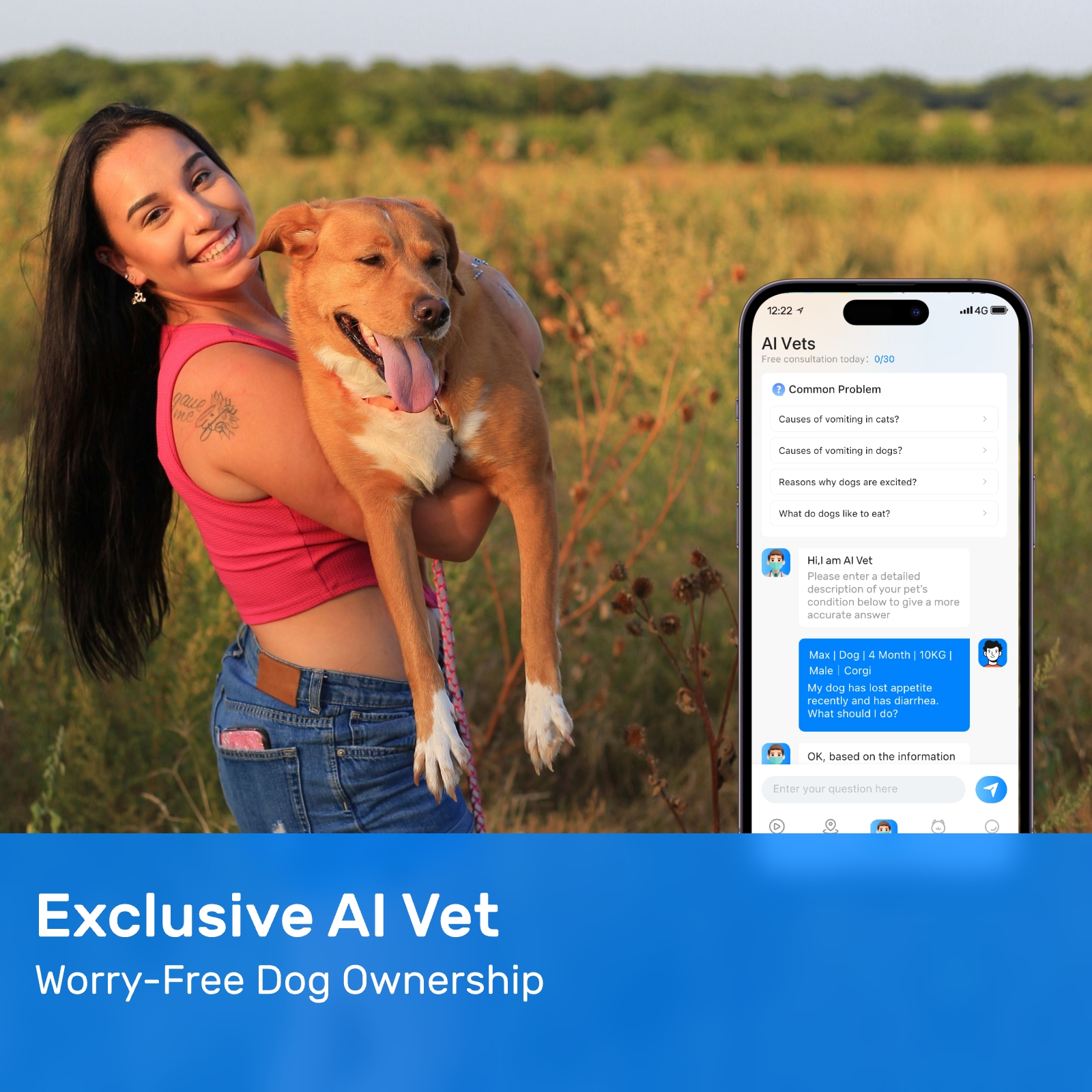
New ArrivalsBack in stock
gps collars for dogs
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D165289239 second hand :D165289239 |
Manufacturer | gps collars | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $45 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | collars for | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Retail Analytics#Pet Behavior Insights
GPS collars for dogs have revolutionized the way pet owners monitor and track their canine companions. These devices use Global Positioning System (GPS) technology to pinpoint a dog's location, providing peace of mind and a safety net for both pets and their owners. The precision of GPS collars for dogs is a critical factor in their effectiveness, and it is important to understand how this technology works and what factors can influence its accuracy.
GPS technology relies on a network of satellites orbiting the Earth to provide location data. When a GPS collar for dogs is activated, it communicates with these satellites to determine the dog's latitude and longitude. The precision of this information is dependent on several factors, including the number of satellites in view, the quality of the GPS receiver in the collar, and the presence of any obstacles that might interfere with the signal.
One of the key elements that contribute to the accuracy of GPS collars for dogs is the number of satellites that the collar can receive signals from. Ideally, a GPS device should be able to "see" at least four satellites to provide an accurate location fix. However, in some areas, especially urban environments with tall buildings or dense foliage, the number of visible satellites can be reduced, which can affect the accuracy of the location data.
The quality of the GPS receiver in the collar is another significant factor. High-quality receivers are more sensitive and can pick up weaker signals, which can be crucial in areas with poor satellite coverage. Some GPS collars for dogs come with advanced receivers that can handle multiple GPS satellite systems, such as GPS, GLONASS, and BeiDou, which can improve accuracy by providing more satellite options to choose from.

Obstacles like buildings, trees, and other physical barriers can also impact the precision of GPS collars for dogs. These obstructions can block or weaken the satellite signals, leading to less accurate location data. To mitigate this issue, some collars are designed with features that use both GPS and cellular network triangulation, which can provide a more accurate location even when GPS signals are obstructed.
In addition to these factors, the software that processes the GPS data also plays a role in the accuracy of the collars. Advanced algorithms can help filter out noise and provide a more precise location, while real-time updates can ensure that the pet owner receives the most current location information.
It's also worth noting that no GPS system is perfect, and there will always be some margin of error. However, most GPS collars for dogs are designed to provide location accuracy within a few meters, which is generally sufficient for tracking a pet within a local area.
Another aspect of accuracy to consider is the battery life of the GPS collar. A collar that needs to be charged or replaced frequently may not provide continuous tracking, which could lead to gaps in the location data. Therefore, the balance between battery life and tracking frequency is crucial for maintaining accuracy over time.
In conclusion, the precision of GPS collars for dogs is a multifaceted issue that depends on a combination of factors, including satellite visibility, receiver quality, software algorithms, and obstacle interference. By understanding these factors, pet owners can make informed decisions when choosing a GPS collar for their dogs, ensuring that they select a product that provides the level of accuracy needed for their specific circumstances. It's also important to remember that while GPS collars offer a significant advantage in tracking pets, they should not replace responsible pet ownership practices such as keeping dogs on a leash in unfamiliar areas and ensuring that they are microchipped for identification in case they are lost.
Update Time:2025-05-15 07:54:25
GPS technology relies on a network of satellites orbiting the Earth to provide location data. When a GPS collar for dogs is activated, it communicates with these satellites to determine the dog's latitude and longitude. The precision of this information is dependent on several factors, including the number of satellites in view, the quality of the GPS receiver in the collar, and the presence of any obstacles that might interfere with the signal.
One of the key elements that contribute to the accuracy of GPS collars for dogs is the number of satellites that the collar can receive signals from. Ideally, a GPS device should be able to "see" at least four satellites to provide an accurate location fix. However, in some areas, especially urban environments with tall buildings or dense foliage, the number of visible satellites can be reduced, which can affect the accuracy of the location data.
The quality of the GPS receiver in the collar is another significant factor. High-quality receivers are more sensitive and can pick up weaker signals, which can be crucial in areas with poor satellite coverage. Some GPS collars for dogs come with advanced receivers that can handle multiple GPS satellite systems, such as GPS, GLONASS, and BeiDou, which can improve accuracy by providing more satellite options to choose from.

Obstacles like buildings, trees, and other physical barriers can also impact the precision of GPS collars for dogs. These obstructions can block or weaken the satellite signals, leading to less accurate location data. To mitigate this issue, some collars are designed with features that use both GPS and cellular network triangulation, which can provide a more accurate location even when GPS signals are obstructed.
In addition to these factors, the software that processes the GPS data also plays a role in the accuracy of the collars. Advanced algorithms can help filter out noise and provide a more precise location, while real-time updates can ensure that the pet owner receives the most current location information.
It's also worth noting that no GPS system is perfect, and there will always be some margin of error. However, most GPS collars for dogs are designed to provide location accuracy within a few meters, which is generally sufficient for tracking a pet within a local area.
Another aspect of accuracy to consider is the battery life of the GPS collar. A collar that needs to be charged or replaced frequently may not provide continuous tracking, which could lead to gaps in the location data. Therefore, the balance between battery life and tracking frequency is crucial for maintaining accuracy over time.
In conclusion, the precision of GPS collars for dogs is a multifaceted issue that depends on a combination of factors, including satellite visibility, receiver quality, software algorithms, and obstacle interference. By understanding these factors, pet owners can make informed decisions when choosing a GPS collar for their dogs, ensuring that they select a product that provides the level of accuracy needed for their specific circumstances. It's also important to remember that while GPS collars offer a significant advantage in tracking pets, they should not replace responsible pet ownership practices such as keeping dogs on a leash in unfamiliar areas and ensuring that they are microchipped for identification in case they are lost.
Update Time:2025-05-15 07:54:25
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form