
New ArrivalsBack in stock
dog bone
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D668623776 second hand :D668623776 |
Manufacturer | dog bone | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $33 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | dog bone | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Smart Cities#Stray Animal Management




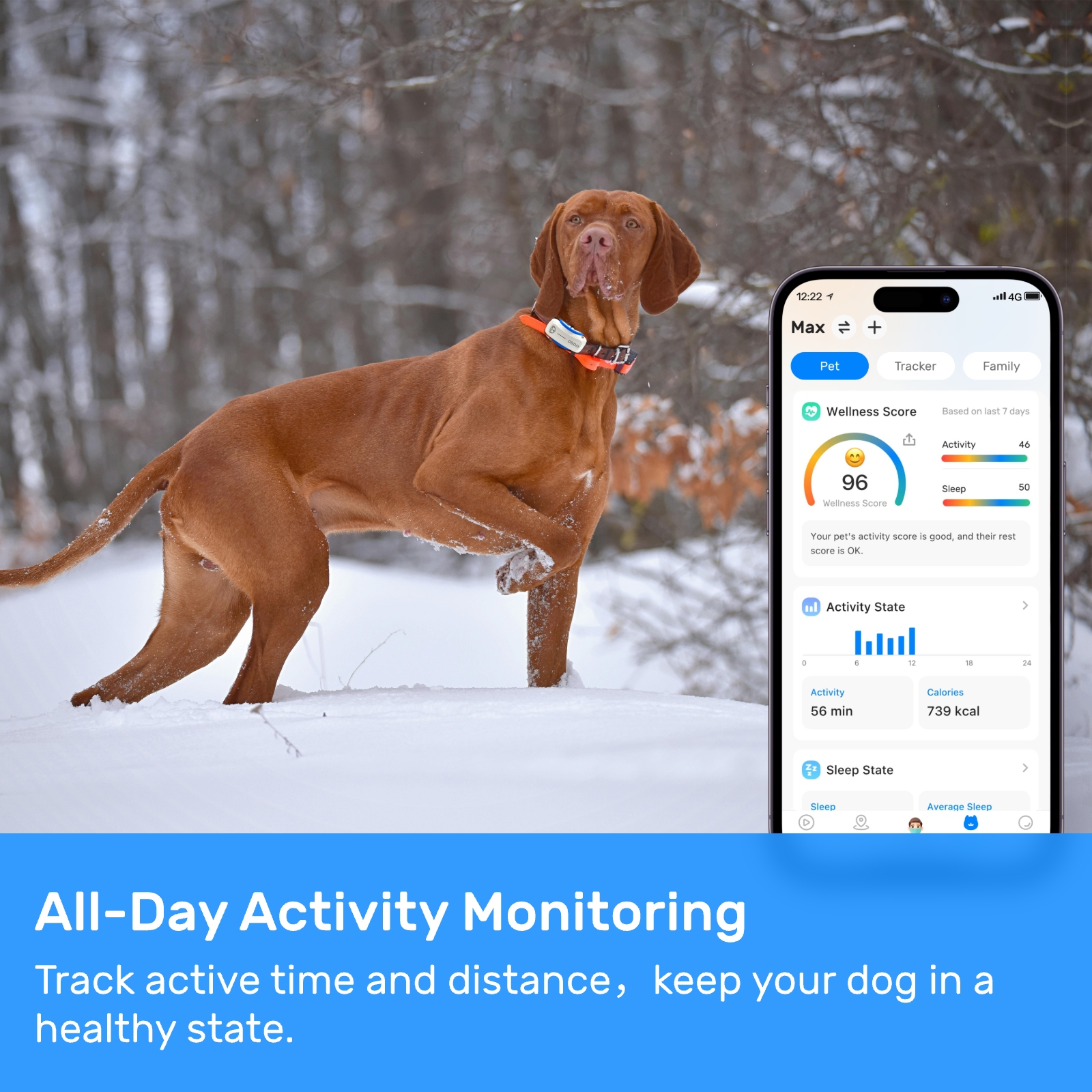





Pet locator devices typically function by using GPS and cellular networks to transmit a pet's location to a smartphone app or web interface. Owners can then monitor their pet's movements and receive alerts if the animal strays beyond a predefined area. While these features offer significant benefits, they also raise questions about how personal data is collected, stored, and used. The sensitive nature of this information necessitates careful consideration of privacy safeguards.
One of the primary concerns regarding pet locator data privacy is the potential for unauthorized access. As with any digital device, there is always a risk that hackers could gain access to the system and misuse the data. If a malicious actor were to infiltrate a pet locator network, they could potentially track not only the pet but also its owner. This scenario becomes even more alarming when considering devices embedded in items like a dog bone, as these may be less conspicuous and thus more vulnerable to tampering.
Another significant issue is the sharing of data with third parties. Many companies that produce pet locator devices partner with other organizations to provide additional services or improve functionality. While these collaborations can enhance the user experience, they also increase the likelihood that personal data will be shared without the owner's explicit consent. For example, a company producing a GPS-enabled dog bone might share location data with advertisers or analytics firms, raising ethical questions about transparency and control over one's information.
Furthermore, the storage of pet locator data presents another layer of complexity. Companies must ensure that the data collected from these devices is securely stored and protected against breaches. Inadequate security measures could result in the exposure of sensitive information, including the locations of both pets and their owners. Given the intimate connection between pets and their families, such breaches could lead to serious consequences, ranging from identity theft to physical harm.

The design of pet locator devices themselves also plays a crucial role in data privacy considerations. Devices embedded in items like a dog bone must balance functionality with discretion. While embedding a tracker in a dog bone ensures that the pet is unlikely to lose it, it also raises questions about the extent to which such devices are integrated into the pet's environment. Owners should be aware of the implications of choosing such a device and consider whether the benefits outweigh the potential risks.
To address these concerns, manufacturers must prioritize data privacy in the design and implementation of their products. This involves adopting robust encryption methods to protect data during transmission and storage, as well as implementing strict access controls to prevent unauthorized use. Additionally, companies should provide clear and concise privacy policies that outline how data is collected, used, and shared. Transparency is key to building trust with consumers and ensuring that they feel comfortable using these technologies.
Regulatory frameworks also play a vital role in safeguarding pet locator data privacy. Governments and industry bodies must establish guidelines that mandate minimum standards for data protection and privacy. These regulations should cover aspects such as data retention periods, user consent mechanisms, and the rights of individuals to access and delete their data. By enforcing these standards, regulators can help ensure that pet locator devices, including those embedded in items like a dog bone, are used responsibly and ethically.
Consumers, too, have a responsibility to educate themselves about the data privacy implications of using pet locator devices. Before purchasing a GPS-enabled dog bone or similar product, owners should carefully review the manufacturer's privacy policy and assess whether it aligns with their expectations and values. They should also take steps to secure their accounts, such as using strong passwords and enabling two-factor authentication, to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
Moreover, owners should be mindful of the data they share with pet locator apps and services. Many of these platforms offer features that encourage users to connect with others, such as social media integration or community forums. While these features can enhance the user experience, they also increase the potential for data exposure. Owners should exercise caution when sharing information and consider limiting the amount of personal data they disclose.
As the demand for pet locator technology continues to grow, so too does the need for innovation in data privacy solutions. Researchers and developers are exploring new ways to enhance the security and privacy of these devices, such as incorporating blockchain technology to create decentralized systems that reduce the risk of data breaches. These advancements hold promise for improving the safety and reliability of pet locator devices while preserving user privacy.
In conclusion, while pet locator devices offer valuable benefits to pet owners, they also raise important data privacy concerns that must be addressed. The integration of these technologies into everyday pet items like a dog bone adds another dimension to these considerations, highlighting the need for careful evaluation of the associated risks and benefits. By prioritizing data privacy through robust security measures, transparent practices, and regulatory oversight, manufacturers can help ensure that pet locator devices remain a trusted tool for enhancing pet safety and well-being. Ultimately, the success of these technologies depends on the ability to balance innovation with respect for user privacy, ensuring that both pets and their owners can enjoy the peace of mind that comes with knowing where their furry friends are at all times.
Update Time:2025-05-15 07:42:42
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form




















