from these devices' ability to track wildlife movements and habitat changes, aiding researchers in developing effective preservation strategies. Medical professionals utilize AI-integrated trackers to monitor patient mobility and recovery progress post-surgery, enabling personalized rehabilitation plans and early detection of complications.
As AI continues to evolve, its integration with tiny trackers with GPS promises even greater advancements in the future. Emerging technologies such as edge computing and 5G networks will further enhance these devices' capabilities, enabling real-time data processing and communication at unprecedented speeds. This progression ensures that tiny trackers with GPS remain at the forefront of innovation, continually expanding their utility across diverse fields and applications.
The ethical implications surrounding the use of tiny trackers with GPS raise important questions about privacy, consent, and appropriate usage boundaries. While these devices offer undeniable benefits in terms of safety and security, their potential for misuse necessitates careful consideration and regulation. Privacy concerns primarily stem from the ability of these trackers to monitor individuals' movements without their knowledge or consent. Unauthorized deployment of a tiny tracker with GPS can lead to invasive surveillance, violating personal freedoms and creating an atmosphere of distrust.
Consent emerges as a crucial factor in determining the ethical application of these devices. Ethical guidelines suggest that all parties involved should explicitly agree to being tracked, ensuring transparency and mutual understanding regarding the purpose and extent of monitoring. For instance, employers utilizing GPS tracking for fleet management must clearly communicate this practice to employees, obtaining informed consent before implementation. Similarly, parents employing trackers to monitor children's activities should engage in open discussions about responsible usage and establish clear boundaries.
Legal frameworks governing the use of tiny trackers with GPS vary significantly across jurisdictions, complicating global standardization efforts. Some regions impose strict regulations limiting tracking activities to specific circumstances, such as law enforcement investigations or court-ordered surveillance. Other areas adopt more permissive approaches, allowing broader usage under certain conditions. Navigating these legal complexities requires users to remain aware of local laws and adhere strictly to compliance requirements.
Appropriate usage boundaries represent another critical aspect of ethical considerations. Even with proper consent and legal authorization, excessive reliance on GPS tracking can create unintended consequences. Over-monitoring may foster dependency on technology rather than encouraging independent behavior, potentially hindering personal growth and decision-making skills. Striking a balance between leveraging the benefits of tracking technology and respecting individual autonomy becomes essential for maintaining healthy relationships and societal norms.
Addressing these ethical challenges involves collaborative efforts from multiple stakeholders, including manufacturers, policymakers, and end-users. Developers should prioritize incorporating privacy-enhancing features into their products, such as encrypted data transmission and user-controlled sharing options. Policymakers must establish comprehensive regulatory frameworks that protect individual rights while acknowledging legitimate tracking needs. End-users bear responsibility for using these devices responsibly, respecting others' privacy, and adhering to established guidelines.

Future advancements in tiny trackers with GPS technology promise exciting possibilities while simultaneously intensifying ethical debates. As these devices become more sophisticated and ubiquitous, fostering open dialogue about their implications becomes increasingly important. Encouraging transparent discussions and establishing universally accepted standards will help ensure that the development and deployment of GPS tracking technology align with societal values and expectations.
The future outlook for tiny trackers with GPS appears exceptionally promising, driven by rapid technological advancements and evolving consumer demands. Innovations in sensor technology will enable these devices to collect more comprehensive data beyond mere location coordinates, incorporating environmental variables such as air quality, humidity levels, and light intensity. This expanded dataset opens new possibilities for applications in smart home automation, agricultural monitoring, and climate research. Miniaturization efforts continue to push boundaries, with researchers exploring nanotechnology to create even smaller yet equally powerful tracking solutions.
Quantum computing breakthroughs hold potential to revolutionize GPS signal processing capabilities, enhancing accuracy and reliability to unprecedented levels. Quantum-enhanced algorithms could resolve current limitations related to signal interference and multipath errors, ensuring consistent performance even in challenging urban environments or underground locations. Additionally, quantum cryptography methods may strengthen data security measures, protecting sensitive information from increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.

Artificial intelligence integration will further accelerate the evolution of tiny trackers with GPS, transforming them into intelligent companions capable of autonomous decision-making. Advanced machine learning algorithms will enable these devices to predict user needs and adjust their behavior accordingly, offering personalized recommendations and preemptive alerts. For example, a fitness tracker could analyze movement patterns to suggest optimal workout routines or warn about potential injuries before they occur. Similarly, industrial trackers might anticipate equipment failures and schedule maintenance automatically, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Blockchain technology presents another intriguing avenue for future development, offering decentralized storage solutions for tracking data. By recording location information on immutable blockchain ledgers, users gain greater control over their personal data while ensuring its integrity and authenticity. This approach addresses growing concerns about data privacy and ownership, empowering individuals to share their information selectively with trusted parties. Furthermore, blockchain-based incentive systems could reward users for contributing valuable tracking data, fostering collaborative ecosystems where shared knowledge benefits all participants.
Environmental sustainability considerations increasingly influence the design and production of tiny trackers with GPS. Manufacturers explore eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient architectures to reduce the ecological footprint of these devices. Solar-powered trackers already demonstrate feasibility for extended usage without frequent charging, while biodegradable components promise reduced waste generation at the end of their lifecycle. As global awareness about climate change grows, prioritizing green technologies becomes essential for maintaining market competitiveness and corporate social responsibility.

The convergence of these emerging technologies creates fertile ground for disruptive innovations in the field of GPS tracking. Future generations of tiny trackers with GPS will likely transcend traditional boundaries, merging seamlessly with other smart devices to form interconnected networks that enhance our daily lives. These networks will facilitate smarter cities, safer communities, and more efficient industries, ultimately shaping a world where real-time location data empowers informed decisions and optimizes resource utilization. As we stand on the brink of this exciting transformation, embracing these advancements responsibly ensures they deliver maximum benefit while minimizing potential risks.
Update Time:2025-05-15 19:27:51
The concept of GPS tracking is not new; however, the miniaturization and affordability of these devices have made them accessible to a broader audience. These trackers can be discreetly attached to various items such as keys, bags, vehicles, or even pets, allowing users to monitor their whereabouts from anywhere in the world via a smartphone app or web interface. The integration of GPS technology ensures pinpoint accuracy, providing users with peace of mind knowing they can locate their belongings or loved ones at any given moment.
Moreover, the tiny tracker with GPS plays a crucial role in industries such as logistics, transportation, and asset management. Companies utilize these devices to track shipments, optimize delivery routes, and ensure the security of valuable assets. In personal contexts, parents can use them to keep tabs on their children's movements, while pet owners can quickly locate lost animals. Additionally, hikers and adventurers rely on these trackers to stay safe during outdoor expeditions, ensuring they can be located if an emergency arises.
As society continues to embrace technological advancements, the demand for reliable and efficient tracking solutions grows. The tiny tracker with GPS addresses this need by offering a versatile, user-friendly, and cost-effective solution. Its ability to seamlessly integrate into various aspects of life makes it an indispensable tool for both individuals and businesses alike. With ongoing developments in GPS technology, the future holds even greater potential for these diminutive yet powerful devices.
The functionality of a tiny tracker with GPS revolves around several core components that work together to provide accurate and reliable tracking capabilities. At its heart lies the GPS module, which communicates with satellites orbiting the Earth to determine the tracker's precise location. This information is then transmitted through a cellular network using a built-in SIM card, enabling the device to send location data to a central server. Users can access this information via a dedicated smartphone application or web platform, where they can view the tracker's real-time position on an interactive map.

One of the key advantages of a tiny tracker with GPS is its ability to offer customizable settings tailored to individual needs. For instance, users can set up geofencing parameters, which allow them to define specific areas where the tracked item or person should remain. If the tracker moves outside these boundaries, the system automatically sends an alert notification to the user's device. This feature proves invaluable for parents monitoring their children's activities or businesses ensuring the security of valuable assets.
Battery life represents another critical aspect of the tiny tracker with GPS. Modern designs incorporate energy-efficient technologies that maximize battery performance while maintaining compact size. Many models offer long-lasting batteries capable of operating for weeks or even months before requiring recharging. Some advanced versions include motion detection sensors that activate the tracker only when movement occurs, further extending battery life. Additionally, solar-powered options are becoming increasingly popular, providing a sustainable solution for extended usage without frequent charging.
Data privacy and security measures play a pivotal role in the design of these devices. Manufacturers implement robust encryption protocols to safeguard sensitive location information from unauthorized access. Two-factor authentication and secure login procedures ensure only authorized users can access tracking data. Furthermore, some models feature tamper-proof mechanisms that notify users if someone attempts to interfere with the device, adding an extra layer of protection.
The versatility of a tiny tracker with GPS extends beyond mere location tracking. Many models incorporate additional features such as SOS buttons, audio recording capabilities, and temperature sensors. These enhancements broaden the device's applicability across various scenarios, from personal safety applications to industrial asset monitoring. The combination of cutting-edge technology and user-friendly interfaces makes the tiny tracker with GPS an essential tool for anyone seeking enhanced situational awareness and control over their environment.

The adoption of tiny trackers with GPS has revolutionized numerous industries, transforming traditional practices into more efficient and secure operations. In the realm of logistics and transportation, companies leverage these devices to track shipments in real-time, optimizing delivery schedules and reducing operational costs. By attaching tiny trackers to cargo containers or individual packages, businesses gain unprecedented visibility into their supply chains, enabling them to respond swiftly to potential delays or security breaches. This level of transparency not only enhances customer satisfaction but also strengthens trust between partners throughout the distribution process.

In the automotive industry, tiny trackers with GPS serve multiple purposes, ranging from vehicle recovery systems to fleet management solutions. Car rental agencies deploy these devices to monitor vehicle locations, ensuring timely returns and preventing misuse. Similarly, taxi services utilize GPS tracking to improve route planning, enhance passenger safety, and streamline billing processes. For private vehicle owners, the installation of a tiny tracker provides peace of mind knowing their car can be easily located in case of theft or unauthorized use.
The healthcare sector has also embraced the capabilities of tiny trackers with GPS, particularly in patient monitoring and elderly care applications. Caregivers employ these devices to ensure the safety of patients suffering from conditions like Alzheimer's disease or dementia, who may wander away from designated areas. The geofencing feature alerts caregivers immediately if the patient ventures beyond predefined boundaries, enabling swift intervention and preventing potentially dangerous situations. Additionally, wearable versions of these trackers help monitor vital signs alongside location data, providing comprehensive health insights for medical professionals.
Retail businesses benefit significantly from implementing tiny trackers with GPS in inventory management and loss prevention strategies. Retailers attach these devices to high-value merchandise, allowing staff to track product movement within stores and identify potential theft incidents promptly. During transit, retailers use GPS tracking to monitor shipments closely, ensuring goods arrive safely at their destinations. This proactive approach minimizes losses due to shrinkage and improves overall profitability.
Law enforcement agencies increasingly adopt tiny trackers with GPS as part of their investigative toolkit. Officers utilize these devices to monitor suspects covertly, gather evidence, and coordinate surveillance operations more effectively. The compact size and long battery life of modern trackers make them ideal for prolonged stakeouts without drawing attention. Furthermore, first responders rely on GPS tracking to locate missing persons quickly, especially in challenging environments such as dense forests or urban areas.
Educational institutions implement tiny trackers with GPS to enhance campus security and student safety. Schools equip buses with these devices to monitor routes and arrival times accurately, ensuring students reach their destinations safely. Administrators also use GPS tracking to manage school assets efficiently, reducing instances of misplaced equipment and improving resource allocation. Parents appreciate the added reassurance provided by knowing their children's whereabouts during school hours.
The widespread adoption of tiny trackers with GPS across various industries demonstrates their versatility and effectiveness in addressing complex challenges. As organizations continue to recognize the value of real-time location data, the demand for innovative tracking solutions will undoubtedly grow, driving further advancements in this transformative technology.
When selecting a tiny tracker with GPS, consumers face a myriad of options catering to different needs and preferences. Key factors influencing the decision-making process include battery life, range, precision, and additional features offered by each model. Battery life remains one of the most critical considerations, as longer-lasting batteries reduce the frequency of recharging and maintenance requirements. Models equipped with motion-activated sensors or solar power extend usability significantly, making them ideal for extended tracking periods without constant supervision.

Range and precision directly impact the effectiveness of a tiny tracker with GPS. Consumers must evaluate whether the device operates globally or within specific regions, considering their intended usage scenarios. High-precision models utilizing advanced satellite technology ensure accurate location data even in challenging environments such as urban canyons or dense forests. For applications requiring extreme accuracy, some trackers incorporate GLONASS or GALILEO systems alongside GPS, enhancing coverage and reliability.
Additional features differentiate premium models from basic versions, offering enhanced functionality tailored to specific needs. SOS buttons provide instant emergency alerts, crucial for personal safety applications. Audio recording capabilities enable users to capture ambient sounds near the tracker, useful for investigating suspicious activities or recovering stolen property. Temperature sensors prove valuable in industrial settings, monitoring environmental conditions of transported goods or stored assets. Geofencing functionality allows users to set virtual boundaries, triggering alerts when the tracker enters or exits designated areas, enhancing security and control.
Cost considerations vary widely depending on the desired features and brand reputation. Entry-level models typically focus on fundamental tracking capabilities at affordable prices, suitable for casual users monitoring everyday items. Mid-range options balance price and performance, incorporating additional features while maintaining competitive pricing. High-end models cater to professional users requiring robust functionality, superior build quality, and extensive support services, justifying higher price points. Subscription fees for data plans and software updates further influence total ownership costs, necessitating careful evaluation of long-term expenses.

Brand reputation and customer support play significant roles in the selection process. Established manufacturers with proven track records offer greater assurance regarding product quality and reliability. Comprehensive warranty programs, accessible technical support, and regular firmware updates contribute to positive user experiences. Reading reviews and comparing user feedback helps prospective buyers assess real-world performance and identify potential issues before committing to a purchase. Ultimately, matching the chosen tiny tracker with GPS to specific needs and budget constraints ensures optimal satisfaction and effective utilization of the device.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into tiny trackers with GPS marks a significant advancement in tracking technology, enhancing their capabilities far beyond simple location monitoring. AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data collected by these devices, identifying patterns and predicting potential issues before they occur. For instance, in fleet management applications, AI-enhanced trackers monitor vehicle performance metrics alongside location data, detecting anomalies that could indicate mechanical failures or unsafe driving behaviors. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and improves overall operational efficiency.
Machine learning techniques enable tiny trackers with GPS to adapt to changing environments and user habits over time. Through continuous data collection and analysis, these devices learn to distinguish between normal and abnormal movements, refining their alert systems accordingly. In personal safety applications, AI-powered trackers assess contextual information such as time of day, weather conditions, and surrounding activity levels to determine appropriate responses to detected threats. This intelligent processing ensures minimal false alarms while maximizing user protection.
Predictive analytics represents another groundbreaking development facilitated by AI integration. By analyzing historical tracking data, these systems forecast future trends and behaviors, providing valuable insights for strategic planning. For example, retail businesses utilize predictive analytics to anticipate peak demand periods for certain products, optimizing inventory levels and reducing stockouts. Similarly, logistics companies leverage AI-driven forecasts to plan optimal delivery routes based on expected traffic conditions and weather patterns, ensuring timely and cost-effective transportation of goods.
Voice recognition technology adds another layer of functionality to tiny trackers with GPS, enabling hands-free operation and improved accessibility. Users can issue voice commands to activate specific features or request location updates without needing physical interaction with the device. This capability proves particularly beneficial in scenarios where manual operation might be inconvenient or impossible, such as during outdoor adventures or emergency situations. Advanced models incorporate natural language processing to understand complex queries and provide detailed responses, enhancing overall user experience.
The fusion of AI with GPS tracking technology creates opportunities for entirely new applications previously unimaginable. Smart cities initiatives incorporate AI-enhanced trackers to monitor public infrastructure usage patterns, optimizing resource allocation and improving service delivery. Environmental conservation efforts benefit from these devices' ability to track wildlife movements and habitat changes, aiding researchers in developing effective preservation strategies. Medical professionals utilize AI-integrated trackers to monitor patient mobility and recovery progress post-surgery, enabling personalized rehabilitation plans and early detection of complications.
As AI continues to evolve, its integration with tiny trackers with GPS promises even greater advancements in the future. Emerging technologies such as edge computing and 5G networks will further enhance these devices' capabilities, enabling real-time data processing and communication at unprecedented speeds. This progression ensures that tiny trackers with GPS remain at the forefront of innovation, continually expanding their utility across diverse fields and applications.
The ethical implications surrounding the use of tiny trackers with GPS raise important questions about privacy, consent, and appropriate usage boundaries. While these devices offer undeniable benefits in terms of safety and security, their potential for misuse necessitates careful consideration and regulation. Privacy concerns primarily stem from the ability of these trackers to monitor individuals' movements without their knowledge or consent. Unauthorized deployment of a tiny tracker with GPS can lead to invasive surveillance, violating personal freedoms and creating an atmosphere of distrust.
Consent emerges as a crucial factor in determining the ethical application of these devices. Ethical guidelines suggest that all parties involved should explicitly agree to being tracked, ensuring transparency and mutual understanding regarding the purpose and extent of monitoring. For instance, employers utilizing GPS tracking for fleet management must clearly communicate this practice to employees, obtaining informed consent before implementation. Similarly, parents employing trackers to monitor children's activities should engage in open discussions about responsible usage and establish clear boundaries.
Legal frameworks governing the use of tiny trackers with GPS vary significantly across jurisdictions, complicating global standardization efforts. Some regions impose strict regulations limiting tracking activities to specific circumstances, such as law enforcement investigations or court-ordered surveillance. Other areas adopt more permissive approaches, allowing broader usage under certain conditions. Navigating these legal complexities requires users to remain aware of local laws and adhere strictly to compliance requirements.
Appropriate usage boundaries represent another critical aspect of ethical considerations. Even with proper consent and legal authorization, excessive reliance on GPS tracking can create unintended consequences. Over-monitoring may foster dependency on technology rather than encouraging independent behavior, potentially hindering personal growth and decision-making skills. Striking a balance between leveraging the benefits of tracking technology and respecting individual autonomy becomes essential for maintaining healthy relationships and societal norms.
Addressing these ethical challenges involves collaborative efforts from multiple stakeholders, including manufacturers, policymakers, and end-users. Developers should prioritize incorporating privacy-enhancing features into their products, such as encrypted data transmission and user-controlled sharing options. Policymakers must establish comprehensive regulatory frameworks that protect individual rights while acknowledging legitimate tracking needs. End-users bear responsibility for using these devices responsibly, respecting others' privacy, and adhering to established guidelines.

Future advancements in tiny trackers with GPS technology promise exciting possibilities while simultaneously intensifying ethical debates. As these devices become more sophisticated and ubiquitous, fostering open dialogue about their implications becomes increasingly important. Encouraging transparent discussions and establishing universally accepted standards will help ensure that the development and deployment of GPS tracking technology align with societal values and expectations.
The future outlook for tiny trackers with GPS appears exceptionally promising, driven by rapid technological advancements and evolving consumer demands. Innovations in sensor technology will enable these devices to collect more comprehensive data beyond mere location coordinates, incorporating environmental variables such as air quality, humidity levels, and light intensity. This expanded dataset opens new possibilities for applications in smart home automation, agricultural monitoring, and climate research. Miniaturization efforts continue to push boundaries, with researchers exploring nanotechnology to create even smaller yet equally powerful tracking solutions.
Quantum computing breakthroughs hold potential to revolutionize GPS signal processing capabilities, enhancing accuracy and reliability to unprecedented levels. Quantum-enhanced algorithms could resolve current limitations related to signal interference and multipath errors, ensuring consistent performance even in challenging urban environments or underground locations. Additionally, quantum cryptography methods may strengthen data security measures, protecting sensitive information from increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.

Artificial intelligence integration will further accelerate the evolution of tiny trackers with GPS, transforming them into intelligent companions capable of autonomous decision-making. Advanced machine learning algorithms will enable these devices to predict user needs and adjust their behavior accordingly, offering personalized recommendations and preemptive alerts. For example, a fitness tracker could analyze movement patterns to suggest optimal workout routines or warn about potential injuries before they occur. Similarly, industrial trackers might anticipate equipment failures and schedule maintenance automatically, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
Blockchain technology presents another intriguing avenue for future development, offering decentralized storage solutions for tracking data. By recording location information on immutable blockchain ledgers, users gain greater control over their personal data while ensuring its integrity and authenticity. This approach addresses growing concerns about data privacy and ownership, empowering individuals to share their information selectively with trusted parties. Furthermore, blockchain-based incentive systems could reward users for contributing valuable tracking data, fostering collaborative ecosystems where shared knowledge benefits all participants.
Environmental sustainability considerations increasingly influence the design and production of tiny trackers with GPS. Manufacturers explore eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient architectures to reduce the ecological footprint of these devices. Solar-powered trackers already demonstrate feasibility for extended usage without frequent charging, while biodegradable components promise reduced waste generation at the end of their lifecycle. As global awareness about climate change grows, prioritizing green technologies becomes essential for maintaining market competitiveness and corporate social responsibility.

The convergence of these emerging technologies creates fertile ground for disruptive innovations in the field of GPS tracking. Future generations of tiny trackers with GPS will likely transcend traditional boundaries, merging seamlessly with other smart devices to form interconnected networks that enhance our daily lives. These networks will facilitate smarter cities, safer communities, and more efficient industries, ultimately shaping a world where real-time location data empowers informed decisions and optimizes resource utilization. As we stand on the brink of this exciting transformation, embracing these advancements responsibly ensures they deliver maximum benefit while minimizing potential risks.
Update Time:2025-05-15 19:27:51
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form