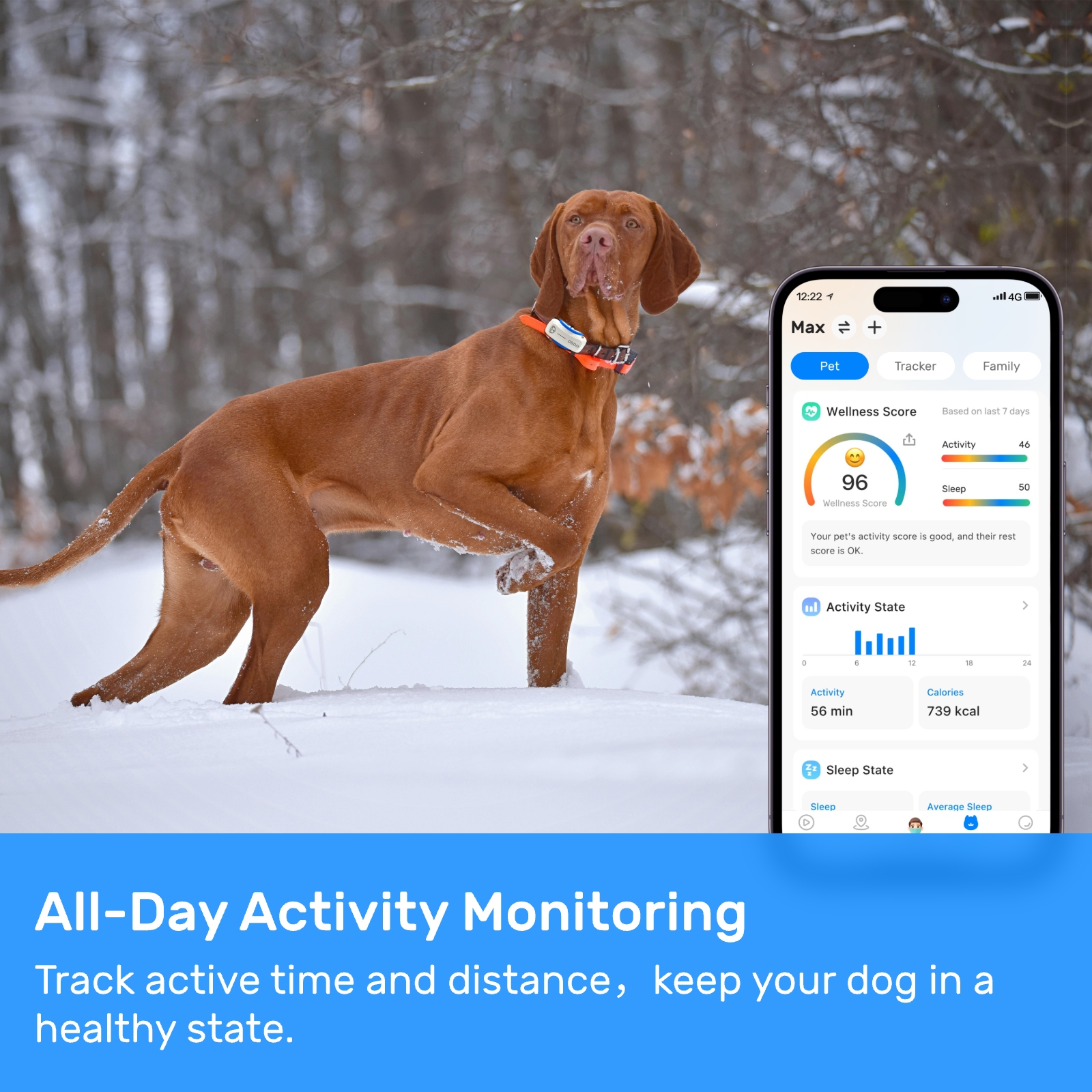
New ArrivalsBack in stock
tracker for dogs
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D664751123 second hand :D664751123 |
Manufacturer | tracker for | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $39 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | for dogs | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Outdoor Gear#Pet Safety Equipment
Dog trackers have been a vital part of human society for centuries, with these highly skilled canines assisting in various roles such as hunting, search and rescue, and even law enforcement. These remarkable animals possess an innate ability to follow scent trails and track individuals or animals over long distances. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of dog trackers, exploring their history, training, and the significant impact they have on modern society.
Historical Context
The use of dogs for tracking purposes dates back to ancient civilizations, where they were employed in hunting and warfare. In Roman times, dogs were bred specifically for their tracking abilities, and these breeds were highly valued for their prowess in scent detection. As time progressed, the role of dogs in tracking expanded to include search and rescue missions, with organizations like the St. Bernard Hospice in Switzerland using dogs to locate and rescue stranded travelers in the Alps.
Throughout history, dog trackers have been instrumental in many significant events. During World War I and II, dogs were used to track enemy soldiers and locate missing comrades. Their ability to follow scent trails over vast distances and in various terrains made them invaluable assets to the military. Today, dog trackers continue to play a crucial role in various sectors, including law enforcement, wildlife management, and humanitarian efforts.
Breeds and Characteristics
Several dog breeds are renowned for their tracking abilities, with some of the most popular breeds being Bloodhounds, German Shepherds, Beagles, and Labrador Retrievers. These breeds possess unique characteristics that make them ideal for tracking tasks, such as an exceptional sense of smell, intelligence, and physical stamina.
Bloodhounds, for example, have an incredible sense of smell, making them one of the most sought-after breeds for tracking tasks. Their drooping ears and loose skin help to capture and concentrate scents, allowing them to follow trails with remarkable accuracy. German Shepherds, on the other hand, are known for their intelligence, trainability, and strong work ethic, making them excellent candidates for various tracking roles.
Training and Development
Training a dog to become an effective tracker is a complex and time-consuming process that requires patience, dedication, and a deep understanding of canine behavior. The training typically begins at a young age, with puppies introduced to basic obedience and scent detection exercises. As the dogs mature, the training becomes more advanced, focusing on developing their tracking skills and building their stamina.
A crucial aspect of training dog trackers is socialization, as these dogs must be comfortable working in various environments and around different people. Handlers must also learn to read their dog's body language and understand their unique communication methods, which is essential for effective teamwork during tracking missions.

Many organizations, such as the American Kennel Club (AKC) and the North American Police Work Dog Association (NAPWDA), offer specialized training programs for dog trackers. These programs cover various aspects of tracking, including following scent trails, searching for missing persons, and locating illegal substances. Handlers and their dogs must complete rigorous training and certification processes to ensure they are prepared for the challenges they may face in the field.
Applications and Impact

Dog trackers play a vital role in numerous fields, with their unique abilities making them indispensable assets in various situations. Here are some of the most common applications of dog trackers:
1. Law Enforcement: Dog trackers are often used in criminal investigations to locate suspects who have fled the scene or to track down evidence. Their ability to follow scent trails can help law enforcement officers solve cases more quickly and efficiently.
2. Search and Rescue: In natural disasters or other emergency situations, dog trackers can be invaluable in locating missing persons or survivors. Their keen sense of smell allows them to detect human scent even in the most challenging conditions, such as heavy rain or extreme temperatures.
3. Wildlife Management: Dog trackers can be used to track and monitor wildlife populations, helping conservationists and researchers gather essential data on animal behavior and habitat usage. This information can be crucial for developing effective conservation strategies.
4. Humanitarian Efforts: Dog trackers are often deployed in humanitarian missions, such as disaster relief operations, to locate survivors or provide assistance in locating resources like food and water.
5. Customs and Border Control: Dog trackers can be used to detect illegal substances, such as drugs or explosives, at border crossings and other entry points. Their ability to sniff out even the smallest traces of these substances makes them a valuable tool in preventing smuggling and other criminal activities.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their incredible abilities, dog trackers do face certain challenges and limitations. One of the primary challenges is the potential for false positives, where a dog may mistakenly identify a scent as the target. This can be due to various factors, such as cross-contamination or environmental conditions affecting the scent trail.

Another limitation is the physical stamina of the dog, as tracking missions can be both physically and mentally demanding. Handlers must be vigilant in monitoring their dog's condition and ensuring they receive adequate rest and nutrition to maintain their performance levels.
Lastly, the success of a dog tracker largely depends on the handler's ability to read their dog
Update Time:2025-05-15 14:08:14
Historical Context
The use of dogs for tracking purposes dates back to ancient civilizations, where they were employed in hunting and warfare. In Roman times, dogs were bred specifically for their tracking abilities, and these breeds were highly valued for their prowess in scent detection. As time progressed, the role of dogs in tracking expanded to include search and rescue missions, with organizations like the St. Bernard Hospice in Switzerland using dogs to locate and rescue stranded travelers in the Alps.
Throughout history, dog trackers have been instrumental in many significant events. During World War I and II, dogs were used to track enemy soldiers and locate missing comrades. Their ability to follow scent trails over vast distances and in various terrains made them invaluable assets to the military. Today, dog trackers continue to play a crucial role in various sectors, including law enforcement, wildlife management, and humanitarian efforts.
Breeds and Characteristics
Several dog breeds are renowned for their tracking abilities, with some of the most popular breeds being Bloodhounds, German Shepherds, Beagles, and Labrador Retrievers. These breeds possess unique characteristics that make them ideal for tracking tasks, such as an exceptional sense of smell, intelligence, and physical stamina.
Bloodhounds, for example, have an incredible sense of smell, making them one of the most sought-after breeds for tracking tasks. Their drooping ears and loose skin help to capture and concentrate scents, allowing them to follow trails with remarkable accuracy. German Shepherds, on the other hand, are known for their intelligence, trainability, and strong work ethic, making them excellent candidates for various tracking roles.
Training and Development
Training a dog to become an effective tracker is a complex and time-consuming process that requires patience, dedication, and a deep understanding of canine behavior. The training typically begins at a young age, with puppies introduced to basic obedience and scent detection exercises. As the dogs mature, the training becomes more advanced, focusing on developing their tracking skills and building their stamina.
A crucial aspect of training dog trackers is socialization, as these dogs must be comfortable working in various environments and around different people. Handlers must also learn to read their dog's body language and understand their unique communication methods, which is essential for effective teamwork during tracking missions.

Many organizations, such as the American Kennel Club (AKC) and the North American Police Work Dog Association (NAPWDA), offer specialized training programs for dog trackers. These programs cover various aspects of tracking, including following scent trails, searching for missing persons, and locating illegal substances. Handlers and their dogs must complete rigorous training and certification processes to ensure they are prepared for the challenges they may face in the field.
Applications and Impact

Dog trackers play a vital role in numerous fields, with their unique abilities making them indispensable assets in various situations. Here are some of the most common applications of dog trackers:
1. Law Enforcement: Dog trackers are often used in criminal investigations to locate suspects who have fled the scene or to track down evidence. Their ability to follow scent trails can help law enforcement officers solve cases more quickly and efficiently.
2. Search and Rescue: In natural disasters or other emergency situations, dog trackers can be invaluable in locating missing persons or survivors. Their keen sense of smell allows them to detect human scent even in the most challenging conditions, such as heavy rain or extreme temperatures.
3. Wildlife Management: Dog trackers can be used to track and monitor wildlife populations, helping conservationists and researchers gather essential data on animal behavior and habitat usage. This information can be crucial for developing effective conservation strategies.
4. Humanitarian Efforts: Dog trackers are often deployed in humanitarian missions, such as disaster relief operations, to locate survivors or provide assistance in locating resources like food and water.
5. Customs and Border Control: Dog trackers can be used to detect illegal substances, such as drugs or explosives, at border crossings and other entry points. Their ability to sniff out even the smallest traces of these substances makes them a valuable tool in preventing smuggling and other criminal activities.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their incredible abilities, dog trackers do face certain challenges and limitations. One of the primary challenges is the potential for false positives, where a dog may mistakenly identify a scent as the target. This can be due to various factors, such as cross-contamination or environmental conditions affecting the scent trail.

Another limitation is the physical stamina of the dog, as tracking missions can be both physically and mentally demanding. Handlers must be vigilant in monitoring their dog's condition and ensuring they receive adequate rest and nutrition to maintain their performance levels.
Lastly, the success of a dog tracker largely depends on the handler's ability to read their dog
Update Time:2025-05-15 14:08:14
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form