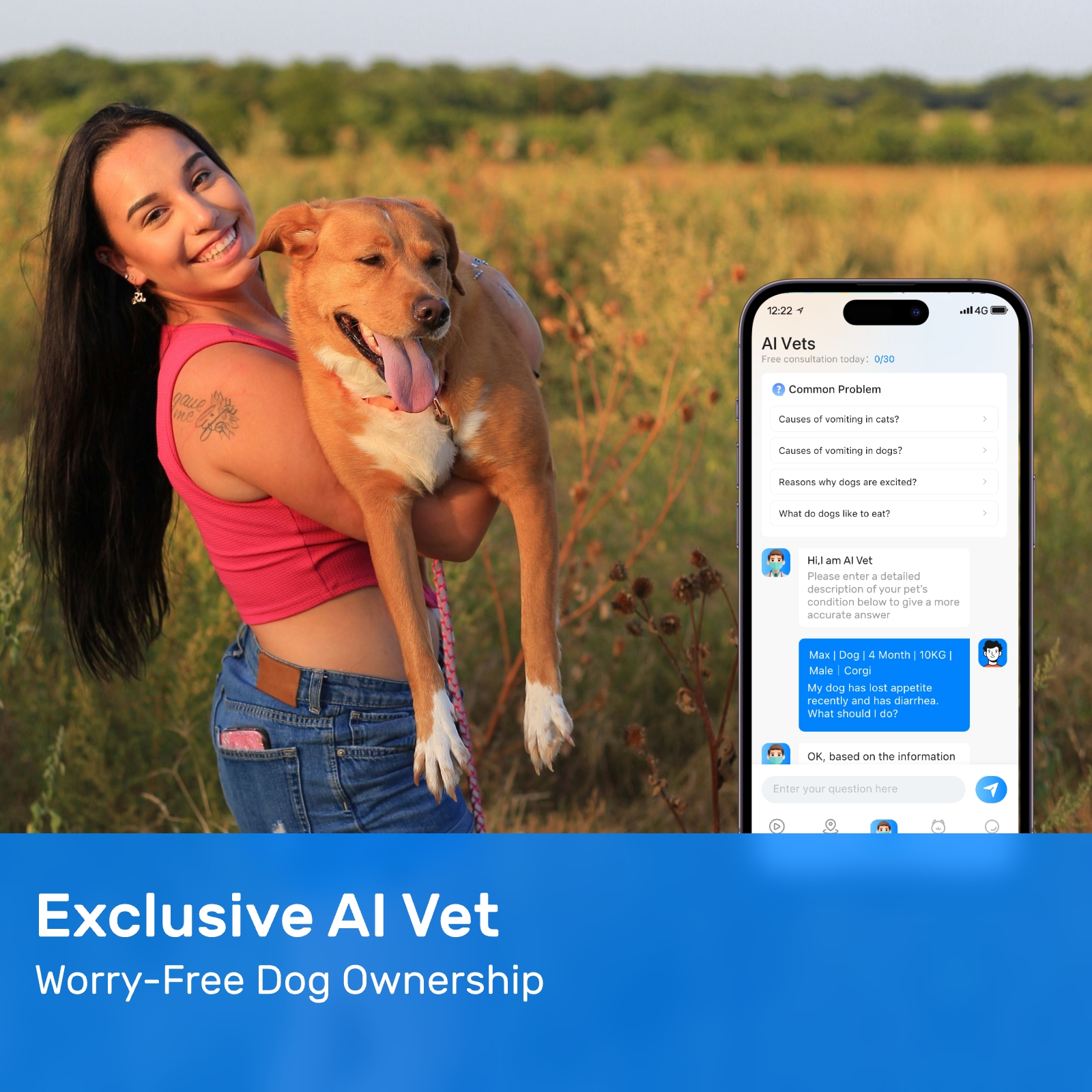
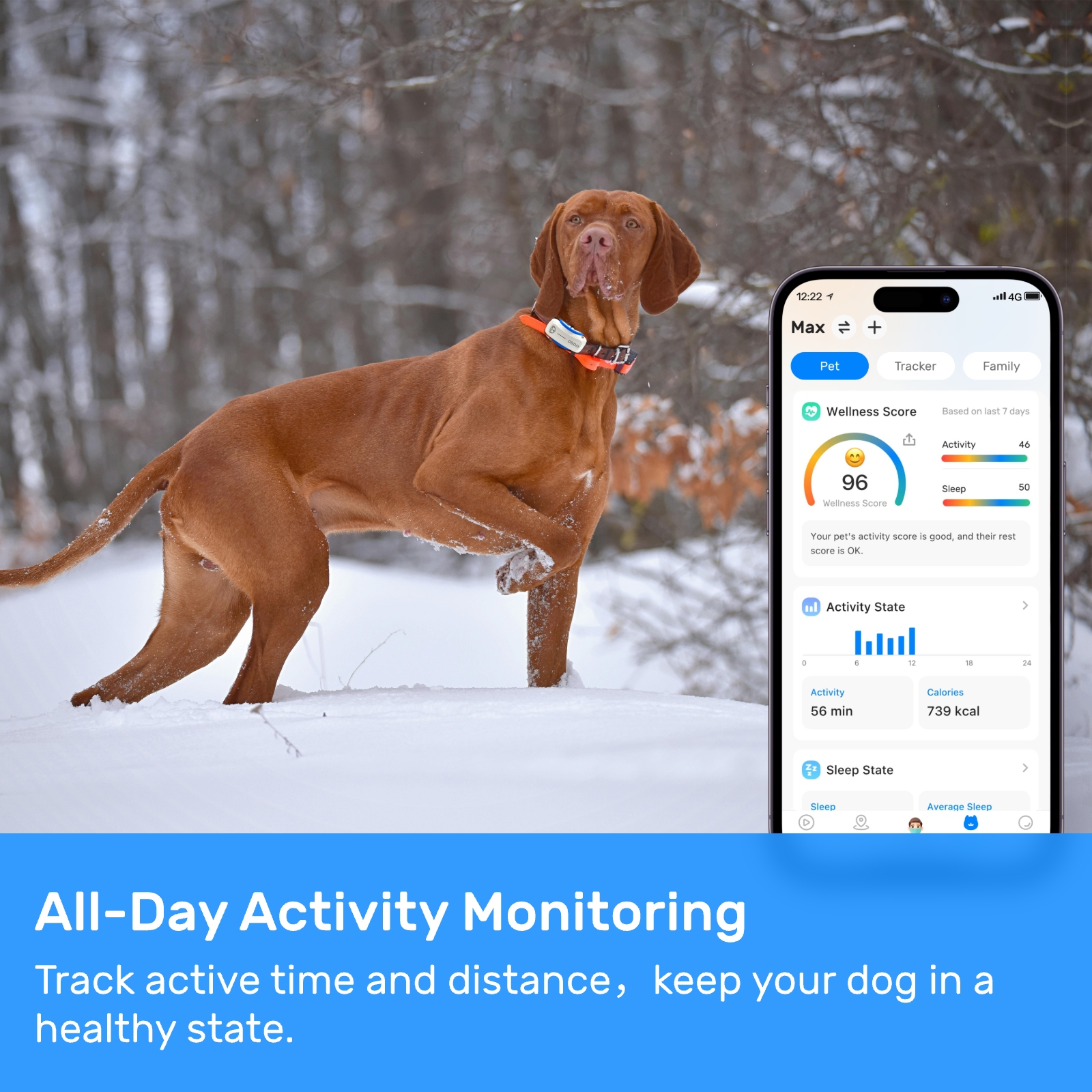
New ArrivalsBack in stock
fi tracker
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D896550636 second hand :D896550636 |
Manufacturer | fi tracker | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $37 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | fi tracker | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Smart Home#Pet Connected Sensors










Introduction to FI Trackers
Financial Intelligence Trackers are advanced software solutions that utilize artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and data analytics to monitor financial transactions in real-time. These tools are capable of identifying unusual patterns, detecting suspicious activities, and providing insights into the financial behavior of individuals and organizations. FI Trackers play a crucial role in the prevention of financial crimes, such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and fraud.
The core functionalities of an FI Tracker include:

1. Transaction Monitoring: FI Trackers continuously monitor financial transactions, analyzing them against predefined rules and parameters to identify any irregularities or suspicious activities.
2. Risk Assessment: By analyzing historical data and current trends, FI Trackers can assess the risk level associated with specific transactions, customers, or products.
3. Reporting and Compliance: FI Trackers generate reports that help financial institutions comply with regulatory requirements, such as the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations.
4. Fraud Detection: FI Trackers use advanced algorithms to detect fraudulent activities, such as identity theft, credit card fraud, and check fraud.

5. Customer Profiling: FI Trackers create detailed profiles of customers, which can be used to tailor financial products and services, as well as to identify potential risks.
6. Data Integration: FI Trackers can integrate data from multiple sources, such as bank accounts, credit bureaus, and public records, to provide a comprehensive view of a customer's financial behavior.
Benefits of FI Trackers

The adoption of FI Trackers offers numerous benefits to financial institutions, including:
1. Enhanced Security: FI Trackers help protect financial institutions from cyber threats and fraud, ensuring the safety of their customers' assets and reputation.
2. Improved Compliance: By automating the process of monitoring transactions and generating compliance reports, FI Trackers help financial institutions meet regulatory requirements more effectively.
3. Reduced Operational Costs: FI Trackers can significantly reduce the time and resources required for manual monitoring and analysis, leading to cost savings for financial institutions.

4. Enhanced Customer Experience: By identifying and addressing potential risks and fraud attempts, FI Trackers help financial institutions provide a safer and more secure environment for their customers.

5. Competitive Advantage: Financial institutions that adopt FI Trackers can differentiate themselves from competitors by offering superior security and compliance capabilities.

Challenges Facing FI Trackers
Despite their numerous benefits, FI Trackers also face several challenges, including:
1. Data Privacy Concerns: The use of FI Trackers raises concerns about data privacy and the potential misuse of personal information. Financial institutions must ensure that they comply with data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
2. Technological Limitations: The effectiveness of FI Trackers depends on the quality and accuracy of the data they analyze. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to false positives and missed alerts, undermining the value of these tools.
3. Cybersecurity Threats: As with any technology, FI Trackers are vulnerable to cyberattacks, which can compromise their functionality and the security of the data they analyze.
4. Integration Challenges: Integrating FI Trackers with existing systems and processes can be complex and time-consuming, particularly for large financial institutions with multiple legacy systems.
5. Skilled Workforce Shortage: The successful implementation and management of FI Trackers require a skilled workforce with expertise in areas such as data analytics, machine learning, and cybersecurity. However, there is a shortage of professionals with these skills, making it difficult for financial institutions to build and maintain their FI Tracker capabilities.
The Evolution of FI Trackers
Over the past decade, FI Trackers have evolved significantly, driven by advancements in technology and changing regulatory landscapes. Some of the key trends shaping the future of FI Trackers include:
1. AI and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and ML algorithms into FI Trackers has significantly improved their ability to detect and analyze complex patterns and relationships in financial data.
2. Big Data Analytics: The increasing availability of large datasets, combined with advancements in data analytics, has enabled FI Trackers to provide more accurate and comprehensive insights into financial transactions and behavior.

3. Cloud Computing: The adoption of cloud computing has allowed financial institutions to leverage the scalability and flexibility of cloud-based infrastructure to support their FI Tracker capabilities.
4. Real-Time Monitoring: The development of real-time monitoring capabilities has enabled FI Trackers to provide instant alerts and insights, allowing financial institutions to respond
Update Time:2025-05-15 08:36:41
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form