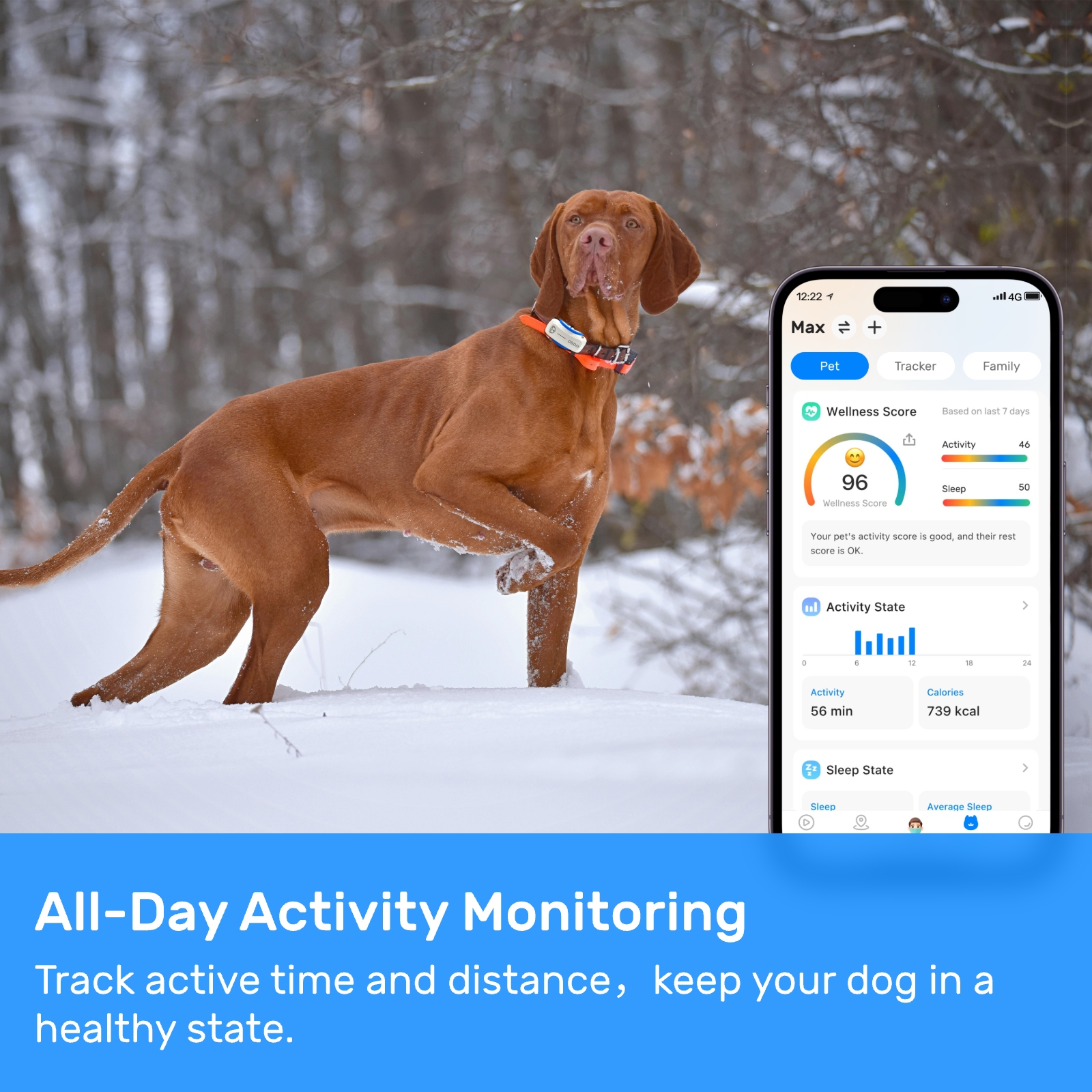
New ArrivalsBack in stock
dog park
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D387751191 second hand :D387751191 |
Manufacturer | dog park | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $35 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | dog park | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
5G Applications#Low-Latency Trackers










To begin with, understanding how dog locators function is crucial in evaluating their accuracy. Most modern dog locators use GPS (Global Positioning System) technology to pinpoint a dog's location. GPS works by triangulating the position of the device using signals from satellites orbiting the Earth. Once the device receives these signals, it calculates the precise coordinates of the dog's location, which are then transmitted to the owner's smartphone or other monitoring devices. In a dog park scenario, this means that even if a dog runs off or gets lost among a group of other animals, the owner can still track its exact position.
However, the accuracy of GPS-based dog locators can be affected by several factors, especially in a bustling environment like a dog park. One primary factor is satellite visibility. For optimal accuracy, the GPS receiver must have a clear line of sight to at least four satellites. Obstructions such as tall buildings, dense tree cover, or even the presence of numerous other dogs and people in the park can interfere with signal reception, leading to reduced accuracy or temporary loss of tracking capability.

Another factor influencing accuracy is the refresh rate of the GPS device. The refresh rate refers to how frequently the device updates the dog's location. A higher refresh rate provides more up-to-date information but may drain the battery faster. In a dog park, where dogs can move quickly and unpredictably, a high refresh rate is essential to ensure that the owner always knows the latest position of their pet. However, balancing the need for frequent updates with the need for extended battery life presents a challenge for manufacturers.
In addition to GPS, some dog locators incorporate additional technologies to enhance accuracy. For example, Wi-Fi and cellular networks can supplement GPS data, providing more reliable positioning indoors or in areas with poor satellite coverage. This hybrid approach can improve the overall accuracy of the locator, making it more effective in complex environments like dog parks. Furthermore, advanced algorithms can analyze patterns in the dog's movement and predict future locations based on past behavior, adding another layer of precision to the tracking process.

Despite these technological enhancements, challenges remain in achieving perfect accuracy in a dog park setting. One such challenge is the density of activity. Dog parks are typically crowded with multiple dogs running around, playing, and socializing. This high level of movement can create confusion for the tracking system, especially if several dogs are wearing similar devices. Cross-interference between different locators might occur, leading to inaccurate readings. To mitigate this issue, manufacturers are exploring ways to make each device's signal unique and less prone to interference from others.
Moreover, the physical environment of a dog park can pose obstacles to accurate tracking. Parks often feature structures such as fences, benches, and play equipment, which can obstruct GPS signals. Additionally, natural elements like trees and water bodies might further complicate the tracking process. Manufacturers address these challenges by designing devices with better signal reception capabilities and incorporating features that compensate for environmental disruptions.

User-related factors also play a role in the accuracy of dog locators. Proper installation and maintenance of the device are critical. If the locator is not securely attached to the dog's collar or if the battery is low, the accuracy of the tracking will suffer. Owners should regularly check the device's settings and firmware updates to ensure optimal performance. Understanding the limitations of the technology and using it appropriately can significantly enhance the effectiveness of the locator.
The importance of accurate dog locators in a dog park cannot be overstated. Losing sight of a dog in such an environment can be stressful and potentially dangerous. Accurate tracking ensures that owners can quickly locate their pets, preventing accidents or altercations with other dogs. Furthermore, knowing the exact location of a dog allows owners to monitor its activity levels and health, contributing to overall well-being.
Looking ahead, advancements in technology promise to improve the accuracy of dog locators even further. Innovations in satellite systems, such as the introduction of new constellations like Galileo and GLONASS, offer enhanced global coverage and increased precision. These systems work alongside GPS to provide more reliable and accurate positioning data. Additionally, developments in artificial intelligence and machine learning could enable locators to learn from past data, improving their ability to predict and track a dog's movements accurately.
Another promising area of development is the integration of wearable sensors with dog locators. These sensors can monitor vital signs such as heart rate and body temperature, providing comprehensive health data alongside location tracking. Such integrated systems would not only help in locating a dog but also in assessing its physical condition, ensuring timely intervention in case of any health issues.

In conclusion, while dog locators have become increasingly accurate and reliable, there are still challenges to overcome, particularly in environments like dog parks. Factors such as satellite visibility, refresh rates, and environmental obstructions can all impact the effectiveness of these devices. However, ongoing advancements in technology, including improved GPS systems, hybrid tracking methods, and AI-driven predictions, hold great promise for enhancing locator accuracy. By addressing current limitations and embracing future innovations, dog locators will continue to evolve, offering pet owners greater peace of mind and ensuring the safety and well-being of their beloved companions in diverse settings like dog parks. As technology progresses, the day may come when losing track of a dog in a park becomes a thing of the past.
Update Time:2025-05-15 07:22:40
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form