New ArrivalsBack in stock
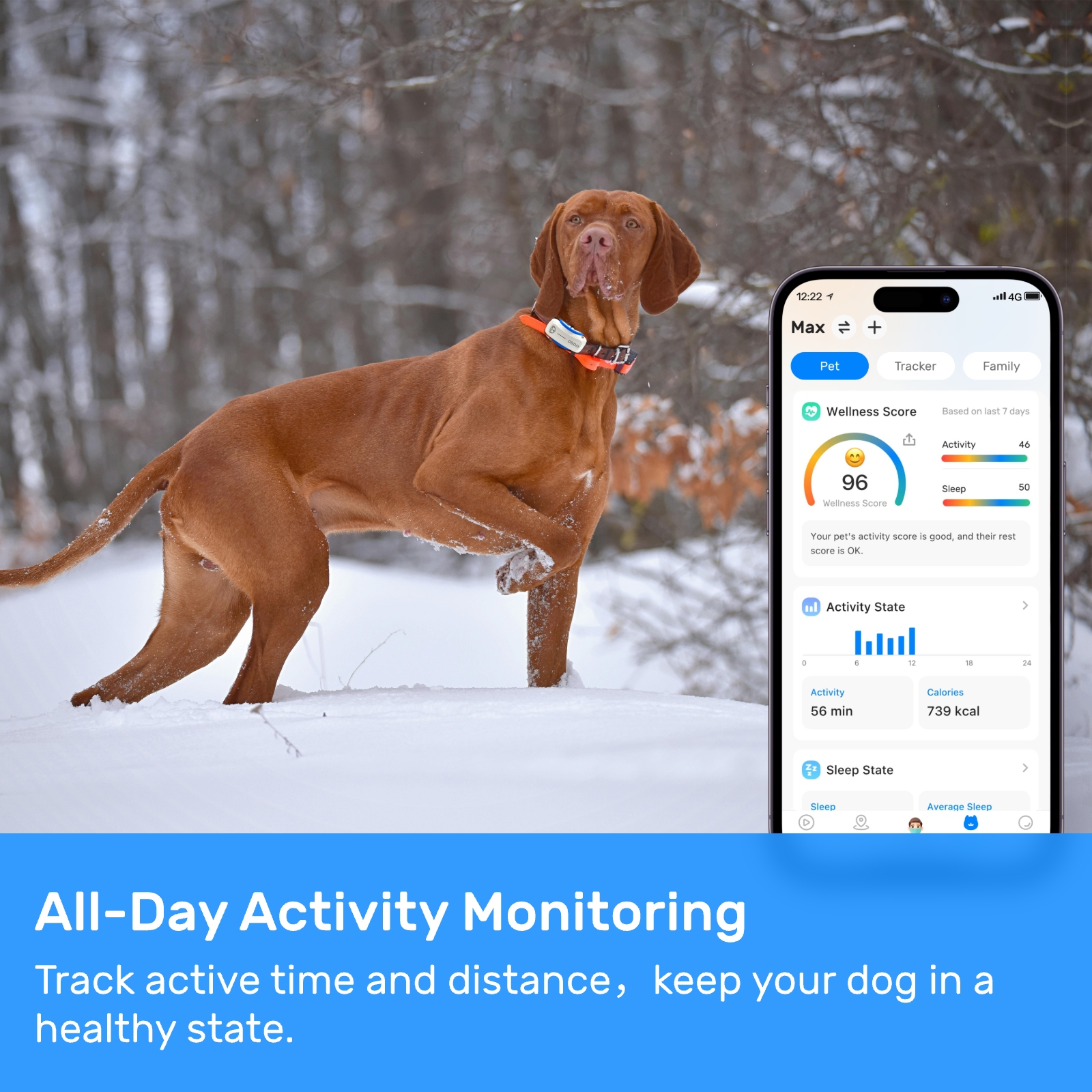
dog gps tracking
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D504385687 second hand :D504385687 |
Manufacturer | dog gps | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $40 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | gps tracking | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Mobile Tech#Bluetooth Tracking Accessories
In recent years, the demand for pet tracking devices has surged as pet owners seek innovative ways to ensure their beloved animals' safety. Among these technologies, dog GPS tracking systems have become increasingly popular. These systems enable pet owners to monitor their dogs' locations in real-time, providing peace of mind and a sense of security. Two primary wireless communication technologies used in these devices are Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. Each technology offers distinct advantages and limitations when it comes to dog GPS tracking. This article explores the differences between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity in dog GPS tracking systems, helping pet owners make informed decisions about which technology best suits their needs.
Bluetooth connectivity in dog GPS tracking is widely recognized for its simplicity and ease of use. Bluetooth operates on short-range radio waves, allowing devices to communicate wirelessly over relatively small distances. In the context of dog GPS tracking, Bluetooth-enabled trackers typically connect directly to a user's smartphone or tablet via an app. The connection is established automatically once the device enters the range of the paired smartphone. One of the key advantages of Bluetooth is its low power consumption. Since Bluetooth operates at short ranges, it requires less energy compared to other wireless technologies, making it ideal for battery-powered devices like GPS trackers.
Moreover, Bluetooth technology has undergone significant advancements with the introduction of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). BLE allows devices to maintain a connection while consuming minimal power, extending the battery life of GPS trackers considerably. For pet owners who prioritize extended battery life and do not require long-distance monitoring, Bluetooth-based dog GPS tracking systems can be an excellent choice. However, one limitation of Bluetooth is its limited range. Most Bluetooth devices operate within a range of 10 to 100 meters, depending on the version and environmental conditions. Therefore, Bluetooth-based trackers are most effective when the dog remains within close proximity to the owner's smartphone.
On the other hand, Wi-Fi connectivity in dog GPS tracking provides several unique benefits that differ from those offered by Bluetooth. Wi-Fi operates on higher frequency bands than Bluetooth, enabling it to transmit data over longer distances and at faster speeds. Wi-Fi-enabled GPS trackers typically connect to a home network or public hotspots, allowing users to track their dogs even when they are out of Bluetooth range. This capability makes Wi-Fi a more suitable option for scenarios where dogs may wander beyond the immediate vicinity of their owners, such as during walks in large parks or trips to dog-friendly venues.
One of the standout features of Wi-Fi-based dog GPS tracking is its ability to leverage geofencing technology. Geofencing involves setting virtual boundaries around specific areas, such as a backyard or park. When a dog equipped with a Wi-Fi tracker crosses these boundaries, the system sends an alert to the owner's smartphone, notifying them of the potential risk. This feature enhances the overall safety and security of the dog, as owners can take immediate action if their pet ventures too far. Additionally, Wi-Fi trackers often provide more detailed location data, including maps and historical movement patterns, giving pet owners deeper insights into their dogs' activities.
Despite its advantages, Wi-Fi connectivity also presents certain challenges. One major drawback is its higher power consumption compared to Bluetooth. Since Wi-Fi operates at higher frequencies and transmits data over longer distances, it drains batteries faster. As a result, Wi-Fi-based GPS trackers may require more frequent charging, which could be inconvenient for some pet owners. Furthermore, the effectiveness of Wi-Fi tracking depends on the availability of network coverage. In areas with weak or no Wi-Fi signals, such as rural regions or remote trails, the tracker may lose functionality, leaving a gap in the dog's location data.
Another consideration when comparing Bluetooth and Wi-Fi in dog GPS tracking is cost. Generally, Bluetooth-based trackers tend to be more affordable due to their simpler design and lower power requirements. They often come with fewer additional features, focusing primarily on basic location tracking. In contrast, Wi-Fi-enabled trackers are usually more expensive, reflecting their advanced capabilities and enhanced functionality. For budget-conscious pet owners, Bluetooth trackers may offer a more cost-effective solution without compromising essential features.
The decision between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity ultimately depends on individual preferences and specific use cases. For example, pet owners who primarily use GPS tracking to monitor their dogs during daily walks or while playing in the yard may find Bluetooth-based systems sufficient. The short-range nature of Bluetooth aligns well with these scenarios, offering reliable performance and extended battery life. On the other hand, pet owners who need to track their dogs over larger areas or want access to advanced features like geofencing and detailed location history might prefer Wi-Fi-based systems. The ability to receive real-time updates regardless of distance can provide greater reassurance and control.
It is also worth noting that some modern dog GPS tracking devices combine both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity to offer the best of both worlds. These hybrid systems utilize Bluetooth for close-range communication and switch to Wi-Fi when the dog moves out of Bluetooth range. This dual-mode approach ensures continuous tracking without sacrificing battery life or functionality. Such devices cater to pet owners seeking versatility and flexibility in their tracking solutions.
Privacy and security are additional factors to consider when choosing between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi for dog GPS tracking. Both technologies employ encryption protocols to protect sensitive information transmitted between the tracker and the user's device. However, Wi-Fi networks, especially public ones, can pose potential security risks if not properly secured. Pet owners should ensure that their Wi-Fi-enabled trackers connect only to trusted networks and implement strong password protection to safeguard their data. Bluetooth, being a short-range technology, inherently reduces the risk of unauthorized access since the connection is limited to nearby devices.

Finally, user experience plays a crucial role in determining the suitability of Bluetooth versus Wi-Fi for dog GPS tracking. Ease of setup, app interface, and notification systems all contribute to how effectively a pet owner can utilize the tracking device. Many manufacturers offer intuitive apps compatible with both Android and iOS platforms, simplifying the process of monitoring and managing the tracker. Regardless of whether Bluetooth or Wi-Fi is chosen, selecting a device with a user-friendly app can enhance the overall satisfaction and effectiveness of the dog GPS tracking system.
In conclusion, both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi offer valuable options for dog GPS tracking, each with its own set of strengths and limitations. Bluetooth excels in terms of low power consumption and simplicity, making it ideal for short-range applications. Wi-Fi, meanwhile, provides extended range and advanced features, catering to scenarios where dogs may roam farther from their owners. By carefully evaluating their specific needs and circumstances, pet owners can choose the connectivity option that best supports their goals for ensuring their dogs' safety and well-being. Whether opting for Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or a combination of both, the growing availability of dog GPS tracking technologies empowers pet owners to stay connected with their furry companions like never before.
Update Time:2025-05-15 06:14:24
Bluetooth connectivity in dog GPS tracking is widely recognized for its simplicity and ease of use. Bluetooth operates on short-range radio waves, allowing devices to communicate wirelessly over relatively small distances. In the context of dog GPS tracking, Bluetooth-enabled trackers typically connect directly to a user's smartphone or tablet via an app. The connection is established automatically once the device enters the range of the paired smartphone. One of the key advantages of Bluetooth is its low power consumption. Since Bluetooth operates at short ranges, it requires less energy compared to other wireless technologies, making it ideal for battery-powered devices like GPS trackers.
Moreover, Bluetooth technology has undergone significant advancements with the introduction of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). BLE allows devices to maintain a connection while consuming minimal power, extending the battery life of GPS trackers considerably. For pet owners who prioritize extended battery life and do not require long-distance monitoring, Bluetooth-based dog GPS tracking systems can be an excellent choice. However, one limitation of Bluetooth is its limited range. Most Bluetooth devices operate within a range of 10 to 100 meters, depending on the version and environmental conditions. Therefore, Bluetooth-based trackers are most effective when the dog remains within close proximity to the owner's smartphone.
On the other hand, Wi-Fi connectivity in dog GPS tracking provides several unique benefits that differ from those offered by Bluetooth. Wi-Fi operates on higher frequency bands than Bluetooth, enabling it to transmit data over longer distances and at faster speeds. Wi-Fi-enabled GPS trackers typically connect to a home network or public hotspots, allowing users to track their dogs even when they are out of Bluetooth range. This capability makes Wi-Fi a more suitable option for scenarios where dogs may wander beyond the immediate vicinity of their owners, such as during walks in large parks or trips to dog-friendly venues.
One of the standout features of Wi-Fi-based dog GPS tracking is its ability to leverage geofencing technology. Geofencing involves setting virtual boundaries around specific areas, such as a backyard or park. When a dog equipped with a Wi-Fi tracker crosses these boundaries, the system sends an alert to the owner's smartphone, notifying them of the potential risk. This feature enhances the overall safety and security of the dog, as owners can take immediate action if their pet ventures too far. Additionally, Wi-Fi trackers often provide more detailed location data, including maps and historical movement patterns, giving pet owners deeper insights into their dogs' activities.
Despite its advantages, Wi-Fi connectivity also presents certain challenges. One major drawback is its higher power consumption compared to Bluetooth. Since Wi-Fi operates at higher frequencies and transmits data over longer distances, it drains batteries faster. As a result, Wi-Fi-based GPS trackers may require more frequent charging, which could be inconvenient for some pet owners. Furthermore, the effectiveness of Wi-Fi tracking depends on the availability of network coverage. In areas with weak or no Wi-Fi signals, such as rural regions or remote trails, the tracker may lose functionality, leaving a gap in the dog's location data.
Another consideration when comparing Bluetooth and Wi-Fi in dog GPS tracking is cost. Generally, Bluetooth-based trackers tend to be more affordable due to their simpler design and lower power requirements. They often come with fewer additional features, focusing primarily on basic location tracking. In contrast, Wi-Fi-enabled trackers are usually more expensive, reflecting their advanced capabilities and enhanced functionality. For budget-conscious pet owners, Bluetooth trackers may offer a more cost-effective solution without compromising essential features.
The decision between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity ultimately depends on individual preferences and specific use cases. For example, pet owners who primarily use GPS tracking to monitor their dogs during daily walks or while playing in the yard may find Bluetooth-based systems sufficient. The short-range nature of Bluetooth aligns well with these scenarios, offering reliable performance and extended battery life. On the other hand, pet owners who need to track their dogs over larger areas or want access to advanced features like geofencing and detailed location history might prefer Wi-Fi-based systems. The ability to receive real-time updates regardless of distance can provide greater reassurance and control.
It is also worth noting that some modern dog GPS tracking devices combine both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity to offer the best of both worlds. These hybrid systems utilize Bluetooth for close-range communication and switch to Wi-Fi when the dog moves out of Bluetooth range. This dual-mode approach ensures continuous tracking without sacrificing battery life or functionality. Such devices cater to pet owners seeking versatility and flexibility in their tracking solutions.
Privacy and security are additional factors to consider when choosing between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi for dog GPS tracking. Both technologies employ encryption protocols to protect sensitive information transmitted between the tracker and the user's device. However, Wi-Fi networks, especially public ones, can pose potential security risks if not properly secured. Pet owners should ensure that their Wi-Fi-enabled trackers connect only to trusted networks and implement strong password protection to safeguard their data. Bluetooth, being a short-range technology, inherently reduces the risk of unauthorized access since the connection is limited to nearby devices.

Finally, user experience plays a crucial role in determining the suitability of Bluetooth versus Wi-Fi for dog GPS tracking. Ease of setup, app interface, and notification systems all contribute to how effectively a pet owner can utilize the tracking device. Many manufacturers offer intuitive apps compatible with both Android and iOS platforms, simplifying the process of monitoring and managing the tracker. Regardless of whether Bluetooth or Wi-Fi is chosen, selecting a device with a user-friendly app can enhance the overall satisfaction and effectiveness of the dog GPS tracking system.
In conclusion, both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi offer valuable options for dog GPS tracking, each with its own set of strengths and limitations. Bluetooth excels in terms of low power consumption and simplicity, making it ideal for short-range applications. Wi-Fi, meanwhile, provides extended range and advanced features, catering to scenarios where dogs may roam farther from their owners. By carefully evaluating their specific needs and circumstances, pet owners can choose the connectivity option that best supports their goals for ensuring their dogs' safety and well-being. Whether opting for Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or a combination of both, the growing availability of dog GPS tracking technologies empowers pet owners to stay connected with their furry companions like never before.
Update Time:2025-05-15 06:14:24
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form