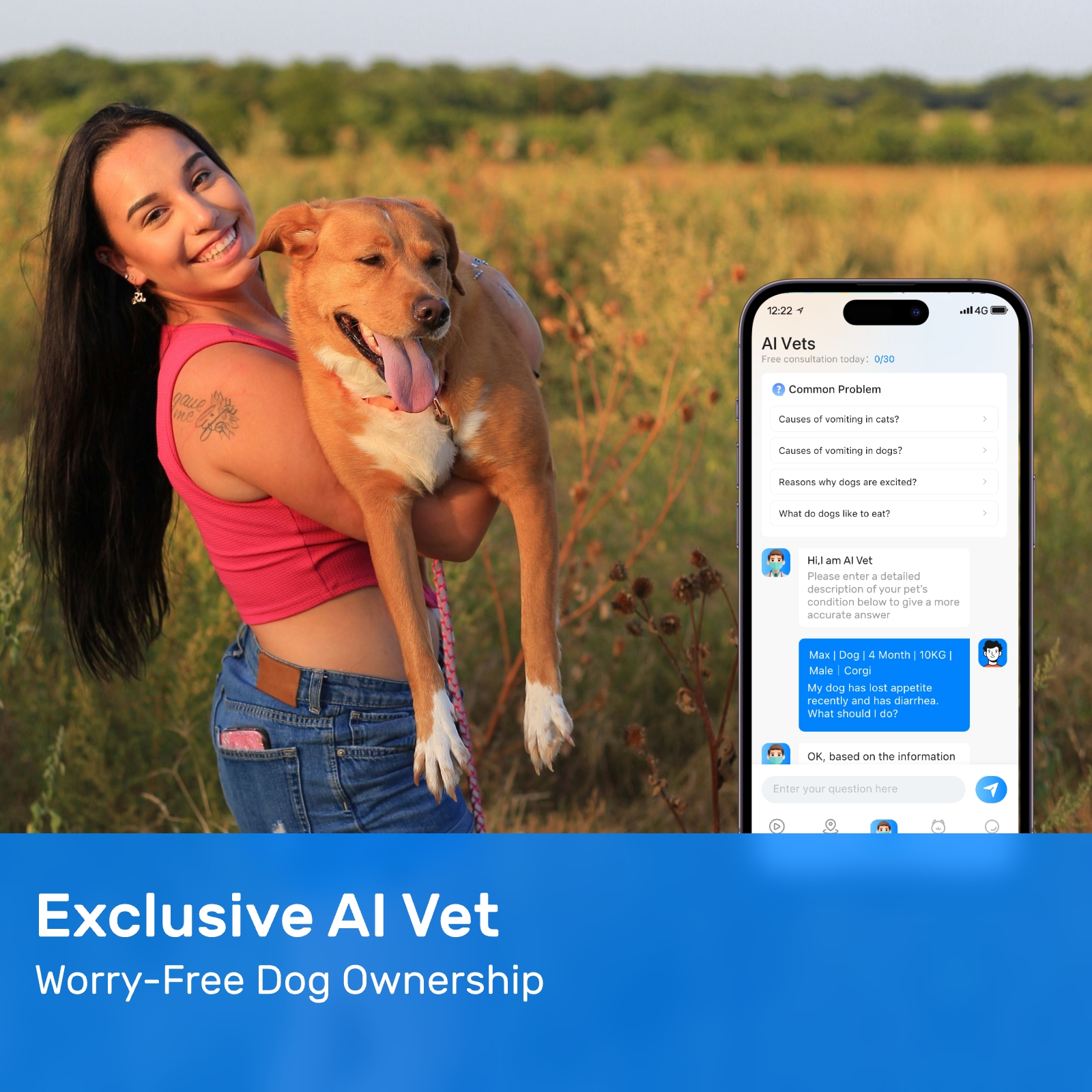
New ArrivalsBack in stock
doge education department contract cuts
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D795877734 second hand :D795877734 |
Manufacturer | doge education | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $36 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | education department | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
E-commerce#Pet Tech Best Sellers
In recent times, the Doge Education Department has been facing significant challenges due to contract cuts, which have led to a ripple effect across various sectors, including the mapping of cellular coverage for GPS trackers. This article aims to delve into the implications of these contract cuts on the mapping of cellular coverage for GPS trackers and the broader impact on educational and technological infrastructure.
The Doge Education Department's contract cuts have been a topic of heated debate, with critics arguing that these reductions are detrimental to the quality and accessibility of educational services. However, the cuts have also extended beyond the educational sector, affecting other areas that rely on the department's funding and support. One such area is the mapping of cellular coverage for GPS trackers, which has become increasingly important in today's interconnected world.
GPS trackers are essential tools for various industries, including transportation, logistics, and security. They rely on cellular networks to transmit location data, which is then used for route optimization, asset tracking, and safety monitoring. The accuracy and reliability of this data depend on the quality of cellular coverage in the areas where the trackers are deployed. Therefore, mapping cellular coverage is a critical task that ensures the effective functioning of GPS trackers and the services they support.
The Doge Education Department's contract cuts have had a direct impact on the resources available for mapping cellular coverage. As a result, there has been a reduction in the number of personnel and funding allocated to this task. This has led to several challenges in the mapping process, including:

1. Incomplete and outdated data: With fewer resources dedicated to mapping cellular coverage, it is increasingly difficult to maintain an up-to-date and comprehensive database of coverage information. This can result in gaps in coverage data, which can impact the accuracy of GPS tracking and the services that rely on it.
2. Limited geographic coverage: The contract cuts have also led to a reduction in the geographic scope of cellular coverage mapping. This means that some areas, particularly remote or rural regions, may not have their cellular coverage accurately mapped, potentially affecting the performance of GPS trackers in these locations.
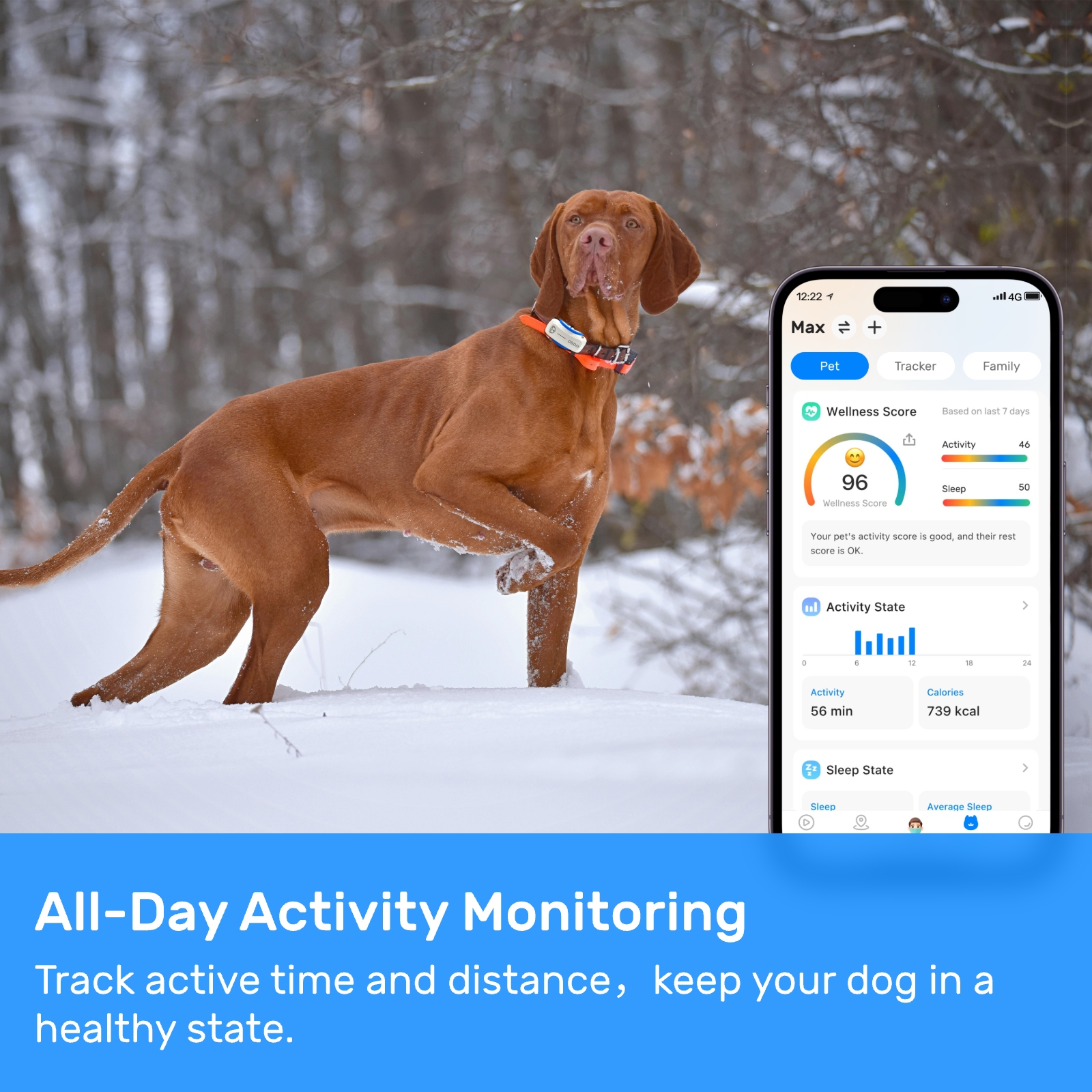
3. decreased investment in technology: The Doge Education Department's contract cuts have also impacted the investment in technology required for mapping cellular coverage. This includes the equipment and software used for data collection and analysis, as well as the development of new methods and techniques for improving the accuracy and efficiency of mapping efforts.
4. Reduced collaboration and knowledge sharing: The contract cuts have also affected the collaboration between different stakeholders involved in the mapping of cellular coverage, including government agencies, educational institutions, and private companies. This can lead to a lack of knowledge sharing and innovation in the field, ultimately hindering the development of more effective and efficient mapping techniques.
The impact of the Doge Education Department's contract cuts on the mapping of cellular coverage for GPS trackers extends beyond the immediate challenges mentioned above. The reduced quality and availability of coverage data can have far-reaching consequences for various industries and services that rely on GPS tracking. Some of these consequences include:
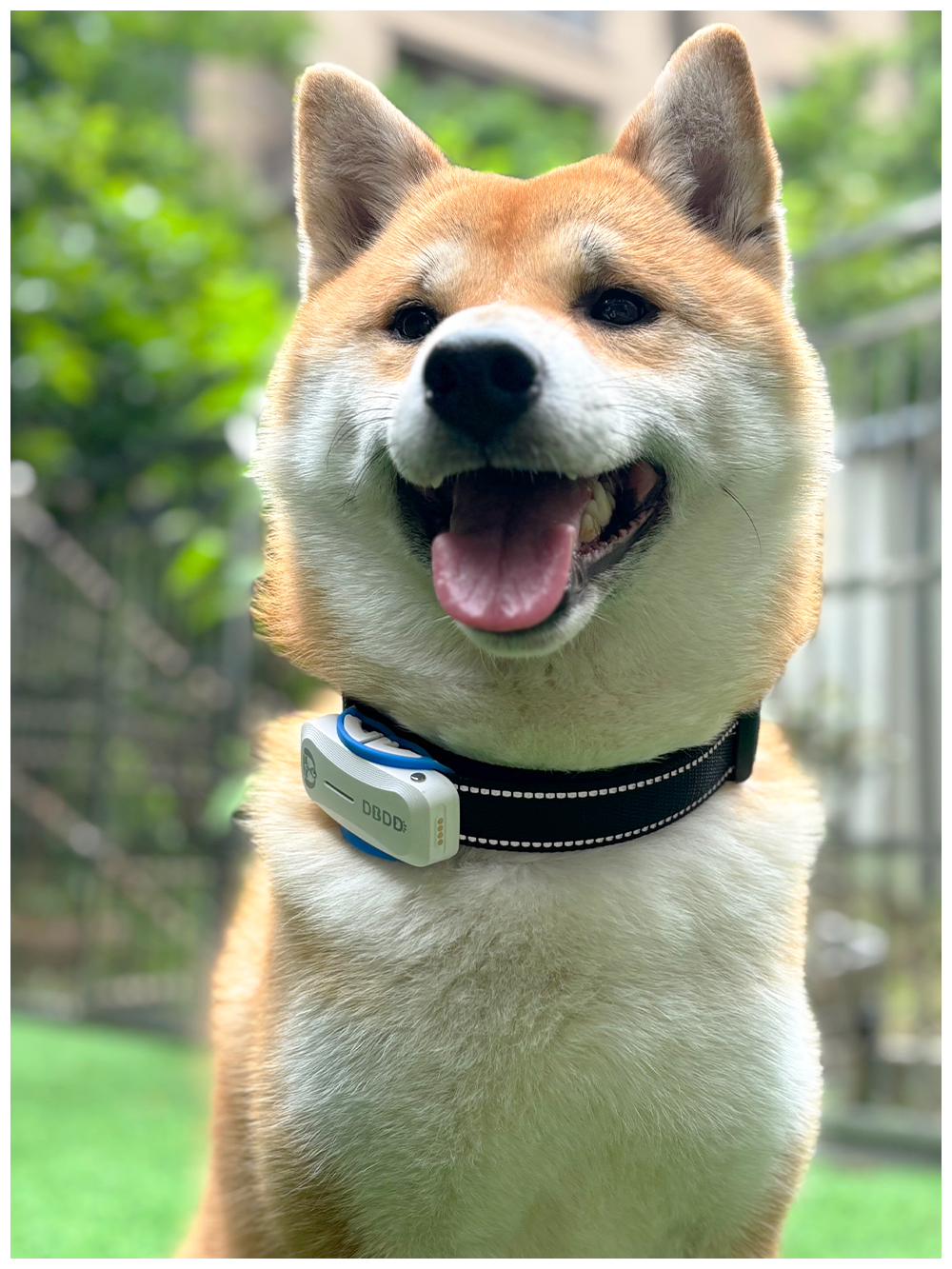

1. Inefficient routing and logistics: Inaccurate or incomplete cellular coverage data can lead to suboptimal routing decisions, resulting in increased travel times, fuel consumption, and costs for transportation and logistics companies.
2. Compromised safety and security: The reliability of GPS tracking for safety and security purposes, such as monitoring the location of vehicles or assets, can be compromised if the cellular coverage data is not accurate or up-to-date. This can put people and valuable assets at risk.
3. Hindered economic development: The mapping of cellular coverage is crucial for the development and expansion of telecommunications infrastructure, which is a key driver of economic growth and development. The contract cuts can slow down this process, limiting the potential for growth in the telecommunications sector and its associated industries.
4. Reduced innovation and competitiveness: The lack of investment in technology and collaboration resulting from the Doge Education Department's contract cuts can hinder innovation in the field of mapping cellular coverage for GPS trackers. This can put the country at a competitive disadvantage in the global market, as other nations continue to invest in and develop cutting-edge technologies in this area.
In conclusion, the Doge Education Department's contract cuts have had a significant impact on the mapping of cellular coverage for GPS trackers, leading to challenges in data accuracy, geographic coverage, technology investment, and collaboration. These challenges, in turn, have far-reaching consequences for various industries and services that rely on GPS tracking, potentially hindering economic development and competitiveness. It is crucial for policymakers and stakeholders to recognize the importance of the mapping of cellular coverage for GPS trackers and work towards addressing the challenges posed by the contract cuts to ensure the continued growth and development of this vital technology.

Update Time:2025-05-15 03:51:31
The Doge Education Department's contract cuts have been a topic of heated debate, with critics arguing that these reductions are detrimental to the quality and accessibility of educational services. However, the cuts have also extended beyond the educational sector, affecting other areas that rely on the department's funding and support. One such area is the mapping of cellular coverage for GPS trackers, which has become increasingly important in today's interconnected world.
GPS trackers are essential tools for various industries, including transportation, logistics, and security. They rely on cellular networks to transmit location data, which is then used for route optimization, asset tracking, and safety monitoring. The accuracy and reliability of this data depend on the quality of cellular coverage in the areas where the trackers are deployed. Therefore, mapping cellular coverage is a critical task that ensures the effective functioning of GPS trackers and the services they support.
The Doge Education Department's contract cuts have had a direct impact on the resources available for mapping cellular coverage. As a result, there has been a reduction in the number of personnel and funding allocated to this task. This has led to several challenges in the mapping process, including:

1. Incomplete and outdated data: With fewer resources dedicated to mapping cellular coverage, it is increasingly difficult to maintain an up-to-date and comprehensive database of coverage information. This can result in gaps in coverage data, which can impact the accuracy of GPS tracking and the services that rely on it.
2. Limited geographic coverage: The contract cuts have also led to a reduction in the geographic scope of cellular coverage mapping. This means that some areas, particularly remote or rural regions, may not have their cellular coverage accurately mapped, potentially affecting the performance of GPS trackers in these locations.

3. decreased investment in technology: The Doge Education Department's contract cuts have also impacted the investment in technology required for mapping cellular coverage. This includes the equipment and software used for data collection and analysis, as well as the development of new methods and techniques for improving the accuracy and efficiency of mapping efforts.
4. Reduced collaboration and knowledge sharing: The contract cuts have also affected the collaboration between different stakeholders involved in the mapping of cellular coverage, including government agencies, educational institutions, and private companies. This can lead to a lack of knowledge sharing and innovation in the field, ultimately hindering the development of more effective and efficient mapping techniques.
The impact of the Doge Education Department's contract cuts on the mapping of cellular coverage for GPS trackers extends beyond the immediate challenges mentioned above. The reduced quality and availability of coverage data can have far-reaching consequences for various industries and services that rely on GPS tracking. Some of these consequences include:

1. Inefficient routing and logistics: Inaccurate or incomplete cellular coverage data can lead to suboptimal routing decisions, resulting in increased travel times, fuel consumption, and costs for transportation and logistics companies.
2. Compromised safety and security: The reliability of GPS tracking for safety and security purposes, such as monitoring the location of vehicles or assets, can be compromised if the cellular coverage data is not accurate or up-to-date. This can put people and valuable assets at risk.
3. Hindered economic development: The mapping of cellular coverage is crucial for the development and expansion of telecommunications infrastructure, which is a key driver of economic growth and development. The contract cuts can slow down this process, limiting the potential for growth in the telecommunications sector and its associated industries.
4. Reduced innovation and competitiveness: The lack of investment in technology and collaboration resulting from the Doge Education Department's contract cuts can hinder innovation in the field of mapping cellular coverage for GPS trackers. This can put the country at a competitive disadvantage in the global market, as other nations continue to invest in and develop cutting-edge technologies in this area.
In conclusion, the Doge Education Department's contract cuts have had a significant impact on the mapping of cellular coverage for GPS trackers, leading to challenges in data accuracy, geographic coverage, technology investment, and collaboration. These challenges, in turn, have far-reaching consequences for various industries and services that rely on GPS tracking, potentially hindering economic development and competitiveness. It is crucial for policymakers and stakeholders to recognize the importance of the mapping of cellular coverage for GPS trackers and work towards addressing the challenges posed by the contract cuts to ensure the continued growth and development of this vital technology.

Update Time:2025-05-15 03:51:31
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form