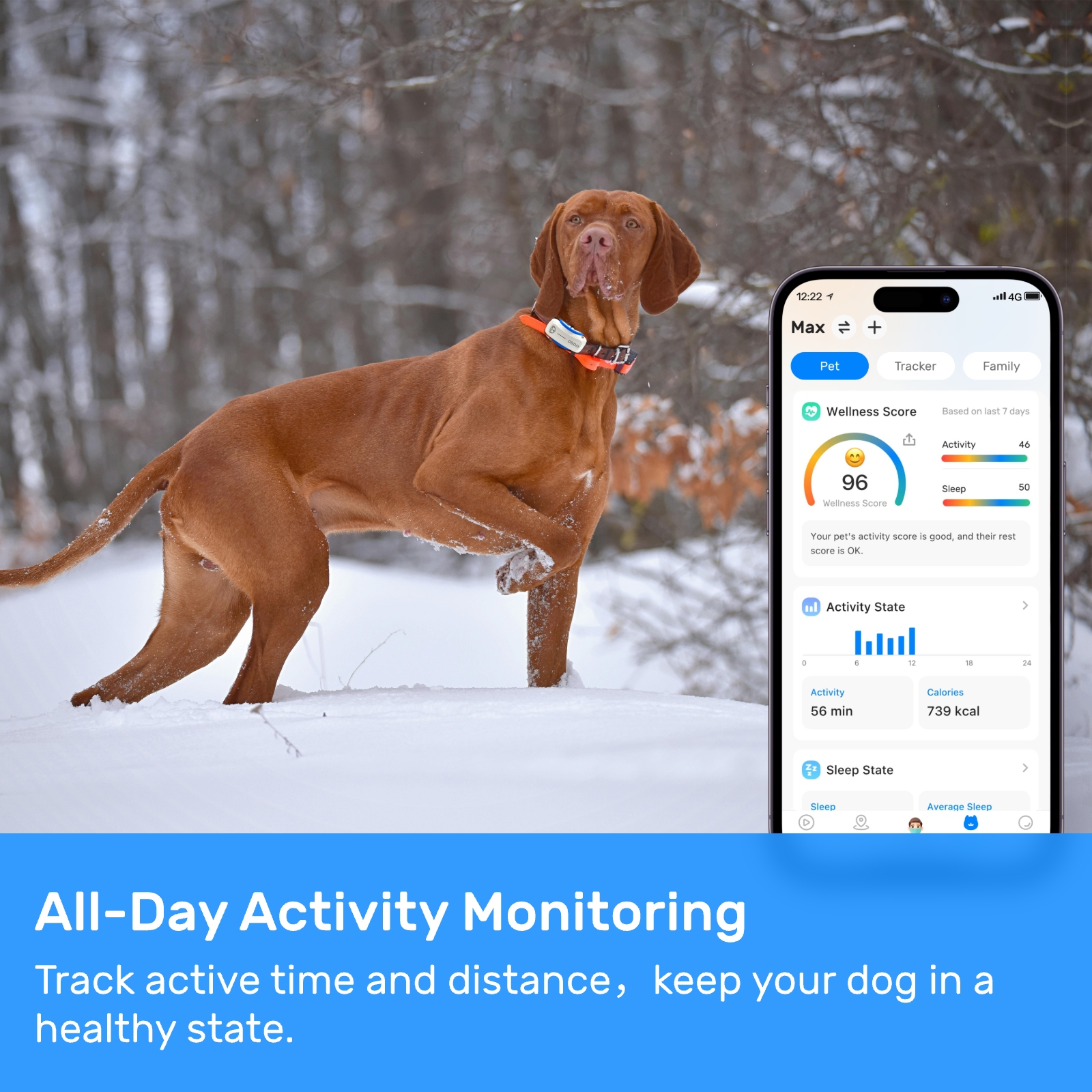
New ArrivalsBack in stock
gps for collar
 Limited Time Sale
Limited Time Sale
Until the end
00
00
00
Free shipping on orders over 999 ※)
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
If you buy it for 999 or more, you can buy it on behalf of the customer. There is no material for the number of hands.
There is stock in your local store.
Please note that the sales price and tax displayed may differ between online and in-store. Also, the product may be out of stock in-store.
Coupon giveaway!
| Control number |
New :D914413117 second hand :D914413117 |
Manufacturer | gps for | release date | 2025-05-15 | List price | $36 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| prototype | for collar | ||||||||
| category | |||||||||
Retail Analytics#Pet Behavior Insights
When it comes to finding lost pets, technology has become an invaluable tool. Two of the most common connectivity options for dog locators are Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. Both technologies have their own advantages and disadvantages, which can make choosing the right option a bit challenging. This article will explore the differences between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locator connectivity, with a focus on gps for collar systems.
Bluetooth technology is widely used in many devices today, including headphones, speakers, and even fitness trackers. For dog collars, Bluetooth provides a reliable and cost-effective way to track your pet within a certain range. The main advantage of Bluetooth is its low power consumption. This means that a Bluetooth-enabled gps for collar can last longer on a single charge compared to other technologies. Additionally, Bluetooth connections are generally faster and more stable when you're within range of your pet. Most Bluetooth dog locators work by syncing with a smartphone app, allowing you to see your pet's location in real-time as long as you're nearby.
However, Bluetooth does have its limitations. The primary drawback is its limited range. Typically, Bluetooth connectivity works best within 30 to 100 feet, depending on the version of Bluetooth being used. If your dog wanders beyond this range, you won't be able to track them using Bluetooth alone. This makes Bluetooth ideal for indoor use or when you're out for a walk with your pet but less effective if your dog gets lost over a larger area.
On the other hand, Wi-Fi dog locators offer a broader range of connectivity. These devices typically connect to a home Wi-Fi network, allowing you to monitor your pet's location from anywhere as long as they remain within the network's coverage area. Some advanced models even allow for GPS tracking once the pet moves out of Wi-Fi range, providing a hybrid solution that combines both Wi-Fi and gps for collar functionalities. One of the key benefits of Wi-Fi is that it doesn't rely on constant proximity like Bluetooth does. As long as your pet is within the Wi-Fi network, you can keep tabs on their movements remotely.
Despite its advantages, Wi-Fi also has some downsides. For one, Wi-Fi dog locators tend to consume more power than their Bluetooth counterparts, which means shorter battery life. Additionally, these devices may not function properly if your pet ventures outside of your Wi-Fi network's coverage area. In such cases, you might need to rely on cellular data or GPS to continue tracking your pet, which could incur additional costs depending on the service plan associated with your device.

Now let’s delve deeper into how gps for collar technology fits into all this. GPS (Global Positioning System) allows for precise location tracking regardless of whether your pet is within Bluetooth or Wi-Fi range. A gps for collar device uses satellites to pinpoint your pet's exact location, making it an excellent choice for scenarios where your dog might wander far from home. Unlike Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, GPS isn’t constrained by local networks or short-range signals. Instead, it offers global coverage, ensuring you can find your pet no matter where they go.

That said, there are trade-offs with GPS as well. While it provides unparalleled accuracy and range, GPS-enabled collars often require a subscription service to access detailed maps and real-time updates. They also tend to drain batteries faster due to the constant communication with satellites. Furthermore, GPS signals can sometimes be obstructed by tall buildings, dense forests, or underground areas, though improvements in technology have mitigated some of these issues.

Another factor to consider when comparing Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and gps for collar solutions is cost. Generally speaking, Bluetooth-based dog locators are the most affordable option, followed by Wi-Fi-enabled devices. GPS collars usually come at a premium price, partly because of the advanced technology involved and partly because of potential ongoing subscription fees. Depending on your budget and specific needs, one option may be more suitable than others.
Ease of use is another important consideration. Bluetooth dog locators are typically straightforward to set up and operate. Simply pair the device with your smartphone via an app, and you're good to go. Wi-Fi-enabled devices might require a bit more setup initially, especially if you need to configure them to connect to your home network. GPS collars, while offering extensive features, can sometimes involve more complex software interfaces and may necessitate regular firmware updates to maintain optimal performance.
Battery life is a critical aspect of any dog locator, and each technology handles it differently. As mentioned earlier, Bluetooth devices generally offer the longest battery life because they consume less power. Wi-Fi devices fall somewhere in the middle, balancing moderate power usage with extended functionality. GPS collars, however, tend to have the shortest battery life due to the intensive nature of satellite communication. Many modern GPS devices now include power-saving modes to help extend battery life, but users should still be prepared for more frequent recharging cycles.
Privacy and security are increasingly important considerations in today's digital age. All three technologies—Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and GPS—have mechanisms in place to protect user data. Bluetooth devices typically encrypt communications between the collar and your phone, ensuring unauthorized access is minimized. Wi-Fi-enabled devices often employ similar encryption protocols, although care must be taken to secure your home network against intrusions. GPS collars, given their reliance on cloud-based services, may store sensitive location data that requires robust protection measures to safeguard against hacking attempts.
Environmental factors also play a role in determining which technology might work best for you. For instance, if you live in a rural area with spotty Wi-Fi coverage, a Bluetooth or GPS-based system might be more appropriate. Conversely, urban dwellers with strong Wi-Fi networks might prefer a Wi-Fi-enabled solution for its convenience and reliability. Similarly, pets that frequently roam large open spaces would benefit more from GPS tracking, whereas those who stay close to home might do just fine with Bluetooth or Wi-Fi options.
In conclusion, choosing between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locator connectivity depends largely on your individual circumstances and preferences. If you prioritize simplicity, affordability, and short-range tracking, a Bluetooth-enabled gps for collar might be the best choice. On the other hand, if you want broader coverage without venturing too far into expensive territory, a Wi-Fi-based solution could serve you well. Finally, for ultimate peace of mind and comprehensive tracking capabilities, investing in a GPS collar may be worth the extra cost and effort. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each technology will empower you to make an informed decision that keeps your furry friend safe and sound.
Update Time:2025-05-15 16:24:07
Bluetooth technology is widely used in many devices today, including headphones, speakers, and even fitness trackers. For dog collars, Bluetooth provides a reliable and cost-effective way to track your pet within a certain range. The main advantage of Bluetooth is its low power consumption. This means that a Bluetooth-enabled gps for collar can last longer on a single charge compared to other technologies. Additionally, Bluetooth connections are generally faster and more stable when you're within range of your pet. Most Bluetooth dog locators work by syncing with a smartphone app, allowing you to see your pet's location in real-time as long as you're nearby.
However, Bluetooth does have its limitations. The primary drawback is its limited range. Typically, Bluetooth connectivity works best within 30 to 100 feet, depending on the version of Bluetooth being used. If your dog wanders beyond this range, you won't be able to track them using Bluetooth alone. This makes Bluetooth ideal for indoor use or when you're out for a walk with your pet but less effective if your dog gets lost over a larger area.
On the other hand, Wi-Fi dog locators offer a broader range of connectivity. These devices typically connect to a home Wi-Fi network, allowing you to monitor your pet's location from anywhere as long as they remain within the network's coverage area. Some advanced models even allow for GPS tracking once the pet moves out of Wi-Fi range, providing a hybrid solution that combines both Wi-Fi and gps for collar functionalities. One of the key benefits of Wi-Fi is that it doesn't rely on constant proximity like Bluetooth does. As long as your pet is within the Wi-Fi network, you can keep tabs on their movements remotely.
Despite its advantages, Wi-Fi also has some downsides. For one, Wi-Fi dog locators tend to consume more power than their Bluetooth counterparts, which means shorter battery life. Additionally, these devices may not function properly if your pet ventures outside of your Wi-Fi network's coverage area. In such cases, you might need to rely on cellular data or GPS to continue tracking your pet, which could incur additional costs depending on the service plan associated with your device.

Now let’s delve deeper into how gps for collar technology fits into all this. GPS (Global Positioning System) allows for precise location tracking regardless of whether your pet is within Bluetooth or Wi-Fi range. A gps for collar device uses satellites to pinpoint your pet's exact location, making it an excellent choice for scenarios where your dog might wander far from home. Unlike Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, GPS isn’t constrained by local networks or short-range signals. Instead, it offers global coverage, ensuring you can find your pet no matter where they go.

That said, there are trade-offs with GPS as well. While it provides unparalleled accuracy and range, GPS-enabled collars often require a subscription service to access detailed maps and real-time updates. They also tend to drain batteries faster due to the constant communication with satellites. Furthermore, GPS signals can sometimes be obstructed by tall buildings, dense forests, or underground areas, though improvements in technology have mitigated some of these issues.

Another factor to consider when comparing Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and gps for collar solutions is cost. Generally speaking, Bluetooth-based dog locators are the most affordable option, followed by Wi-Fi-enabled devices. GPS collars usually come at a premium price, partly because of the advanced technology involved and partly because of potential ongoing subscription fees. Depending on your budget and specific needs, one option may be more suitable than others.
Ease of use is another important consideration. Bluetooth dog locators are typically straightforward to set up and operate. Simply pair the device with your smartphone via an app, and you're good to go. Wi-Fi-enabled devices might require a bit more setup initially, especially if you need to configure them to connect to your home network. GPS collars, while offering extensive features, can sometimes involve more complex software interfaces and may necessitate regular firmware updates to maintain optimal performance.
Battery life is a critical aspect of any dog locator, and each technology handles it differently. As mentioned earlier, Bluetooth devices generally offer the longest battery life because they consume less power. Wi-Fi devices fall somewhere in the middle, balancing moderate power usage with extended functionality. GPS collars, however, tend to have the shortest battery life due to the intensive nature of satellite communication. Many modern GPS devices now include power-saving modes to help extend battery life, but users should still be prepared for more frequent recharging cycles.
Privacy and security are increasingly important considerations in today's digital age. All three technologies—Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and GPS—have mechanisms in place to protect user data. Bluetooth devices typically encrypt communications between the collar and your phone, ensuring unauthorized access is minimized. Wi-Fi-enabled devices often employ similar encryption protocols, although care must be taken to secure your home network against intrusions. GPS collars, given their reliance on cloud-based services, may store sensitive location data that requires robust protection measures to safeguard against hacking attempts.
Environmental factors also play a role in determining which technology might work best for you. For instance, if you live in a rural area with spotty Wi-Fi coverage, a Bluetooth or GPS-based system might be more appropriate. Conversely, urban dwellers with strong Wi-Fi networks might prefer a Wi-Fi-enabled solution for its convenience and reliability. Similarly, pets that frequently roam large open spaces would benefit more from GPS tracking, whereas those who stay close to home might do just fine with Bluetooth or Wi-Fi options.
In conclusion, choosing between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi dog locator connectivity depends largely on your individual circumstances and preferences. If you prioritize simplicity, affordability, and short-range tracking, a Bluetooth-enabled gps for collar might be the best choice. On the other hand, if you want broader coverage without venturing too far into expensive territory, a Wi-Fi-based solution could serve you well. Finally, for ultimate peace of mind and comprehensive tracking capabilities, investing in a GPS collar may be worth the extra cost and effort. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each technology will empower you to make an informed decision that keeps your furry friend safe and sound.
Update Time:2025-05-15 16:24:07
Correction of product information
If you notice any omissions or errors in the product information on this page, please use the correction request form below.
Correction Request Form