
New ArrivalsBack in stock
dog rescue
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D565833245 second hand :D565833245 |
Manufacturer | dog rescue | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $35 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | dog rescue | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Pet Healthcare#Vital Monitoring Systems
Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locator connectivity have become increasingly popular in the realm of pet technology. Both options provide innovative solutions for dog rescue operations, allowing pet owners and rescue teams to track lost dogs more effectively. Each connectivity method has its own set of advantages and disadvantages that can influence how efficiently they function in various scenarios. This article will explore both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators, focusing on their applications in dog rescue missions.
To begin with, Bluetooth-based dog locators are generally small devices that attach to a dog's collar. They use Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology to connect with a smartphone or tablet within a certain range, typically around 300 feet. The primary advantage of Bluetooth locators is their low power consumption, which means they can operate for extended periods without requiring frequent battery changes. For dog rescue operations conducted in areas where the dog is likely to be within a short distance, such as a local park or neighborhood, Bluetooth trackers can be highly effective. Rescue teams can move through these areas while maintaining a connection with the device, signaling when they are getting closer to the lost dog.
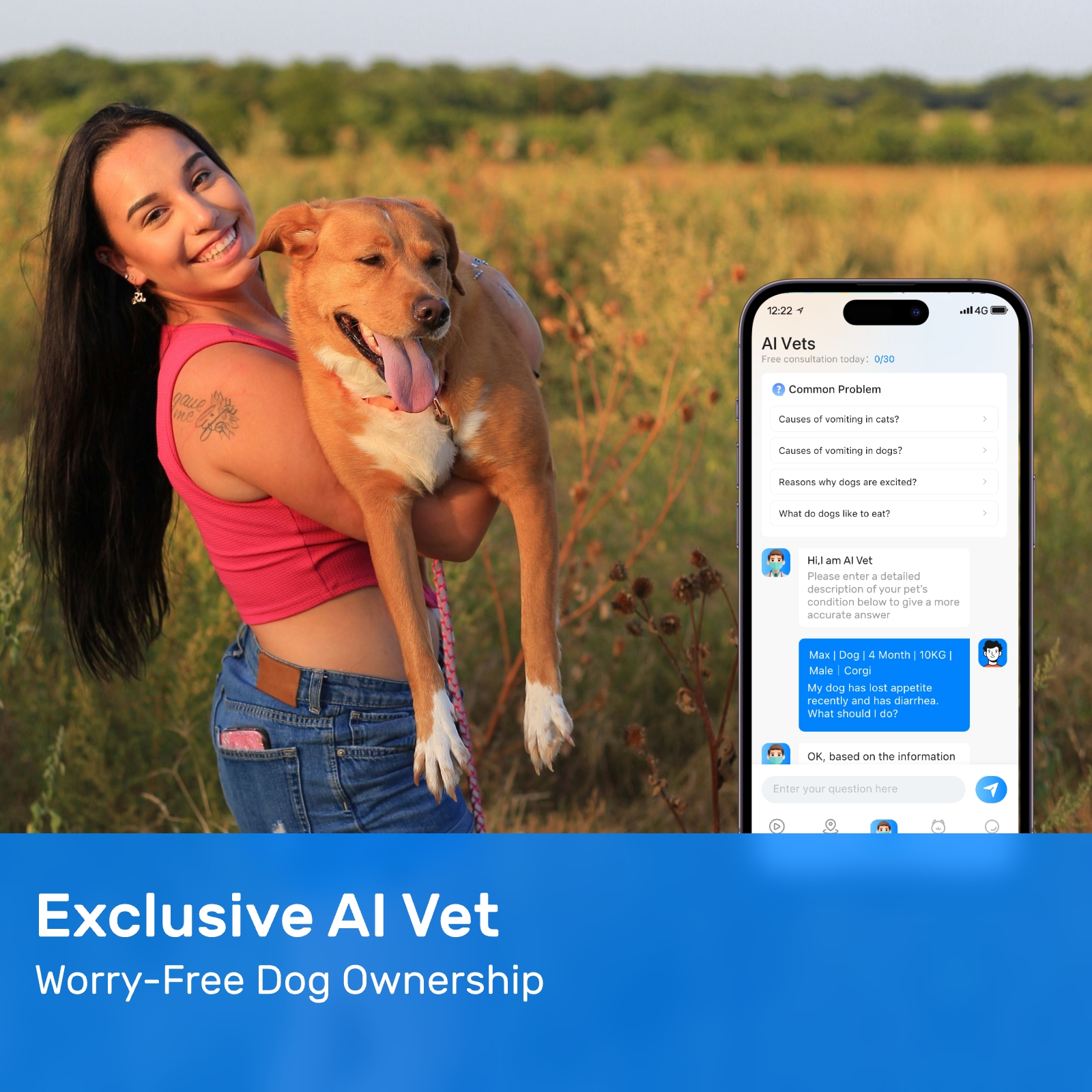
However, one major limitation of Bluetooth dog locators is their limited range. If a dog wanders beyond the effective range of the Bluetooth signal, the tracker becomes useless until the dog comes back into range. This drawback can hinder dog rescue efforts if the missing animal has traveled further than anticipated. Additionally, Bluetooth devices require a direct line of sight or minimal obstruction between the tracker and the receiver, meaning buildings, trees, or other obstacles can weaken or disrupt the signal.
On the other hand, Wi-Fi-based dog locators offer a different set of capabilities. These devices connect to nearby Wi-Fi networks to report the dog’s location to a cloud-based server. As long as the device is within range of a Wi-Fi network, it can transmit its location data, making it possible for rescue teams to pinpoint the dog's position even if it is miles away. This makes Wi-Fi dog locators particularly useful for long-range dog rescue missions where the dog may have wandered far from home.
One of the key benefits of Wi-Fi dog locators is their ability to provide real-time updates on a dog's location. Unlike Bluetooth trackers, which only work when within range, Wi-Fi trackers can continuously update the dog's position as it moves from one network to another. This feature allows rescue teams to monitor the dog's movements and adjust their search strategy accordingly. Moreover, some advanced Wi-Fi locators come equipped with GPS functionality, providing even more precise location data.
Despite these advantages, Wi-Fi dog locators also have their downsides. One significant issue is battery life. Since Wi-Fi trackers must constantly scan for networks and upload data to the cloud, they tend to consume more power than Bluetooth devices. This can result in shorter battery life, necessitating more frequent charging or battery replacements. Furthermore, Wi-Fi coverage can be spotty in rural or remote areas, potentially leaving gaps in the tracker's ability to report the dog's location. In such cases, the effectiveness of Wi-Fi-based dog rescue efforts could be compromised.
Another consideration when choosing between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators is cost. Generally speaking, Bluetooth devices tend to be less expensive than their Wi-Fi counterparts. This price difference can be an important factor for individual pet owners or smaller rescue organizations operating on limited budgets. However, it's worth noting that the initial purchase price of a Wi-Fi tracker might be offset by its superior range and functionality, especially in situations where long-distance tracking is necessary.
In terms of usability, both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators are relatively easy to set up and use. Most devices come with accompanying mobile apps that allow users to view the dog's location, receive alerts, and configure settings. For Bluetooth trackers, the app typically shows the strength of the signal, helping rescuers determine how close they are to the dog. With Wi-Fi trackers, the app displays a map with the dog's current and past locations, enabling rescuers to trace its path and predict where it might go next.

When it comes to dog rescue, the choice between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity often depends on the specific circumstances of the situation. For example, if a dog goes missing during a walk in a suburban area, a Bluetooth locator might be sufficient since the dog is likely to remain within a few hundred feet. Conversely, if a dog escapes from a fenced yard and travels several miles away, a Wi-Fi locator would be better suited to the task due to its broader coverage area.
It's also worth considering hybrid devices that combine both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi technologies. These trackers leverage the strengths of each connectivity method to provide comprehensive coverage. For instance, they might use Bluetooth for short-range tracking and switch to Wi-Fi or cellular networks for long-range tracking. Such devices offer the best of both worlds but usually come at a higher price point.
Another aspect to consider is the environmental impact of these devices. Both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators rely on batteries, which eventually need to be disposed of. It's essential for manufacturers and users alike to adopt eco-friendly practices, such as using rechargeable batteries and recycling old ones properly. Additionally, the production and disposal of electronic components can contribute to electronic waste, so it's crucial to choose durable, long-lasting devices whenever possible.
Dog rescue organizations can benefit greatly from incorporating these technologies into their operations. By equipping their vehicles with Bluetooth and Wi-Fi receivers, rescue teams can quickly locate missing dogs and reunite them with their owners. Some organizations have even developed community-based systems where volunteers install Wi-Fi routers in their homes, creating a network that enhances the tracking capabilities of Wi-Fi dog locators. This collaborative approach can significantly improve the success rate of dog rescue missions.
Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are enhancing the capabilities of both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators. AI algorithms can analyze patterns in a dog's movement to predict where it might go, while machine learning can optimize the performance of the trackers based on usage data. These innovations promise to make dog rescue operations more efficient and effective in the future.
In conclusion, both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators have their place in the world of dog rescue. Bluetooth trackers are ideal for short-range missions where the dog is likely to be nearby, offering simplicity and low power consumption. Wi-Fi trackers, on the other hand, excel in long-range scenarios, providing real-time updates and greater coverage. Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on factors such as budget, range requirements, and environmental considerations. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each technology, pet owners and rescue teams can make informed decisions that enhance their ability to find and recover lost dogs. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated solutions to emerge, further improving the chances of successful dog rescue missions.
Update Time:2025-05-15 04:51:06
To begin with, Bluetooth-based dog locators are generally small devices that attach to a dog's collar. They use Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology to connect with a smartphone or tablet within a certain range, typically around 300 feet. The primary advantage of Bluetooth locators is their low power consumption, which means they can operate for extended periods without requiring frequent battery changes. For dog rescue operations conducted in areas where the dog is likely to be within a short distance, such as a local park or neighborhood, Bluetooth trackers can be highly effective. Rescue teams can move through these areas while maintaining a connection with the device, signaling when they are getting closer to the lost dog.

However, one major limitation of Bluetooth dog locators is their limited range. If a dog wanders beyond the effective range of the Bluetooth signal, the tracker becomes useless until the dog comes back into range. This drawback can hinder dog rescue efforts if the missing animal has traveled further than anticipated. Additionally, Bluetooth devices require a direct line of sight or minimal obstruction between the tracker and the receiver, meaning buildings, trees, or other obstacles can weaken or disrupt the signal.
On the other hand, Wi-Fi-based dog locators offer a different set of capabilities. These devices connect to nearby Wi-Fi networks to report the dog’s location to a cloud-based server. As long as the device is within range of a Wi-Fi network, it can transmit its location data, making it possible for rescue teams to pinpoint the dog's position even if it is miles away. This makes Wi-Fi dog locators particularly useful for long-range dog rescue missions where the dog may have wandered far from home.
One of the key benefits of Wi-Fi dog locators is their ability to provide real-time updates on a dog's location. Unlike Bluetooth trackers, which only work when within range, Wi-Fi trackers can continuously update the dog's position as it moves from one network to another. This feature allows rescue teams to monitor the dog's movements and adjust their search strategy accordingly. Moreover, some advanced Wi-Fi locators come equipped with GPS functionality, providing even more precise location data.
Despite these advantages, Wi-Fi dog locators also have their downsides. One significant issue is battery life. Since Wi-Fi trackers must constantly scan for networks and upload data to the cloud, they tend to consume more power than Bluetooth devices. This can result in shorter battery life, necessitating more frequent charging or battery replacements. Furthermore, Wi-Fi coverage can be spotty in rural or remote areas, potentially leaving gaps in the tracker's ability to report the dog's location. In such cases, the effectiveness of Wi-Fi-based dog rescue efforts could be compromised.
Another consideration when choosing between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators is cost. Generally speaking, Bluetooth devices tend to be less expensive than their Wi-Fi counterparts. This price difference can be an important factor for individual pet owners or smaller rescue organizations operating on limited budgets. However, it's worth noting that the initial purchase price of a Wi-Fi tracker might be offset by its superior range and functionality, especially in situations where long-distance tracking is necessary.
In terms of usability, both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators are relatively easy to set up and use. Most devices come with accompanying mobile apps that allow users to view the dog's location, receive alerts, and configure settings. For Bluetooth trackers, the app typically shows the strength of the signal, helping rescuers determine how close they are to the dog. With Wi-Fi trackers, the app displays a map with the dog's current and past locations, enabling rescuers to trace its path and predict where it might go next.

When it comes to dog rescue, the choice between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi connectivity often depends on the specific circumstances of the situation. For example, if a dog goes missing during a walk in a suburban area, a Bluetooth locator might be sufficient since the dog is likely to remain within a few hundred feet. Conversely, if a dog escapes from a fenced yard and travels several miles away, a Wi-Fi locator would be better suited to the task due to its broader coverage area.
It's also worth considering hybrid devices that combine both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi technologies. These trackers leverage the strengths of each connectivity method to provide comprehensive coverage. For instance, they might use Bluetooth for short-range tracking and switch to Wi-Fi or cellular networks for long-range tracking. Such devices offer the best of both worlds but usually come at a higher price point.
Another aspect to consider is the environmental impact of these devices. Both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators rely on batteries, which eventually need to be disposed of. It's essential for manufacturers and users alike to adopt eco-friendly practices, such as using rechargeable batteries and recycling old ones properly. Additionally, the production and disposal of electronic components can contribute to electronic waste, so it's crucial to choose durable, long-lasting devices whenever possible.
Dog rescue organizations can benefit greatly from incorporating these technologies into their operations. By equipping their vehicles with Bluetooth and Wi-Fi receivers, rescue teams can quickly locate missing dogs and reunite them with their owners. Some organizations have even developed community-based systems where volunteers install Wi-Fi routers in their homes, creating a network that enhances the tracking capabilities of Wi-Fi dog locators. This collaborative approach can significantly improve the success rate of dog rescue missions.
Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are enhancing the capabilities of both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators. AI algorithms can analyze patterns in a dog's movement to predict where it might go, while machine learning can optimize the performance of the trackers based on usage data. These innovations promise to make dog rescue operations more efficient and effective in the future.
In conclusion, both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locators have their place in the world of dog rescue. Bluetooth trackers are ideal for short-range missions where the dog is likely to be nearby, offering simplicity and low power consumption. Wi-Fi trackers, on the other hand, excel in long-range scenarios, providing real-time updates and greater coverage. Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on factors such as budget, range requirements, and environmental considerations. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each technology, pet owners and rescue teams can make informed decisions that enhance their ability to find and recover lost dogs. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated solutions to emerge, further improving the chances of successful dog rescue missions.
Update Time:2025-05-15 04:51:06
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form























