New ArrivalsBack in stock
gps collars for dogs
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D424654118 second hand :D424654118 |
Manufacturer | gps collars | release date | 2025-05-16 | List price | $38 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | collars for | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Mobile Tech#Bluetooth Tracking Accessories
When it comes to ensuring the safety and well-being of our beloved pets, technology has made significant strides in recent years. Among these advancements are GPS collars for dogs, which have become increasingly popular as a means of tracking and locating lost pets. However, pet owners now face a choice between two primary types of tracking devices: collar-mounted trackers and implantable ones. Each option has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision.
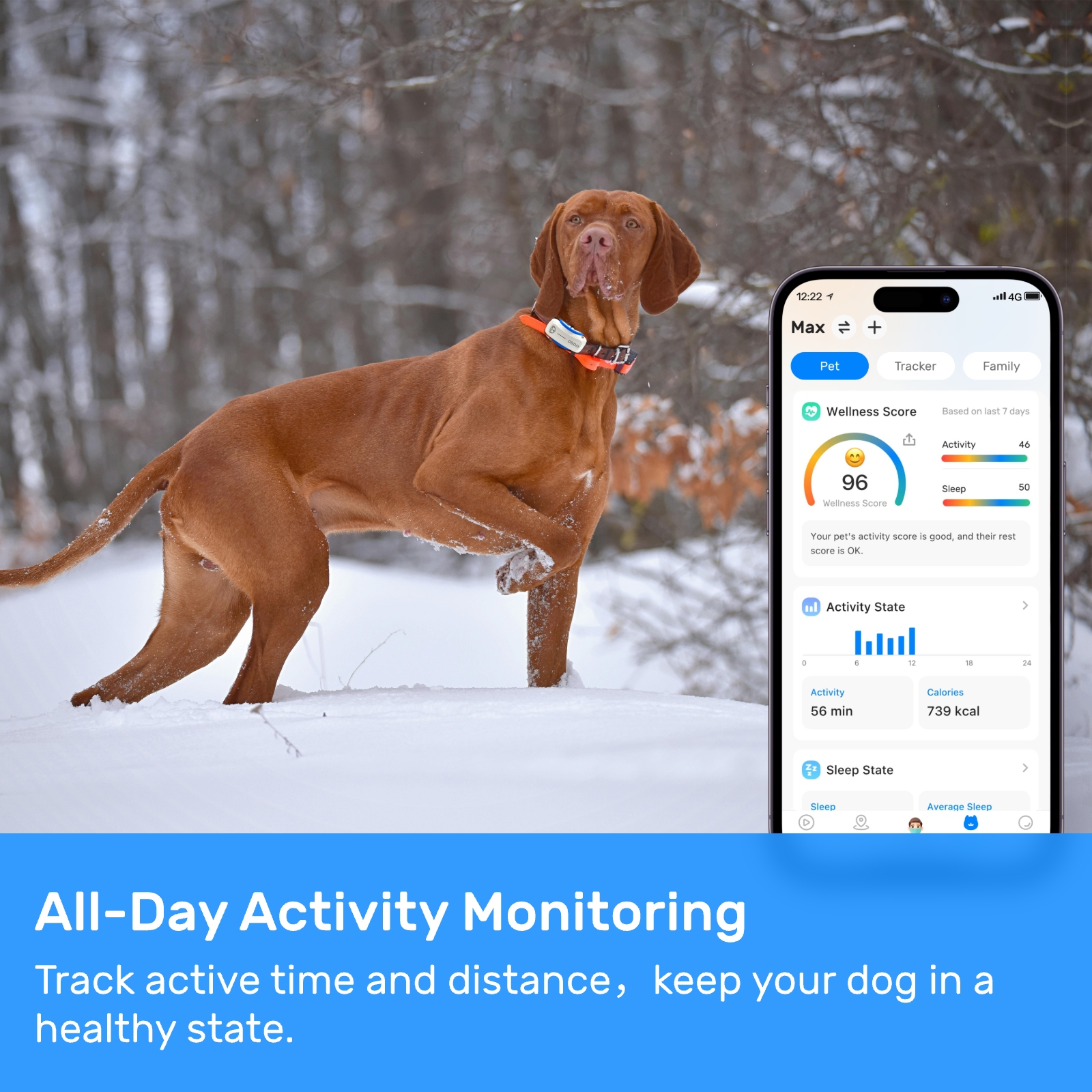
Collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs are perhaps the most familiar type of pet tracker. These devices are designed to be attached to a dog's collar, providing real-time location updates through GPS technology. One of the key benefits of collar-mounted trackers is their ease of use. They are simple to install and remove, allowing pet owners to quickly check their dog's location at any time. Additionally, many collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs come with additional features such as activity tracking, geofencing, and health monitoring, which can provide valuable insights into a pet's daily routine and overall well-being.

Another advantage of collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs is their affordability. Compared to implantable trackers, collar-mounted devices tend to be less expensive both in terms of initial cost and ongoing maintenance. Many models also offer rechargeable batteries, reducing the need for frequent replacements and lowering long-term costs. Furthermore, collar-mounted trackers are often compatible with a wide range of collars, giving pet owners flexibility in choosing a style that suits their dog's needs and preferences.
However, collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs are not without their drawbacks. One of the main concerns is the possibility of the device being lost or removed. If a dog loses its collar or if someone intentionally removes it, the tracker will no longer be able to provide location data. This limitation can be particularly problematic in situations where a dog becomes lost or stolen. Additionally, some collar-mounted trackers may be bulkier or heavier, which could cause discomfort for smaller or more sensitive breeds. Pet owners must carefully consider the weight and size of the device when selecting a collar-mounted GPS collar for dogs.
In contrast, implantable pet trackers offer a more permanent solution for pet tracking. These devices are surgically implanted beneath the skin, typically in the scruff of the neck, and function similarly to microchips but with added GPS capabilities. One of the primary advantages of implantable trackers is their permanence. Unlike collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs, implantable devices cannot be easily removed or lost, ensuring that the tracker remains with the pet at all times. This feature makes implantable trackers particularly appealing for pet owners who are concerned about theft or accidental loss.
Implantable pet trackers also offer peace of mind in terms of durability. Since they are protected by the pet's skin and tissue, these devices are less susceptible to damage from external factors such as water, dirt, or rough play. This durability can lead to a longer lifespan for the tracker, potentially reducing the need for frequent replacements. Moreover, implantable trackers eliminate the need for regular battery changes, as many models are powered by the pet's own body energy or utilize advanced battery technologies that last for several years.
Despite these advantages, implantable pet trackers do have certain limitations. The initial cost of an implantable tracker is generally higher than that of a collar-mounted GPS collar for dogs, and the procedure itself may involve additional expenses such as veterinary fees. Furthermore, while implantable trackers are designed to be minimally invasive, some pets may experience discomfort or complications during or after the procedure. It is important for pet owners to consult with a veterinarian to determine whether their pet is a suitable candidate for an implantable tracker.
Another consideration is the current technological limitations of implantable pet trackers. While collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs often provide real-time location updates and detailed tracking data, implantable trackers may not offer the same level of precision or functionality. Some models may only provide approximate location data or require periodic updates rather than continuous tracking. As the technology continues to evolve, these limitations may be addressed, but for now, pet owners should weigh the trade-offs between accuracy and permanence when choosing between collar-mounted and implantable trackers.

In addition to cost and functionality, pet owners should also consider the ethical implications of each type of tracker. Collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs are generally viewed as non-invasive and pose minimal risk to the pet's health. However, they require regular maintenance and attention to ensure proper functioning. Implantable trackers, on the other hand, involve a surgical procedure that some pet owners may find concerning. While the procedure is considered safe and routine, there is always a small risk of complications such as infection or rejection. Pet owners must carefully evaluate their comfort level with these potential risks before proceeding with an implantable tracker.
The decision between collar-mounted and implantable GPS collars for dogs ultimately depends on individual circumstances and priorities. For pet owners who value convenience and affordability, collar-mounted trackers may be the better choice. These devices offer a wide range of features at a lower cost, making them accessible to a broader audience. However, for those who prioritize permanence and durability, implantable trackers may provide greater peace of mind. Despite their higher upfront cost and potential procedural risks, implantable trackers offer a reliable solution for ensuring that a pet can always be located, even in the absence of a collar.

It is worth noting that both collar-mounted and implantable GPS collars for dogs have their place in the market, and the best choice often depends on the specific needs of the pet and its owner. For example, a pet that spends most of its time indoors or in a secure yard may benefit more from a collar-mounted tracker, which can provide detailed activity and location data without the need for surgical intervention. On the other hand, a pet that frequently ventures outdoors or travels with its owner may be better suited to an implantable tracker, which ensures that the device remains with the pet at all times.
As technology continues to advance, both collar-mounted and implantable GPS collars for dogs are likely to become more sophisticated and user-friendly. Future developments may include improved battery life, enhanced tracking accuracy, and expanded compatibility with smart home systems. These advancements will undoubtedly make pet tracking more accessible and effective for a growing number of pet owners.

In conclusion, the choice between collar-mounted and implantable GPS collars for dogs requires careful consideration of various factors, including cost, functionality, permanence, and ethical concerns. While collar-mounted trackers offer affordability and versatility, implantable trackers provide permanence and durability. By evaluating their pet's lifestyle and their own priorities, pet owners can make an informed decision that best serves the needs of both themselves and their furry companions. Ultimately, the goal of using GPS collars for dogs is to enhance the safety and well-being of our pets, and choosing the right tracker is an important step in achieving that goal.
Update Time:2025-05-16 04:09:24
Collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs are perhaps the most familiar type of pet tracker. These devices are designed to be attached to a dog's collar, providing real-time location updates through GPS technology. One of the key benefits of collar-mounted trackers is their ease of use. They are simple to install and remove, allowing pet owners to quickly check their dog's location at any time. Additionally, many collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs come with additional features such as activity tracking, geofencing, and health monitoring, which can provide valuable insights into a pet's daily routine and overall well-being.

Another advantage of collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs is their affordability. Compared to implantable trackers, collar-mounted devices tend to be less expensive both in terms of initial cost and ongoing maintenance. Many models also offer rechargeable batteries, reducing the need for frequent replacements and lowering long-term costs. Furthermore, collar-mounted trackers are often compatible with a wide range of collars, giving pet owners flexibility in choosing a style that suits their dog's needs and preferences.
However, collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs are not without their drawbacks. One of the main concerns is the possibility of the device being lost or removed. If a dog loses its collar or if someone intentionally removes it, the tracker will no longer be able to provide location data. This limitation can be particularly problematic in situations where a dog becomes lost or stolen. Additionally, some collar-mounted trackers may be bulkier or heavier, which could cause discomfort for smaller or more sensitive breeds. Pet owners must carefully consider the weight and size of the device when selecting a collar-mounted GPS collar for dogs.
In contrast, implantable pet trackers offer a more permanent solution for pet tracking. These devices are surgically implanted beneath the skin, typically in the scruff of the neck, and function similarly to microchips but with added GPS capabilities. One of the primary advantages of implantable trackers is their permanence. Unlike collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs, implantable devices cannot be easily removed or lost, ensuring that the tracker remains with the pet at all times. This feature makes implantable trackers particularly appealing for pet owners who are concerned about theft or accidental loss.
Implantable pet trackers also offer peace of mind in terms of durability. Since they are protected by the pet's skin and tissue, these devices are less susceptible to damage from external factors such as water, dirt, or rough play. This durability can lead to a longer lifespan for the tracker, potentially reducing the need for frequent replacements. Moreover, implantable trackers eliminate the need for regular battery changes, as many models are powered by the pet's own body energy or utilize advanced battery technologies that last for several years.
Despite these advantages, implantable pet trackers do have certain limitations. The initial cost of an implantable tracker is generally higher than that of a collar-mounted GPS collar for dogs, and the procedure itself may involve additional expenses such as veterinary fees. Furthermore, while implantable trackers are designed to be minimally invasive, some pets may experience discomfort or complications during or after the procedure. It is important for pet owners to consult with a veterinarian to determine whether their pet is a suitable candidate for an implantable tracker.
Another consideration is the current technological limitations of implantable pet trackers. While collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs often provide real-time location updates and detailed tracking data, implantable trackers may not offer the same level of precision or functionality. Some models may only provide approximate location data or require periodic updates rather than continuous tracking. As the technology continues to evolve, these limitations may be addressed, but for now, pet owners should weigh the trade-offs between accuracy and permanence when choosing between collar-mounted and implantable trackers.

In addition to cost and functionality, pet owners should also consider the ethical implications of each type of tracker. Collar-mounted GPS collars for dogs are generally viewed as non-invasive and pose minimal risk to the pet's health. However, they require regular maintenance and attention to ensure proper functioning. Implantable trackers, on the other hand, involve a surgical procedure that some pet owners may find concerning. While the procedure is considered safe and routine, there is always a small risk of complications such as infection or rejection. Pet owners must carefully evaluate their comfort level with these potential risks before proceeding with an implantable tracker.
The decision between collar-mounted and implantable GPS collars for dogs ultimately depends on individual circumstances and priorities. For pet owners who value convenience and affordability, collar-mounted trackers may be the better choice. These devices offer a wide range of features at a lower cost, making them accessible to a broader audience. However, for those who prioritize permanence and durability, implantable trackers may provide greater peace of mind. Despite their higher upfront cost and potential procedural risks, implantable trackers offer a reliable solution for ensuring that a pet can always be located, even in the absence of a collar.

It is worth noting that both collar-mounted and implantable GPS collars for dogs have their place in the market, and the best choice often depends on the specific needs of the pet and its owner. For example, a pet that spends most of its time indoors or in a secure yard may benefit more from a collar-mounted tracker, which can provide detailed activity and location data without the need for surgical intervention. On the other hand, a pet that frequently ventures outdoors or travels with its owner may be better suited to an implantable tracker, which ensures that the device remains with the pet at all times.
As technology continues to advance, both collar-mounted and implantable GPS collars for dogs are likely to become more sophisticated and user-friendly. Future developments may include improved battery life, enhanced tracking accuracy, and expanded compatibility with smart home systems. These advancements will undoubtedly make pet tracking more accessible and effective for a growing number of pet owners.

In conclusion, the choice between collar-mounted and implantable GPS collars for dogs requires careful consideration of various factors, including cost, functionality, permanence, and ethical concerns. While collar-mounted trackers offer affordability and versatility, implantable trackers provide permanence and durability. By evaluating their pet's lifestyle and their own priorities, pet owners can make an informed decision that best serves the needs of both themselves and their furry companions. Ultimately, the goal of using GPS collars for dogs is to enhance the safety and well-being of our pets, and choosing the right tracker is an important step in achieving that goal.
Update Time:2025-05-16 04:09:24
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form