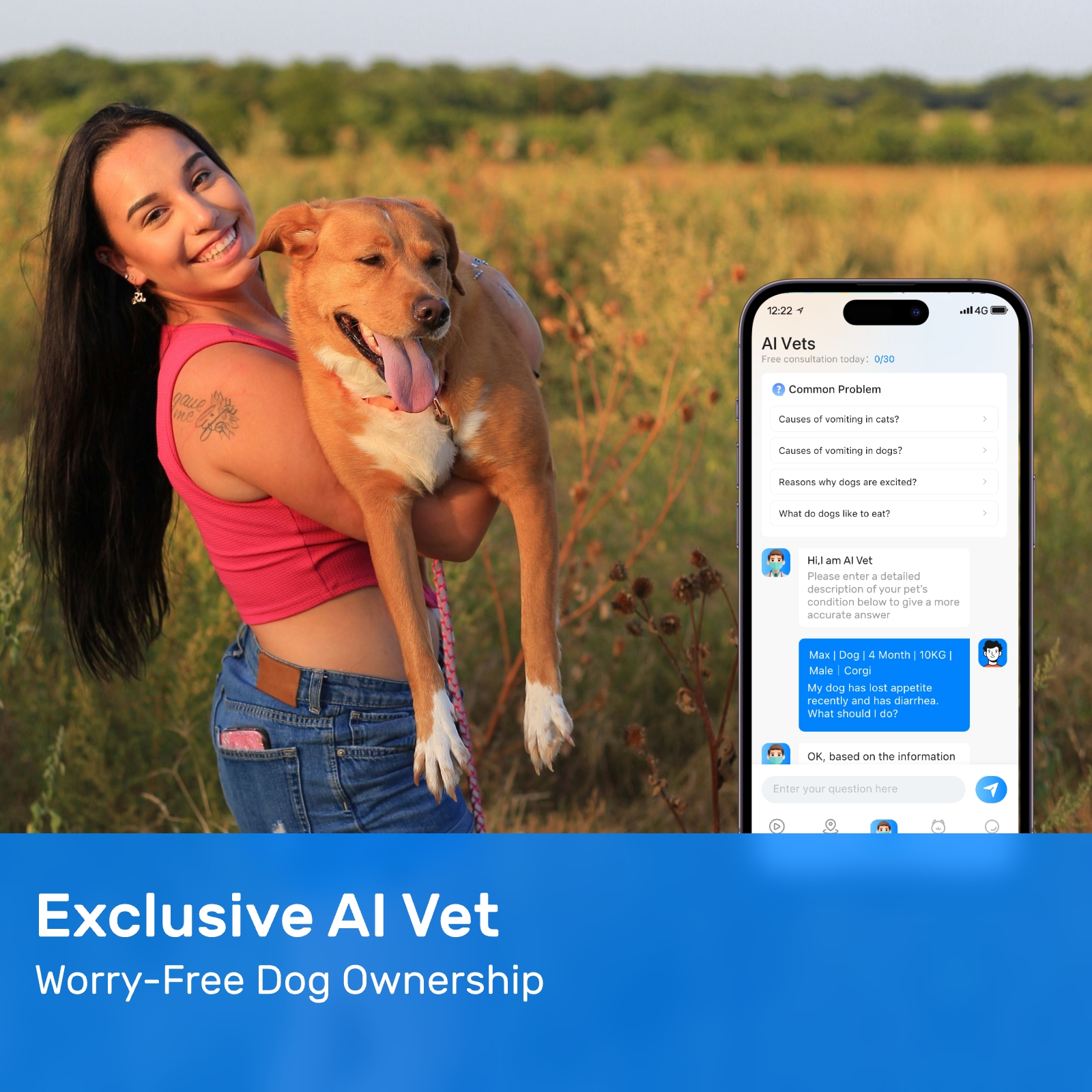
New ArrivalsBack in stock
gps collar for dogs
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D907230630 second hand :D907230630 |
Manufacturer | gps collar | release date | 2025-05-18 | List price | $42 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | collar for | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Precision Agriculture#Livestock Tracking
Dog owners worldwide have been increasingly adopting GPS collars for dogs to ensure their pets' safety and security. These collars are designed to track a dog's location in real-time, allowing owners to monitor their pets' movements and quickly locate them in case they go missing. However, the accuracy of these GPS collars for dogs is a crucial factor that determines their effectiveness in providing peace of mind and ensuring the safety of our furry companions. In this article, we will delve into the factors that affect the accuracy of GPS collars for dogs, analyze their performance, and discuss the potential improvements in technology.
GPS technology relies on a network of satellites orbiting the Earth, which transmit signals that can be picked up by GPS devices, such as collars for dogs. These devices use the signals to calculate their position on Earth. However, several factors can influence the accuracy of these GPS collars for dogs, including:
1. Satellite Signal Strength: The accuracy of a GPS collar for dogs depends on the strength and number of satellite signals it can receive. In open areas with a clear line of sight to the sky, the collar can receive strong signals from multiple satellites, resulting in high accuracy. However, in urban or densely forested areas, the signal strength may be weaker due to obstructions like buildings or trees, leading to reduced accuracy.
2. Multipath Errors: Multipath errors occur when a satellite signal reflects off surfaces like buildings or other structures before reaching the GPS collar for dogs. This reflection can cause the device to receive a delayed or distorted signal, leading to inaccuracies in the calculated position.

3. Atmospheric Conditions: Weather conditions can also impact the accuracy of GPS collars for dogs. Ionospheric and tropospheric delays can cause variations in the speed of satellite signals, affecting the device's ability to calculate its position accurately.
4. GPS Satellite Constellation: The accuracy of GPS collars for dogs is also influenced by the number and distribution of satellites in the GPS constellation. A more extensive and evenly distributed constellation can provide better coverage and more accurate positioning.
5. GPS Receiver Quality: The quality of the GPS receiver in the collar plays a significant role in determining its accuracy. High-quality receivers can process signals more efficiently and are less prone to errors, resulting in more accurate location data.
To analyze the accuracy of GPS collars for dogs, several tests and comparisons can be conducted. These tests can involve placing the collar in various environments, such as open fields, urban areas, and forests, and comparing the calculated positions with known reference points. Additionally, comparing the performance of different GPS collars for dogs can provide insights into the best options available in the market.
Several studies have been conducted to assess the accuracy of GPS collars for dogs. A study published in the Journal of Veterinary Behavior found that the accuracy of GPS collars for dogs ranged from 2.5 meters to 15 meters, with the majority of the tested collars providing an accuracy of 5 meters or less. This level of accuracy is generally considered sufficient for most pet owners, as it allows them to locate their dogs quickly and efficiently.
However, there are instances where higher accuracy may be required, such as in search and rescue operations or tracking wild animals. In these cases, GPS collars for dogs with sub-meter accuracy may be necessary. Some advanced GPS collars for dogs are now incorporating additional technologies, such as inertial measurement units (IMUs) and barometers, to improve their accuracy and provide more reliable location data.

IMUs are sensors that measure a device's acceleration, rotation, and orientation, allowing them to calculate the distance traveled and direction of movement. By combining this data with GPS signals, the collar can provide more accurate and continuous tracking, even in areas with weak or obstructed satellite signals.
Barometers, on the other hand, measure atmospheric pressure and can be used to determine the device's altitude with high precision. This information can be beneficial in hilly or mountainous terrains, where the elevation can significantly impact the accuracy of GPS signals.
In addition to these advanced technologies, some GPS collars for dogs are also incorporating cellular and Wi-Fi connectivity to improve their accuracy and functionality. By connecting to nearby Wi-Fi networks or cellular towers, these collars can use trilateration to determine their position more accurately. This method involves measuring the signal strength from multiple access points and calculating the device's position based on the differences in signal strength.

Moreover, these connected GPS collars for dogs can also provide additional features, such as real-time location updates, virtual fencing, and geo-fencing, which can further enhance the safety and security of pets.

Despite the advancements in GPS collar technology for dogs, there is still room for improvement. Future developments may focus on enhancing the accuracy and reliability of these collars, particularly in challenging environments like urban areas or dense forests. Some potential improvements include:
1. Integration of Other Satellite Systems: Combining GPS signals with other satellite systems, such as Russia's GLONASS or Europe's Galileo, can improve the accuracy and coverage of GPS collars for dogs. This
Update Time:2025-05-18 18:53:36
GPS technology relies on a network of satellites orbiting the Earth, which transmit signals that can be picked up by GPS devices, such as collars for dogs. These devices use the signals to calculate their position on Earth. However, several factors can influence the accuracy of these GPS collars for dogs, including:
1. Satellite Signal Strength: The accuracy of a GPS collar for dogs depends on the strength and number of satellite signals it can receive. In open areas with a clear line of sight to the sky, the collar can receive strong signals from multiple satellites, resulting in high accuracy. However, in urban or densely forested areas, the signal strength may be weaker due to obstructions like buildings or trees, leading to reduced accuracy.
2. Multipath Errors: Multipath errors occur when a satellite signal reflects off surfaces like buildings or other structures before reaching the GPS collar for dogs. This reflection can cause the device to receive a delayed or distorted signal, leading to inaccuracies in the calculated position.

3. Atmospheric Conditions: Weather conditions can also impact the accuracy of GPS collars for dogs. Ionospheric and tropospheric delays can cause variations in the speed of satellite signals, affecting the device's ability to calculate its position accurately.
4. GPS Satellite Constellation: The accuracy of GPS collars for dogs is also influenced by the number and distribution of satellites in the GPS constellation. A more extensive and evenly distributed constellation can provide better coverage and more accurate positioning.
5. GPS Receiver Quality: The quality of the GPS receiver in the collar plays a significant role in determining its accuracy. High-quality receivers can process signals more efficiently and are less prone to errors, resulting in more accurate location data.
To analyze the accuracy of GPS collars for dogs, several tests and comparisons can be conducted. These tests can involve placing the collar in various environments, such as open fields, urban areas, and forests, and comparing the calculated positions with known reference points. Additionally, comparing the performance of different GPS collars for dogs can provide insights into the best options available in the market.
Several studies have been conducted to assess the accuracy of GPS collars for dogs. A study published in the Journal of Veterinary Behavior found that the accuracy of GPS collars for dogs ranged from 2.5 meters to 15 meters, with the majority of the tested collars providing an accuracy of 5 meters or less. This level of accuracy is generally considered sufficient for most pet owners, as it allows them to locate their dogs quickly and efficiently.
However, there are instances where higher accuracy may be required, such as in search and rescue operations or tracking wild animals. In these cases, GPS collars for dogs with sub-meter accuracy may be necessary. Some advanced GPS collars for dogs are now incorporating additional technologies, such as inertial measurement units (IMUs) and barometers, to improve their accuracy and provide more reliable location data.

IMUs are sensors that measure a device's acceleration, rotation, and orientation, allowing them to calculate the distance traveled and direction of movement. By combining this data with GPS signals, the collar can provide more accurate and continuous tracking, even in areas with weak or obstructed satellite signals.
Barometers, on the other hand, measure atmospheric pressure and can be used to determine the device's altitude with high precision. This information can be beneficial in hilly or mountainous terrains, where the elevation can significantly impact the accuracy of GPS signals.
In addition to these advanced technologies, some GPS collars for dogs are also incorporating cellular and Wi-Fi connectivity to improve their accuracy and functionality. By connecting to nearby Wi-Fi networks or cellular towers, these collars can use trilateration to determine their position more accurately. This method involves measuring the signal strength from multiple access points and calculating the device's position based on the differences in signal strength.

Moreover, these connected GPS collars for dogs can also provide additional features, such as real-time location updates, virtual fencing, and geo-fencing, which can further enhance the safety and security of pets.

Despite the advancements in GPS collar technology for dogs, there is still room for improvement. Future developments may focus on enhancing the accuracy and reliability of these collars, particularly in challenging environments like urban areas or dense forests. Some potential improvements include:
1. Integration of Other Satellite Systems: Combining GPS signals with other satellite systems, such as Russia's GLONASS or Europe's Galileo, can improve the accuracy and coverage of GPS collars for dogs. This
Update Time:2025-05-18 18:53:36
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form