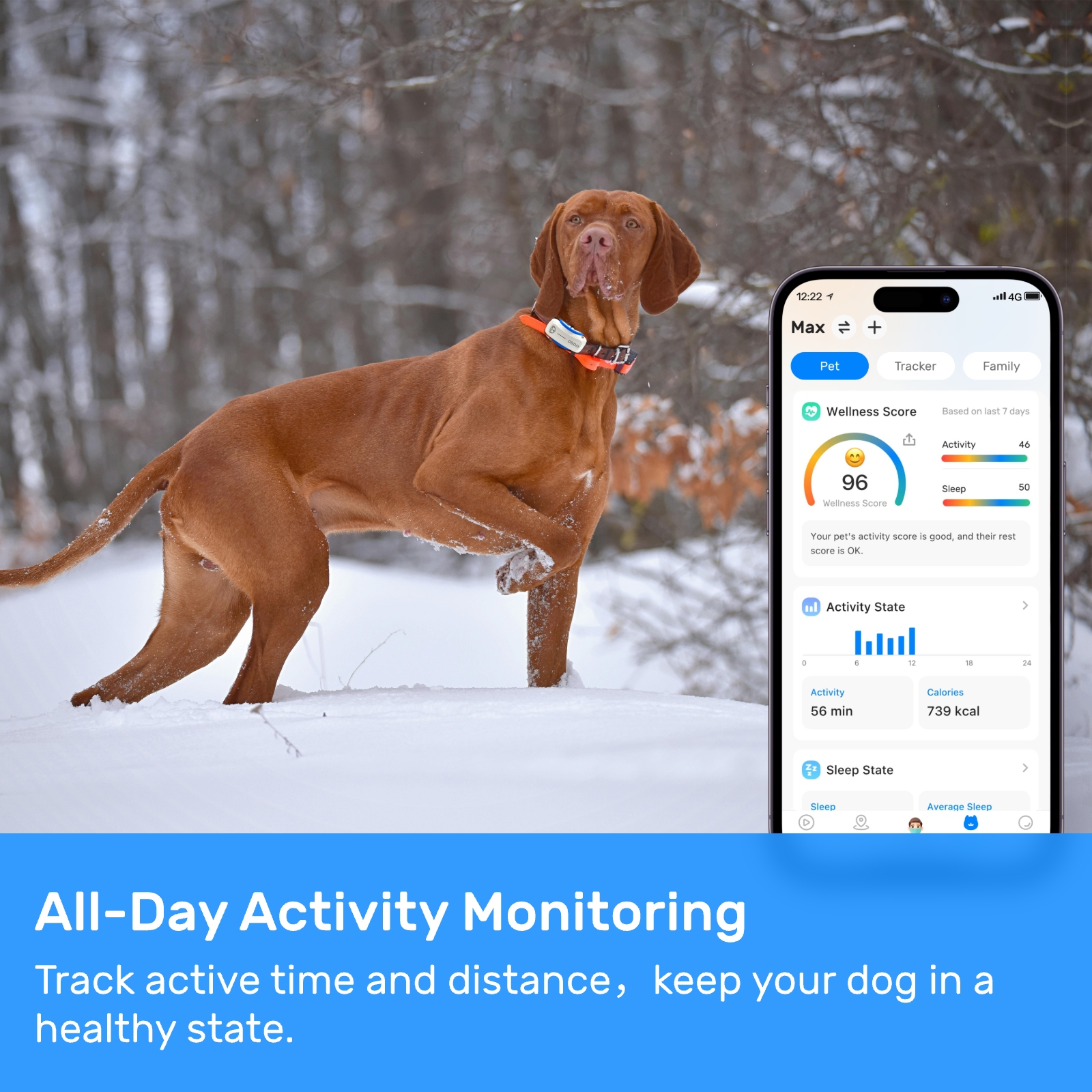
New ArrivalsBack in stock
war dogs
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D411728086 second hand :D411728086 |
Manufacturer | war dogs | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $41 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | war dogs | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Behavioral Science#Activity Analysis Tools
War dogs have been a crucial part of military operations for centuries, playing an integral role in various missions. From detecting explosives to providing security and tracking down enemies, these highly trained canines have proven their worth time and again. However, one critical aspect that often comes under scrutiny is the accuracy of dog locators used in conjunction with war dogs. These locators are essential tools that help handlers keep track of their canine partners, especially in challenging environments such as combat zones. This article delves into the analysis of dog locator accuracy, focusing on its significance, challenges, and advancements.
The primary purpose of a dog locator is to ensure that war dogs remain within reach of their handlers during operations. In high-stakes scenarios where visibility might be compromised due to environmental factors like fog, smoke, or darkness, locators provide real-time data about the dog's position. This information is vital for maintaining communication and ensuring the safety of both the dog and the handler. Furthermore, it aids in strategic decision-making, as commanders can use this data to coordinate movements more effectively.

Despite their importance, dog locators face several challenges that can impact their accuracy. One of the most significant challenges is signal interference. In a battlefield setting, there are numerous sources of electromagnetic interference, including radio communications, radar systems, and even enemy jamming devices. These interferences can disrupt the signals transmitted by the locators, leading to inaccuracies in determining the dog's location. Additionally, the terrain itself can pose obstacles. Mountainous regions, dense forests, and urban areas with tall buildings can all obstruct GPS signals, further complicating the process of accurately pinpointing a dog's position.
Another factor affecting locator accuracy is the technology used in the device. Early versions of dog locators relied heavily on basic GPS systems, which were prone to errors caused by satellite misalignment and atmospheric conditions. Over time, advancements in technology have improved the reliability of these devices. Modern locators now incorporate multi-satellite systems, allowing them to receive signals from multiple constellations such as GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo. This redundancy helps mitigate the effects of signal blockage and enhances overall accuracy.

Moreover, the integration of inertial navigation systems (INS) has provided an additional layer of precision. INS uses sensors like accelerometers and gyroscopes to track movement independently of external signals. By combining INS with GPS, locators can maintain accurate positioning even when GPS signals are temporarily lost. This hybrid approach significantly boosts the reliability of dog locators, making them more suitable for the demanding conditions faced by war dogs.
However, technological advancements alone are not enough to guarantee perfect accuracy. Human factors also play a crucial role in the effectiveness of dog locators. Handlers must be well-trained in using these devices and interpreting the data they provide. Misinterpretation or improper use of the locator can lead to incorrect assumptions about the dog's location, potentially jeopardizing the mission. Therefore, continuous training and familiarization with the equipment are essential components of ensuring locator accuracy.
Furthermore, the physical condition of the war dogs themselves can influence the performance of locators. Dogs that are tired, injured, or stressed may move unpredictably, making it harder for the locator to keep up with their exact position. It is imperative that handlers monitor their dogs' health and well-being to prevent such issues from arising. Regular check-ups and rest periods should be incorporated into the routine to ensure that the dogs are always at their best during operations.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on developing specialized locators tailored specifically for war dogs. These devices take into account the unique needs of military operations, offering features such as extended battery life, rugged construction, and waterproofing. Some advanced models even include biometric sensors that monitor the dog's vital signs, providing valuable health information alongside positional data. Such innovations not only enhance the accuracy of the locators but also contribute to the overall welfare of the war dogs.

Despite these advancements, challenges remain in achieving 100% accuracy. Environmental variables, technological limitations, and human error all contribute to potential discrepancies in the data provided by dog locators. Researchers and developers continue to explore new ways to overcome these obstacles, investing in cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and make predictions about a dog's likely movements, thereby improving the accuracy of the locator system.

Machine learning, on the other hand, enables locators to adapt and learn from past experiences. By processing historical data, the system can recognize common behaviors and adjust its calculations accordingly. For instance, if a particular dog tends to veer off course in certain situations, the locator can anticipate this behavior and provide more accurate predictions of its future positions. This adaptive capability represents a significant step forward in enhancing the reliability of dog locators.
Collaboration between militaries, research institutions, and private companies is essential for driving progress in this field. By pooling resources and expertise, stakeholders can accelerate the development of more sophisticated locator systems. Joint projects and initiatives aim to address existing gaps in technology and create solutions that meet the specific requirements of war dogs and their handlers.

In conclusion, the accuracy of dog locators is a critical factor in the success of military operations involving war dogs. While significant strides have been made in improving this technology, challenges such as signal interference, terrain obstacles, and human factors still persist. Continued investment in research and development, along with enhanced training programs for handlers, will be key to overcoming these hurdles. As technology evolves, so too will the capabilities of dog locators, ensuring that war dogs and their handlers can operate with greater efficiency and safety in the field. The future looks promising, with innovations like AI and machine learning paving the way for even more accurate and reliable locator systems.

Update Time:2025-05-15 05:02:19
The primary purpose of a dog locator is to ensure that war dogs remain within reach of their handlers during operations. In high-stakes scenarios where visibility might be compromised due to environmental factors like fog, smoke, or darkness, locators provide real-time data about the dog's position. This information is vital for maintaining communication and ensuring the safety of both the dog and the handler. Furthermore, it aids in strategic decision-making, as commanders can use this data to coordinate movements more effectively.

Despite their importance, dog locators face several challenges that can impact their accuracy. One of the most significant challenges is signal interference. In a battlefield setting, there are numerous sources of electromagnetic interference, including radio communications, radar systems, and even enemy jamming devices. These interferences can disrupt the signals transmitted by the locators, leading to inaccuracies in determining the dog's location. Additionally, the terrain itself can pose obstacles. Mountainous regions, dense forests, and urban areas with tall buildings can all obstruct GPS signals, further complicating the process of accurately pinpointing a dog's position.
Another factor affecting locator accuracy is the technology used in the device. Early versions of dog locators relied heavily on basic GPS systems, which were prone to errors caused by satellite misalignment and atmospheric conditions. Over time, advancements in technology have improved the reliability of these devices. Modern locators now incorporate multi-satellite systems, allowing them to receive signals from multiple constellations such as GPS, GLONASS, and Galileo. This redundancy helps mitigate the effects of signal blockage and enhances overall accuracy.

Moreover, the integration of inertial navigation systems (INS) has provided an additional layer of precision. INS uses sensors like accelerometers and gyroscopes to track movement independently of external signals. By combining INS with GPS, locators can maintain accurate positioning even when GPS signals are temporarily lost. This hybrid approach significantly boosts the reliability of dog locators, making them more suitable for the demanding conditions faced by war dogs.
However, technological advancements alone are not enough to guarantee perfect accuracy. Human factors also play a crucial role in the effectiveness of dog locators. Handlers must be well-trained in using these devices and interpreting the data they provide. Misinterpretation or improper use of the locator can lead to incorrect assumptions about the dog's location, potentially jeopardizing the mission. Therefore, continuous training and familiarization with the equipment are essential components of ensuring locator accuracy.
Furthermore, the physical condition of the war dogs themselves can influence the performance of locators. Dogs that are tired, injured, or stressed may move unpredictably, making it harder for the locator to keep up with their exact position. It is imperative that handlers monitor their dogs' health and well-being to prevent such issues from arising. Regular check-ups and rest periods should be incorporated into the routine to ensure that the dogs are always at their best during operations.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on developing specialized locators tailored specifically for war dogs. These devices take into account the unique needs of military operations, offering features such as extended battery life, rugged construction, and waterproofing. Some advanced models even include biometric sensors that monitor the dog's vital signs, providing valuable health information alongside positional data. Such innovations not only enhance the accuracy of the locators but also contribute to the overall welfare of the war dogs.

Despite these advancements, challenges remain in achieving 100% accuracy. Environmental variables, technological limitations, and human error all contribute to potential discrepancies in the data provided by dog locators. Researchers and developers continue to explore new ways to overcome these obstacles, investing in cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and make predictions about a dog's likely movements, thereby improving the accuracy of the locator system.

Machine learning, on the other hand, enables locators to adapt and learn from past experiences. By processing historical data, the system can recognize common behaviors and adjust its calculations accordingly. For instance, if a particular dog tends to veer off course in certain situations, the locator can anticipate this behavior and provide more accurate predictions of its future positions. This adaptive capability represents a significant step forward in enhancing the reliability of dog locators.
Collaboration between militaries, research institutions, and private companies is essential for driving progress in this field. By pooling resources and expertise, stakeholders can accelerate the development of more sophisticated locator systems. Joint projects and initiatives aim to address existing gaps in technology and create solutions that meet the specific requirements of war dogs and their handlers.

In conclusion, the accuracy of dog locators is a critical factor in the success of military operations involving war dogs. While significant strides have been made in improving this technology, challenges such as signal interference, terrain obstacles, and human factors still persist. Continued investment in research and development, along with enhanced training programs for handlers, will be key to overcoming these hurdles. As technology evolves, so too will the capabilities of dog locators, ensuring that war dogs and their handlers can operate with greater efficiency and safety in the field. The future looks promising, with innovations like AI and machine learning paving the way for even more accurate and reliable locator systems.

Update Time:2025-05-15 05:02:19
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form